Abstract
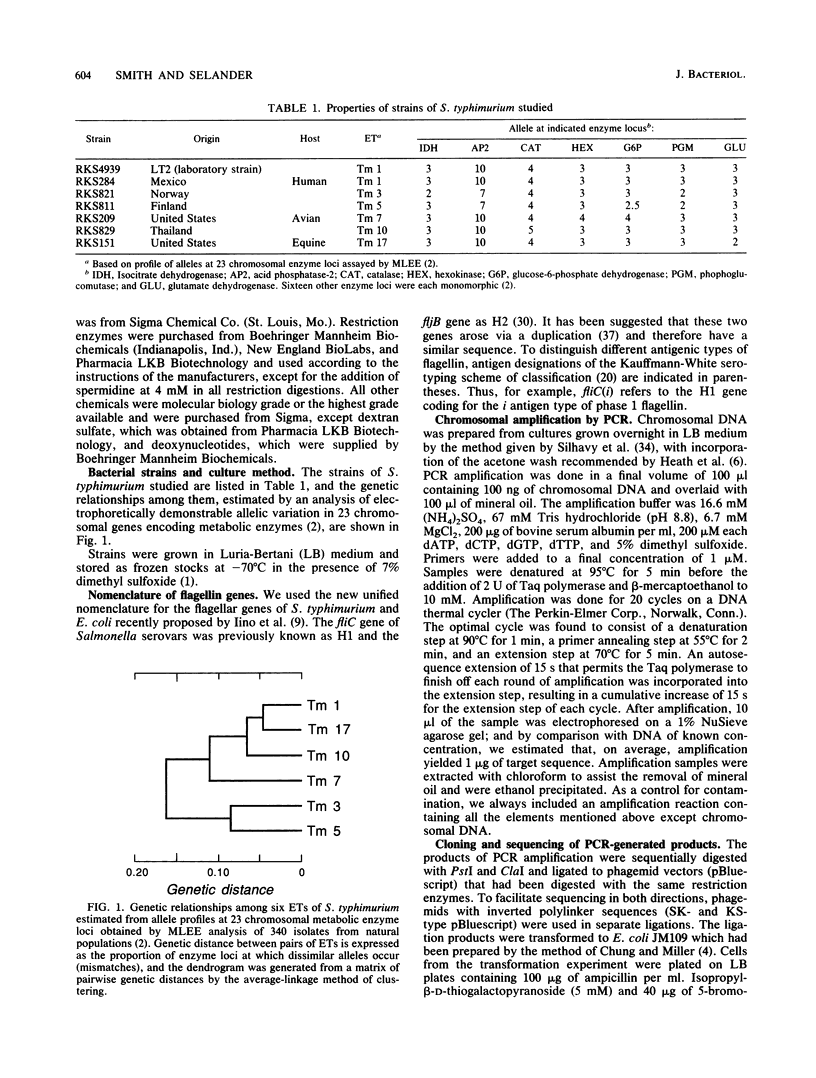
Previous studies of the phase 1 flagellar filament protein (flagellin) in strains of five serovars of Salmonella indicated that the central region of the fliC gene encoding the antigenic part of the protein is hypervariable both between and within serovars. To explore the possible use of this variation as a source of information on the phylogenetic relationships of closely related strains, we used the polymerase chain reaction technique to sequence part of the central region of the phase 1 flagellar genes of seven strains of Salmonella typhimurium that were known to differ in chromosomal genotype, as indexed by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. We found that the nucleotide sequences of the central region were identical in all seven strains and determined that both the previously published sequence of the fliC gene in S. typhimurium LT2 and a report of a marked difference in the amino acid sequence of the phase 1 flagellins of two isolates of this serovar are erroneous. Our finding that the fliC gene is not evolving by sequence drift at an unusually rapid rate is compatible with a model that invokes lateral transfer and recombination of the flagellin genes as a major evolutionary process generating new serovars (antigen combinations) of salmonellae.
Full text
PDF





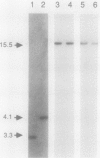
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beltran P., Musser J. M., Helmuth R., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Frerichs W. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Ferris K., McWhorter A. C., Wells J. G., Cravioto A. Toward a population genetic analysis of Salmonella: genetic diversity and relationships among strains of serotypes S. choleraesuis, S. derby, S. dublin, S. enteritidis, S. heidelberg, S. infantis, S. newport, and S. typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7753–7757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruist M. F., Simon M. I. Phase variation and the Hin protein: in vivo activity measurements, protein overproduction, and purification. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.71-79.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Miller R. H. A rapid and convenient method for the preparation and storage of competent bacterial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3580–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath L. S., Sloan G. L., Heath H. E. A simple and generally applicable procedure for releasing DNA from bacterial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):1138–1140. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.1138-1140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Fujita H., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Regions of Salmonella typhimurium flagellin essential for its polymerization and excretion. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):291–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.291-296.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Iino T. Locations of hook-associated proteins in flagellar structures of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.183-189.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Komeda Y., Kutsukake K., Macnab R. M., Matsumura P., Parkinson J. S., Simon M. I., Yamaguchi S. New unified nomenclature for the flagellar genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):533–535. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.533-535.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOYS T. M., STOCKER B. A. Mutation and recombination of flagellar antigen i of Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1963 Jan 26;197:413–414. doi: 10.1038/197413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. Identification of an antibody binding site in the phase-1 flagellar protein of Salmonella typhimurium. Microbios. 1976;15(61-62):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M., Martin J. F., Wilson H. L., Rankis V. Differences in the primary structure of the phase-1 flagellins of two strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 7;351(2):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G., Asaka J., Fujiwara T., Fujiwara T., Node K., Kondo E. Nucleotide sequence of the hag gene encoding flagellin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1479–1483. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1479-1483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G. Construction of a minimum-size functional flagellin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3305–3309. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3305-3309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman R. E. The occurrence of antigenic determinants common to flagella of different salmonella strains. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):582–586. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONOUGH M. W. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF ANTIGENICALLY DISTINCT SALMONELLA FLAGELLAR PROTEINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:342–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Savage D. C. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and taxonomic implications of the flagellin gene of Roseburia cecicola. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2612–2617. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2612-2617.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R., Crawford I. P. Clustered third-base substitutions among wild strains of Escherichia coli. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):378–380. doi: 10.1126/science.6346486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R., Stoltzfus A. Molecular evolution of the Escherichia coli chromosome. II. Clonal segments. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):359–366. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton S. M., Jacob C. O., Stocker B. A. Immune response to cholera toxin epitope inserted in Salmonella flagellin. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.2468182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The rate of synonymous substitution in enterobacterial genes is inversely related to codon usage bias. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):222–230. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala V., Ames G. F. Amplification of bacterial genomic DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing after asymmetric amplification: application to the study of periplasmic permeases. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1602–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1602-1608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus A., Leslie J. F., Milkman R. Molecular evolution of the Escherichia coli chromosome. I. Analysis of structure and natural variation in a previously uncharacterized region between trp and tonB. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):345–358. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely E., Simon M. DNA sequence adjacent to flagellar genes and evolution of flagellar-phase variation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.74-81.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg S., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the flagellar filament of Caulobacter crescentus. A flagellin lacking the outer domain and its amino acid sequence lacking an internal segment. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):787–808. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. The nucleotide sequence of the H-1r gene of Salmonella rubislaw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8227–8227. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Genetic determination of the antigenic specificity of flagellar protein in salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jan;55(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]