Abstract
The Tar chemoreceptor of Escherichia coli mediates attractant responses to aspartate, maltose, and phenol, repellent responses to Ni2+ and Co2+, and thermoresponses. To understand the role of threonine residue 154, which is located in the ligand-binding domain of Tar, we replaced the residue with serine, isoleucine, and proline by site-directed mutagenesis. The replacements caused reductions in aspartate sensing but had only a small effect on maltose sensing and almost no effect on phenol sensing, repellent sensing, and thermosensing. These results indicate that Thr-154 of Tar is rather specifically involved in aspartate sensing. The reductions in the response threshold for aspartate by the replacements with serine, isoleucine, and proline were less than 1, about 2, and more than 5 orders of magnitude, respectively. When the corresponding threonine residue in the Tsr chemoreceptor was replaced with the same amino acids, roughly similar reductions in the response threshold for serine resulted. Thus, these threonine residues seem to have a common role in detecting the aspartate and serine attractant families. A mechanism by which these chemoreceptors detect the amino acid attractants is discussed.
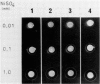
Full text
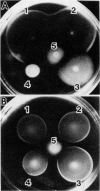
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd A., Kendall K., Simon M. I. Structure of the serine chemoreceptor in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):623–626. doi: 10.1038/301623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Genetic and biochemical properties of Escherichia coli mutants with defects in serine chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1048–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1048-1060.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imae Y., Oosawa K., Mizuno T., Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Phenol: a complex chemoeffector in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):371–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.371-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossmann M., Wolff C., Manson M. D. Maltose chemoreceptor of Escherichia coli: interaction of maltose-binding protein and the tar signal transducer. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4516–4521. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4516-4521.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Conley M. P., Boyd A., Berg H. C., Simon M. I. Chimeric chemosensory transducers of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1326–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Mizuno T., Imae Y. Thermosensing properties of Escherichia coli tsr mutants defective in serine chemoreception. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4769–4774. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4769-4774.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Boos W., Bassford P. J., Jr, Rasmussen B. A. Dependence of maltose transport and chemotaxis on the amount of maltose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9727–9733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Imae Y. Conditional inversion of the thermoresponse in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):360–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.360-367.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray S. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Additive and independent responses in a single receptor: aspartate and maltose stimuli on the tar protein. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa K., Imae Y. Demethylation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli induced by the repellents glycerol and ethylene glycol. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):576–581. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.576-581.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Macnab R. M., Alger J. R., Castle A. M. Effects of pH and repellent tactic stimuli on protein methylation levels in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):384–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.384-399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor structure in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Kramer T. J., Berg H. C. Reconstitution of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1878–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1878-1885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff C., Parkinson J. S. Aspartate taxis mutants of the Escherichia coli tar chemoreceptor. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4509–4515. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4509-4515.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]