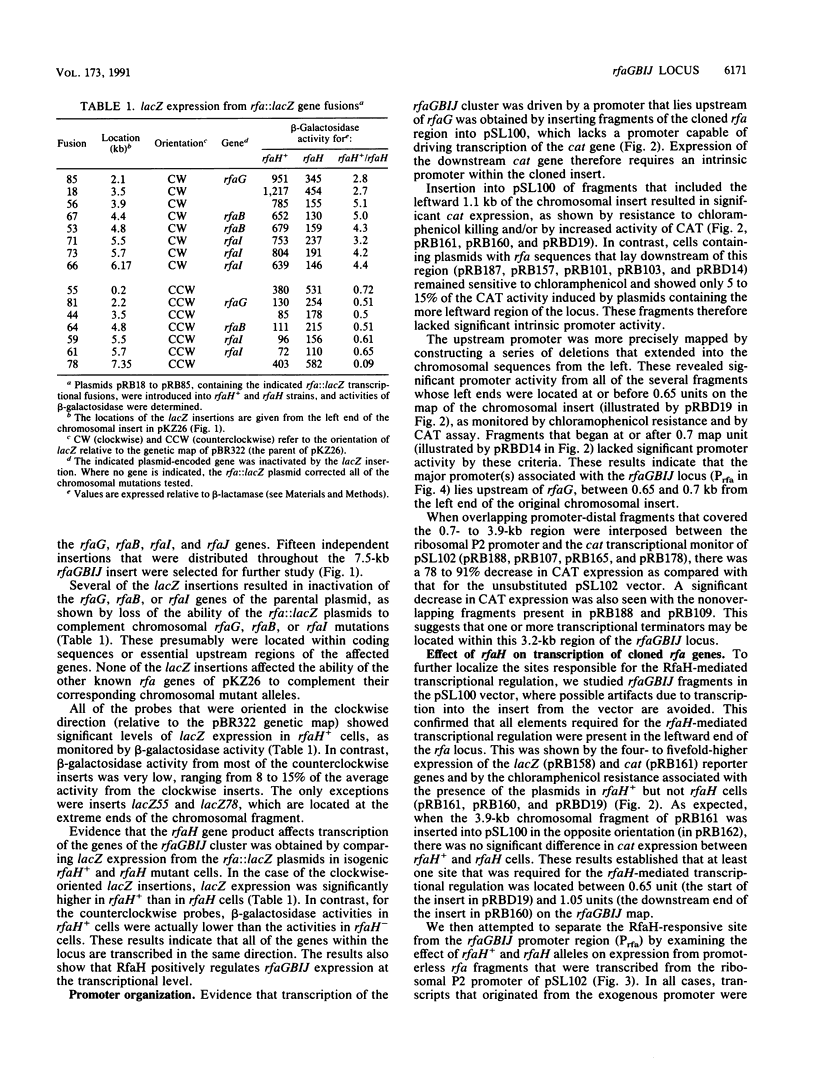
Abstract
The transcriptional organization of the rfaGBIJ gene cluster of Salmonella typhimurium was studied by using lacZ and cat transcriptional probes. The results indicated that the leftward end of the gene cluster (rfaG-rfaB-rfaI) is an operon that is transcribed from one or more promoters that lie upstream of rfaG. The results further indicated that the product of the rfaH (sfrB) gene acts as a positive regulator of transcription of the entire rfaGBIJ cluster. At least one site required for the RfaH-mediated transcriptional regulation lies within or very close to the upstream promoter.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin E. A., Graves J. F., Hite L. A., Parker C. T., Schnaitman C. A. Genetic analysis of lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis by Escherichia coli K-12: insertion mutagenesis of the rfa locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5312–5325. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5312-5325.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Manning P. A., Achtman M., Willetts N. sfrA and sfrB products of Escherichia coli K-12 are transcriptional control factors. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):840–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.840-844.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstenius P., Flock J. I., Lindberg A. Nucleotide sequence of rfaI and rfaJ genes encoding lipopolysaccharide glycosyl transferases from Salmonella typhimurium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6128–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeger E. S., Schulte T., Rothfield L. I. Regulation of membrane glycosyltransferases by the sfrB and rfaH genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3064–3069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Howe M. M., Ingraham J. L., Pierson L. S., 3rd, Turnbough C. L., Jr Infection of Salmonella typhimurium with coliphage Mu d1 (Apr lac): construction of pyr::lac gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.299-305.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farewell A., Brazas R., Davie E., Mason J., Rothfield L. I. Suppression of the abnormal phenotype of Salmonella typhimurium rfaH mutants by mutations in the gene for transcription termination factor Rho. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5188–5193. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5188-5193.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney D., Skurray R., Willetts N. Regulation of the F conjugation genes studied by hybridization and tra-lacZ fusion. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):103–122. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayhack E. J., Yang X. J., Lau L. F., Roberts J. W. Phage lambda gene Q antiterminator recognizes RNA polymerase near the promoter and accelerates it through a pause site. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson H. P., Lindberg A. A., Stocker B. A. Lipopolysaccharide core defects in Salmonella typhimurium mutants which are resistant to Felix O phage but retain smooth character. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):97–112. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadam S. K., Rehemtulla A., Sanderson K. E. Cloning of rfaG, B, I, and J genes for glycosyltransferase enzymes for synthesis of the lipopolysaccharide core of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):277–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.277-284.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Squires C. L., Squires C. Antitermination of E. coli rRNA transcription is caused by a control region segment containing lambda nut-like sequences. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Phage lambda and the regulation of transcription termination. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W., O'Callaghan C. H. Beta-lactamase assays. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:69–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. J., Roberts J. W. Gene Q antiterminator proteins of Escherichia coli phages 82 and lambda suppress pausing by RNA polymerase at a rho-dependent terminator and at other sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5301–5305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



