Abstract
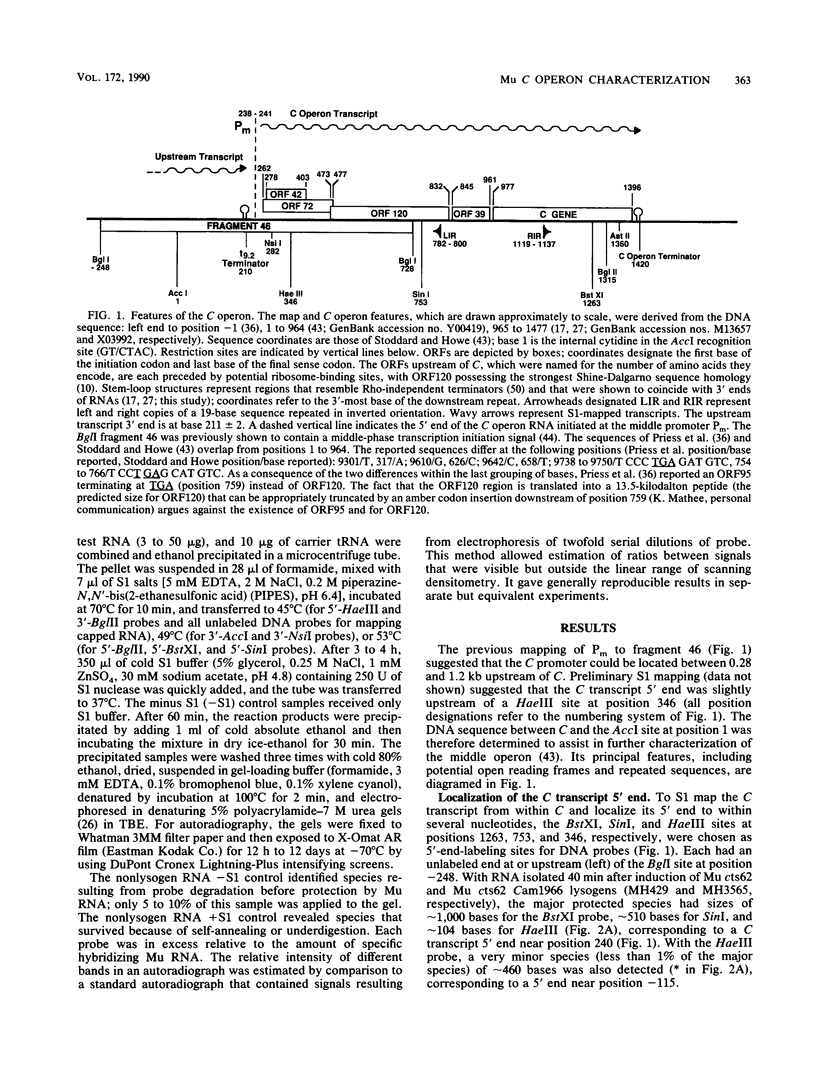
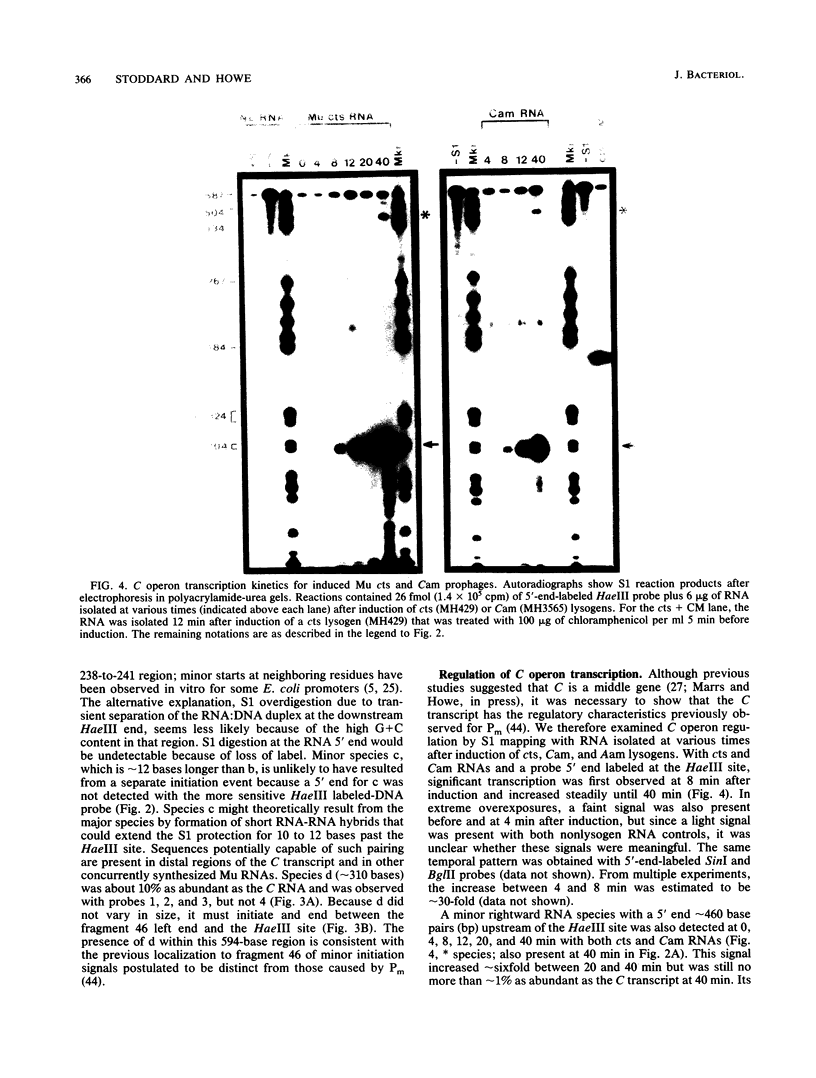
Mu transcription occurs in three phases: early, middle, and late. Middle transcription occurs in the region of the C gene, which encodes the transactivator for late transcription. A middle promoter, Pm, was previously localized between 0.28 and 1.2 kilobase pairs upstream of C. We used S1 nuclease mapping with both unlabeled and radiolabeled capped RNAs from induced lysogens to characterize C transcription and identify its promoter. The C transcription initiation site was localized to a 4-base-pair region, approximately 740 base pairs upstream of C within the region containing Pm. Transcription of C was activated between 4 and 8 min after induction of cts and Cam lysogens and increased throughout the lytic cycle. Significant C transcription did not occur in replication-defective Aam lysogens. These kinetic and regulatory characteristics identify the C transcript as a middle RNA species and demonstrate that Pm is the C promoter. DNA sequence analysis of the Pm region showed a good -10, but poor -35, site homology to the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase consensus sequence. In addition, the sequence demonstrated that C is the distal gene in a middle operon containing several open reading frames. S1 mapping also showed an upstream transcript with a 3' end in the Pm region at a sequence strongly resembling a Rho-independent terminator. The regulatory characteristics of this RNA are consistent with this terminator, t9.2, being the early operon terminator.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bade E. G. Asymmetric transcription of bacteriophage Mu-1. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1205–1207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1205-1207.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Cate R. L., Perlmutter A. P. Precise location of two promoters for the beta-lactamase gene of pBR322. S1 mapping of ribonucleic acid isolated from Escherichia coli or synthesized in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9205–9210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. P., Obukowicz M. G., Lynn D. L., Howe M. M. Isolation of point mutations in bacteriophage Mu attachment regions cloned in a lambda::mini-Mu phage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Gross C. A., Watanabe K. K., Burgess R. R. The operon that encodes the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase also encodes ribosomal protein S21 and DNA primase in E. coli K12. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):335–349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90453-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölker M., Kahmann R. The Escherichia coli regulatory protein OxyR discriminates between methylated and unmethylated states of the phage Mu mom promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2403–2410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölker M., Wulczyn F. G., Kahmann R. Role of bacteriophage Mu C protein in activation of the mom gene promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2019–2027. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2019-2027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Site-specific recognition of the bacteriophage Mu ends by the Mu A protein. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goosen N., van Heuvel M., Moolenaar G. F., van de Putte P. Regulation of Mu transposition. II. The escherichia coli HimD protein positively controls two repressor promoters and the early promoter of bacteriophage Mu. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goosen N., van de Putte P. Role of ner protein in bacteriophage Mu transposition. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):503–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.503-507.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goosen T., Giphart-Gassler M., Van de Putte P. Bacteriophage Mu DNA replication is stimulated by non-essential early functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(1):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00422925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Lauth M. R., Wells R. G., Wityk R. J., Salvo J. J., Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: identification of three binding sites for resolvase at the res sites of gamma delta and Tn3. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Howe M. M. Involvement of the invertible G segment in bacteriophage mu tail fiber biosynthesis. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):296–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig P., Kahmann R. The sequence and mom-transactivation function of the C gene of bacteriophage Mu. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiestand-Nauer R., Iida S. Sequence of the site-specific recombinase gene cin and of its substrates serving in the inversion of the C segment of bacteriophage P1. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1733–1740. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Collier D. A., Kilpatrick M. W., Krause H. M. Supercoiling and integration host factor change the DNA conformation and alter the flow of convergent transcription in phage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3035–3042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M. Prophage deletion mapping of bacteriophage Mu-1. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause H. M., Higgins N. P. Positive and negative regulation of the Mu operator by Mu repressor and Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3744–3752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause H. M., Rothwell M. R., Higgins N. P. The early promoter of bacteriophage Mu: definition of the site of transcript initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5483–5495. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. M. The nucleotide sequence of the lactose messenger ribonucleic acid transcribed from the UV5 promoter mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin W., Howe M. M. Localization and DNA sequence analysis of the C gene of bacteriophage Mu, the positive regulator of Mu late transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4881–4897. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin W., Rao G., Howe M. M. Bacteriophage Mu late promoters: four late transcripts initiate near a conserved sequence. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2003–2018. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2003-2018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Moss B. Modification of RNA by mRNA guanylyltransferase and mRNA (guanine-7-)methyltransferase from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9330–9335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Day K., Schultz D., Ericsen W., Rawluk L., Howe M. Correction and refinement of the genetic map of bacteriophage Mu. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):320–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. L., Reich C. Instability of transposase activity: evidence from bacteriophage mu DNA replication. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Brinkman A., van de Putte P. DNA inversions in the chromosome of Escherichia coli and in bacteriophage Mu: relationship to other site-specific recombination systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5355–5358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett G., 3rd, Echols H. Retroregulation of the bacteriophage lambda int gene: limited secondary degradation of the RNase III-processed transcript. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):588–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.588-592.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P., Schmitt R. Resolution of a hybrid cointegrate between transposons Tn501 and Tn1721 defines the recombination site. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):162–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00327431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumm J. W., Moore D. D., Blattner F. R., Howe M. M. Correlation of the genetic and physical maps in the central region of the bacteriophage Mu genome. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard S. F., Howe M. M. DNA sequence within the Mu C operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7198–7198. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
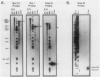
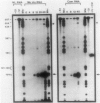
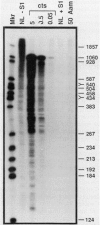
- Stoddard S. F., Howe M. M. Localization and regulation of bacteriophage Mu promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3440–3448. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3440-3448.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A., Lecocq J. P. Sensitivity of bacteriophage Mu-1 development to rifampicin and streptolydigin. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Mar 14;129(2):185–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00268631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leerdam E., Karreman C., van de Putte P. Ner, a cro-like function of bacteriophage Mu. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner B. T., Pato M. L. Early events in the replication of Mu prophage DNA. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.587-594.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijffelman C., Gassler M., Stevens W. F., van de Putte P. On the control of transcription of bacteriophage Mu. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(2):85–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00266145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijffelman C., Lotterman B. Kinetics of Mu DNA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):169–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00338691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijffelman C., van de Putte P. Transcription of bacteriophage mu. An analysis of the transcription pattern in the early phase of phage development. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(4):327–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00271147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]