Abstract
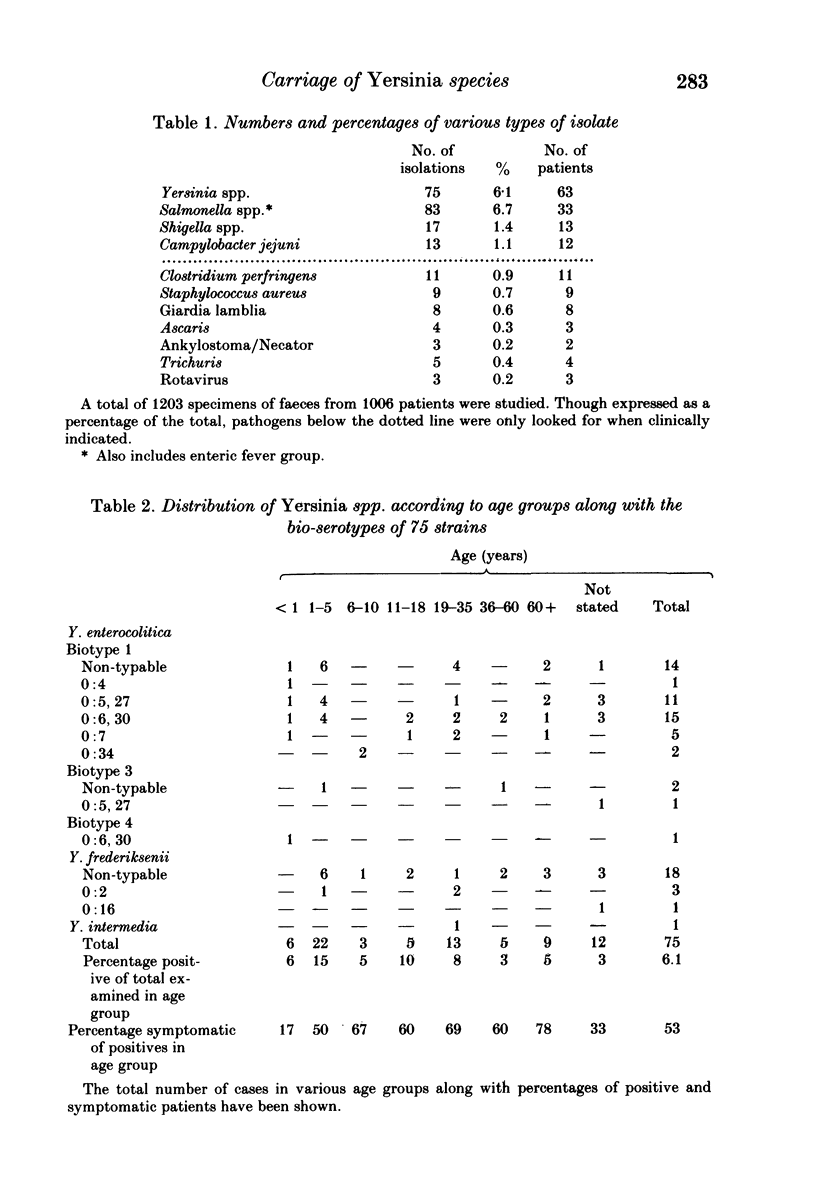
A total of 1,203 unselected routine faecal samples from 1,006 patients were cultured for Yersinia species by a cold enrichment technique. Seventy-five specimens (6.1%) from 63 patients were culture-positive for Yersinia spp. Fifty-two were Yersinia enterocolitica, 22 Yersinia frederiksenii and 1 Yersinia intermedia. The predominant Y. enterocolitica isolates belonged to biotype 1 - serotype 0:6, 30 or serotype 0:5, 27. Y. frederiksenii strains were non-typable. Forty isolates were recovered from 33 patients with gastroenteritis. During the study period 83 Salmonella spp. from 33 patients, 17 Shigella sonnei from 13 patients and 13 Campylobacter jejuni from 12 patients were cultured. Yersinia spp. was isolated in association with salmonella on three occasions, twice with rotavirus and once each with Shigella sonnei, Campylobacter jejuni and Trichuris trichiura.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asakawa Y., Akahane S., Shiozawa K., Honma T. Investigations of source and route of Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Flanigan S. M., Pickett M. J., Martin W. J. Clinical isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica: cold temperature enrichment. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Dec;2(6):559–560. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.6.559-560.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith A. K., Feeley J. C., Morris G. K. Yersinia enterocolitica: a review of the bacterium and recommended laboratory methodology. Health Lab Sci. 1977 Oct;14(4):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., de Koning J., Samsom J. P. Incidence of human infection with Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O3, O8, and O9 and the use of indirect immunofluorescence in diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):138–141. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa Y., Ikemura K. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from human specimens and their drug-resistance in the Niigata District of Japan. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Jacobson J. A., Nahmias A. Yersinia enterocolitica infections in children. J Pediatr. 1976 Jul;89(1):77–79. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80932-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. H. The spectrum of clinical manifestations of infections with Yersinia enterocolitica and their pathogenesis. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:257–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Pai C. H., Lafleur L., Lackman L., Hammerberg O. Yersinia enterocolitica gastroenteritis: a prospective study of clinical, bacteriologic, and epidemiologic features. J Pediatr. 1980 Jan;96(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner R. K., Marks M. I., Weber A., Pai C. H. Yersinia enterocolitica: comparative in vitro activities of seven new beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):140–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto W. H., Lau J. T. Septicaemia due to Yersinia enterocolitica biotype I in Hong Kong. J Infect. 1984 Jan;8(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)93246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan B., Harmon M. C., Mehlman I. J. Yersinia enterocolitica. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;52(2):151–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb04838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma S., Lafleur L. Survey on the incidence of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in Canada. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):469–473. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.469-473.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noyen R., Vandepitte J., Wauters G., Selderslaghs R. Yersinia enterocolitica: its isolation by cold enrichment from patients and healthy subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):1052–1056. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandepitte J., Wauters G. Epidemiological and clinical aspects of human Yersinia enterocolitica infections in Belgium. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:150–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissfeld A. S., Sonnenwirth A. C. Yersinia enterocolitica in adults with gastrointestinal disturbances: need for cold enrichment. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):196–197. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.196-197.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


