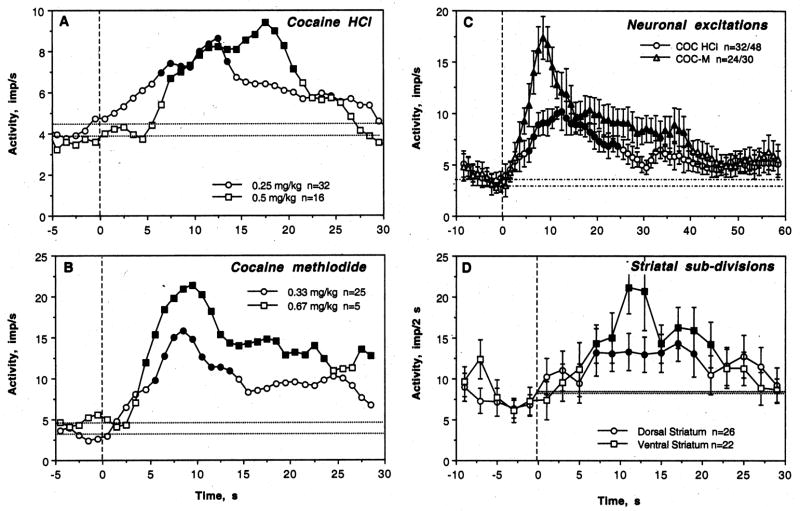
Fig. 7.
A and B. Dose-response relationships for the effects of cocaine HCl and COC-methiodide on discharge rate in awake rats during DA receptor blockade. Each graph shows mean changes in discharge rate (imp/s) after injection of either COC (A) or COC-M (B) at a single (0.25 and 0.33 mg/kg) or double dose (0.5 and 0.67 mg/kg). For clarity, data are shown without standard errors. n depicts the numbers of tests in each group. The effect of COC HCl was significant for both doses, but stronger at higher (F15,495=3.06, p<0.001) than lower dose (F31,991=1.63, p <0.03). The effect of COC-M was significant for both doses (0.33 mg/kg: F24,774=4.72, p<0.01; 0.67 mg/kg: F4,309=2.49, p<0.001), but the amplitude of rate increase was higher at larger dose. Values statistically different from baseline are shown as filled symbols. C. Time-course of neuronal excitations induced by COC and COC-M in awake rats during DA receptor blockade. In this case, only excitations were averaged and shown as mean changes for 10 s before and 60 s after the injection start. Filled symbols show values significantly different from baseline. D. Differences in the pattern of phasic excitation induced by COC in dorsal and ventral striatal neurons in awake rats during DA receptor blockade. To decrease variability, data are shown for each subsequent 2-s intervals. While the effect of cocaine on discharge rate was significant in both striatal sub-divisions, it was quantitatively stronger in the NAcc (F21,351=3.12, p<0.001) than in the caudo-putamen (F25,415=1.91, p=0.02).