Abstract
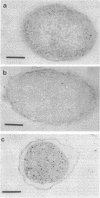
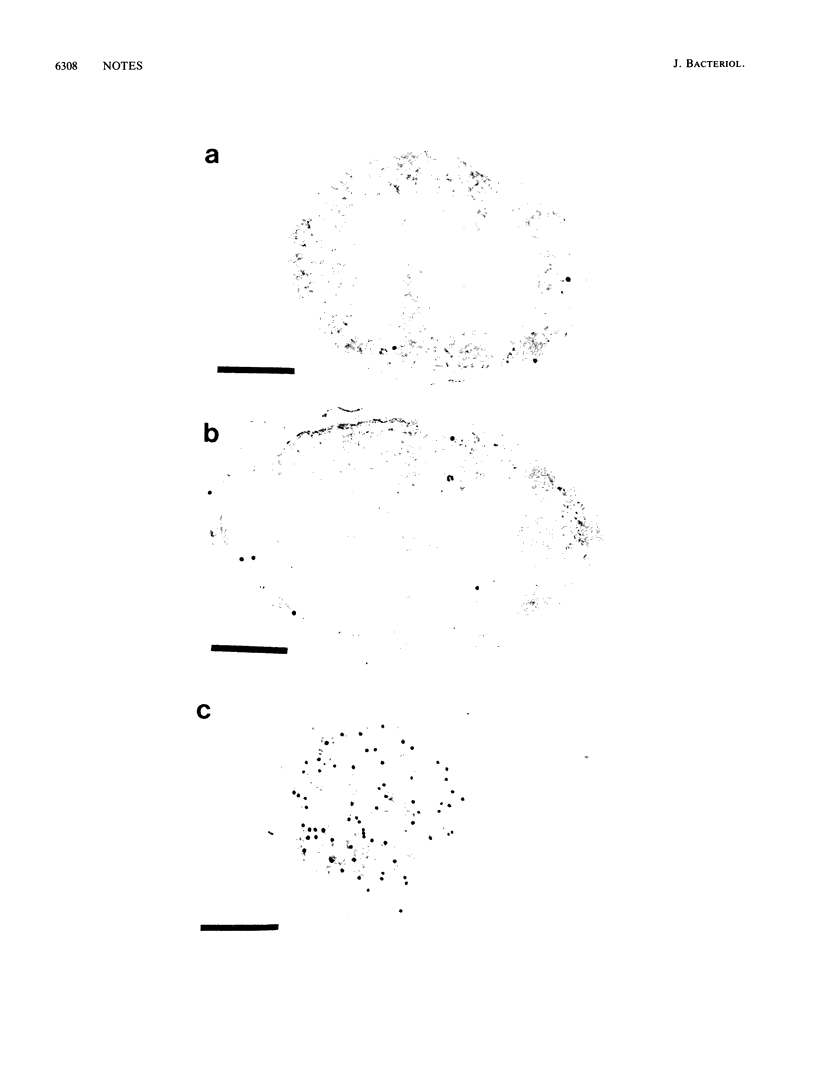
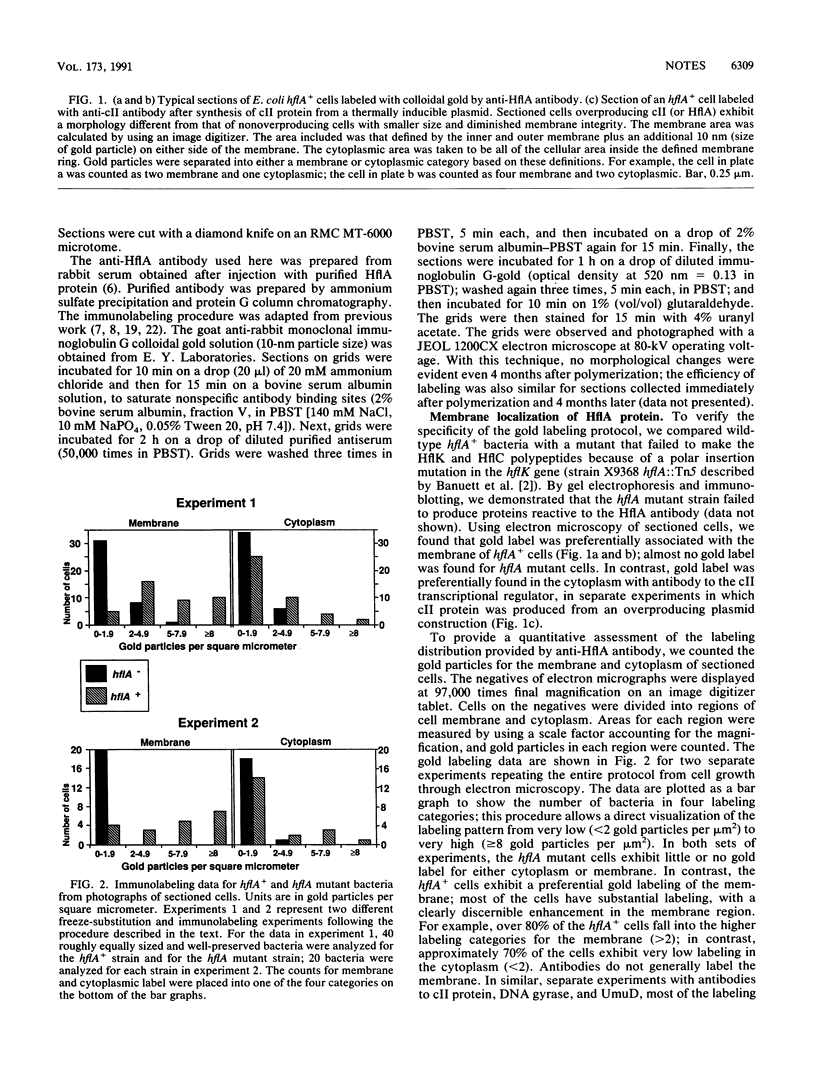
The hflA locus of Escherichia coli specifies a multisubunit protease that selectively degrades the cII transcriptional activator of phage lambda. The regulated turnover of cII is critical for the choice between the lytic and lysogenic pathways of viral development. Previous cell fractionation work has indicated that HflA is associated with the inner membrane fraction. We have sought to demonstrate that the HflA protease is localized in the cell membrane of intact cells. To achieve this goal, we have combined electron microscopy of thin-sectioned E. coli cells with antibody tagging by a colloidal gold label. Using antibody to purified HflA protein, we have found preferential membrane labeling for hflA+ cells but not for hflA mutant cells. We conclude that HflA protease is localized in the cell membrane. The membrane location for HflA protein may serve as a component of a targeting mechanism to limit the action of the regulatory protease to selected cytoplasmic proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banuett F., Herskowitz I. Identification of polypeptides encoded by an Escherichia coli locus (hflA) that governs the lysis-lysogeny decision of bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4076–4085. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4076-4085.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F., Hoyt M. A., McFarlane L., Echols H., Herskowitz I. hflB, a new Escherichia coli locus regulating lysogeny and the level of bacteriophage lambda cII protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Wulff D. L. Genetic and biochemical investigation of the Escherichia coli mutant hfl-1 which is lysogenized at high frequency by bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):299–306. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.299-306.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Wulff D. The roles of the lambda c3 gene and the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activation system in the establishment of lysogeny by bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):779–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. H., Echols H. A class of Escherichia coli proteins controlled by the hflA locus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):737–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. H., Muhlrad P. J., Hoyt M. A., Echols H. Cleavage of the cII protein of phage lambda by purified HflA protease: control of the switch between lysis and lysogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7882–7886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger M. B. Removal of background label in immunocytochemistry with the apolar Lowicryls by using washed protein A-gold-precoupled antibodies in a one-step procedure. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1989 Feb;11(2):109–116. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger M., Bjornsti M. A., Uetz T., Hobot J. A., Kellenberger E. Intracellular location of the histonelike protein HU in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4757–4768. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4757-4768.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch J. W., Wulff D. L. Fine structure mapping, complementation, and physiology of Escherichia coli hfl mutants. Genetics. 1974 Jul;77(3):435–448. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L., Beveridge T. J. Evaluation of freeze-substitution and conventional embedding protocols for routine electron microscopic processing of eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2141–2149. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2141-2149.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Hagen D. The lysis-lysogeny decision of phage lambda: explicit programming and responsiveness. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:399–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y., Lewis M., Rosenberg M. Purification and properties of a transcriptional activator. The cII protein of phage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9128–9134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., Knight D. M., Das A., Miller H. I., Echols H. Control of phage lambda development by stability and synthesis of cII protein: role of the viral cIII and host hflA, himA and himD genes. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D. Mutations in a temperate bacteriophage affecting its ability to lysogenize Escherichia coli. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller R. D., Goldstein R. V., Nishimoto K. R. Metabolism of individual proteins in exponentially growing Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2524–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padrón R., Alamo L., Craig R., Caputo C. A method for quick-freezing live muscles at known instants during contraction with simultaneous recording of mechanical tension. J Microsc. 1988 Aug;151(Pt 2):81–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb04616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattray A., Altuvia S., Mahajna G., Oppenheim A. B., Gottesman M. Control of bacteriophage lambda CII activity by bacteriophage and host functions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):238–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.238-242.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson-Gomes A., Simon G. T. Flat mold embedding with LR white and Lowicryl K4M. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1989 Nov;13(3):266–267. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060130312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R., Rine J. Transmission electron microscopy and immunocytochemical studies of yeast: analysis of HMG-CoA reductase overproduction by electron microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:473–512. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]