Abstract
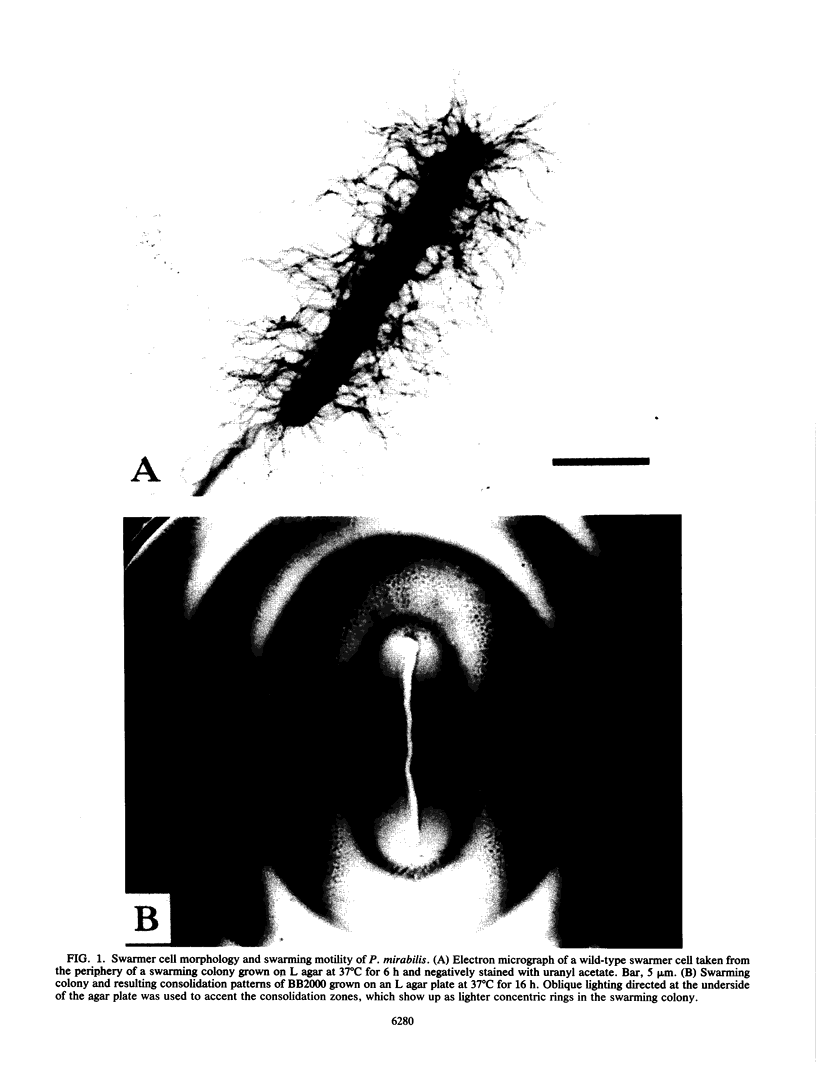
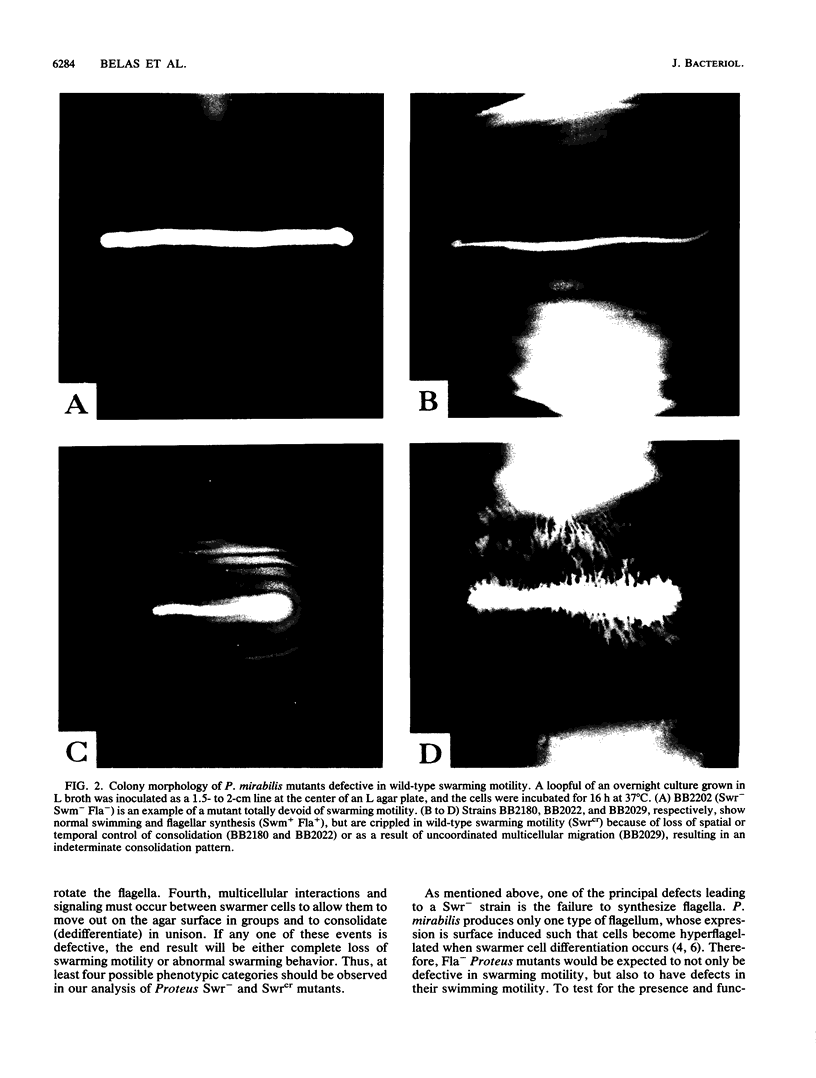
Proteus mirabilis is a dimorphic bacterium which exists in liquid cultures as a 1.5- to 2.0-microns motile swimmer cell possessing 6 to 10 peritrichous flagella. When swimmer cells are placed on a surface, they differentiate by a combination of events that ultimately produce a swarmer cell. Unlike the swimmer cell, the polyploid swarmer cell is 60 to 80 microns long and possesses hundreds to thousands of surface-induced flagella. These features, combined with multicellular behavior, allow the swarmer cells to move over a surface in a process called swarming. Transposon Tn5 was used to produce P. mirabilis mutants defective in wild-type swarming motility. Two general classes of mutants were found to be defective in swarming. The first class was composed of null mutants that were completely devoid of swarming motility. The majority of nonswarming mutations were the result of defects in the synthesis of flagella or in the ability to rotate the flagella. The remaining nonswarming mutants produced flagella but were defective in surface-induced elongation. Strains in the second general class of mutants, which made up more than 65% of all defects in swarming were motile but were defective in the control and coordination of multicellular swarming. Analysis of consolidation zones produced by such crippled mutants suggested that this pleiotropic phenotype was caused by a defect in the regulation of multicellular behavior. A possible mechanism controlling the cyclic process of differentiation and dediferentiation involved in the swarming behavior of P. mirabilis is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti L., Harshey R. M. Differentiation of Serratia marcescens 274 into swimmer and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4322–4328. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4322-4328.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P. Changes in metabolic activity of Proteus mirabilis during swarming. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Aug;125(2):445–450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-2-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Smith D. G., Rowbury R. J. Alterations in the cell envelope composition of Proteus mirabilis during the development of swarmer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 16;584(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Erskine D., Flaherty D. Transposon mutagenesis in Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6289–6293. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6289-6293.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Mileham A., Simon M., Silverman M. Transposon mutagenesis of marine Vibrio spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):890–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.890-896.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Simon M., Silverman M. Regulation of lateral flagella gene transcription in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):210–218. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.210-218.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisset K. A. The motion of the swarm in Proteus mirabilis. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):33–35. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. W., Bisset K. A. Development of concentric zones in the Proteus swarm colony. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):497–500. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkinham J. O., 3rd, Hoffman P. S. Unique developmental characteristics of the swarm and short cells of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1037–1040. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1037-1040.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Sarnow E., Milde K. Cell cycle parameters of Proteus mirabilis: interdependence of the biosynthetic cell cycle and the interdivision cycle. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.741-748.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOENIGER J. F. CELLULAR CHANGES ACCOMPANYING THE SWARMING OF PROTEUS MIRABILIS. I. OBSERVATIONS OF LIVING CULTURES. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Feb;10:1–9. doi: 10.1139/m64-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Bacterial surface translocation: a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):478–503. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.478-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeniger J. F. Cellular changes accompanying the swarming of Proteus mirabilis. II. Observations of stained organisms. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):113–123. doi: 10.1139/m66-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries C. D., Rogers H. E. Enhancing effect of agar on swarming by Proteus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):732–733. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.732-733.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Control of multicellular development: Dictyostelium and Myxococcus. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:539–566. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. Regulation of cell division in E. coli. Trends Genet. 1990 Jan;6(1):22–25. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Hilmen M., Silverman M. Flagellar dynamometer controls swarmer cell differentiation of V. parahaemolyticus. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Silverman M. Iron regulation of swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):731–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.731-736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Silverman M. Surface-induced swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1057–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORY P. Proteus infections in hospital. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):55–62. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sar N., McCarter L., Simon M., Silverman M. Chemotactic control of the two flagellar systems of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):334–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.334-341.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W. Proteus morgani is less frequently associated with urinary tract infections than Proteus mirabilis--an explanation. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Aug;16(3):317–322. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Stewart K. R., Williams F. D. Extracellular slime associated with Proteus mirabilis during swarming. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.930-937.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Anderson D. M., Hoffman P. S., Schwarzhoff R. H., Leonard S. Evidence against the involvement of chemotaxis in swarming of Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):237–248. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.237-248.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Schwarzhoff R. H. Nature of the swarming phenomenon in Proteus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:101–122. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Herrero M., Jakubzik U., Timmis K. N. Mini-Tn5 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis, promoter probing, and chromosomal insertion of cloned DNA in gram-negative eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6568–6572. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6568-6572.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]