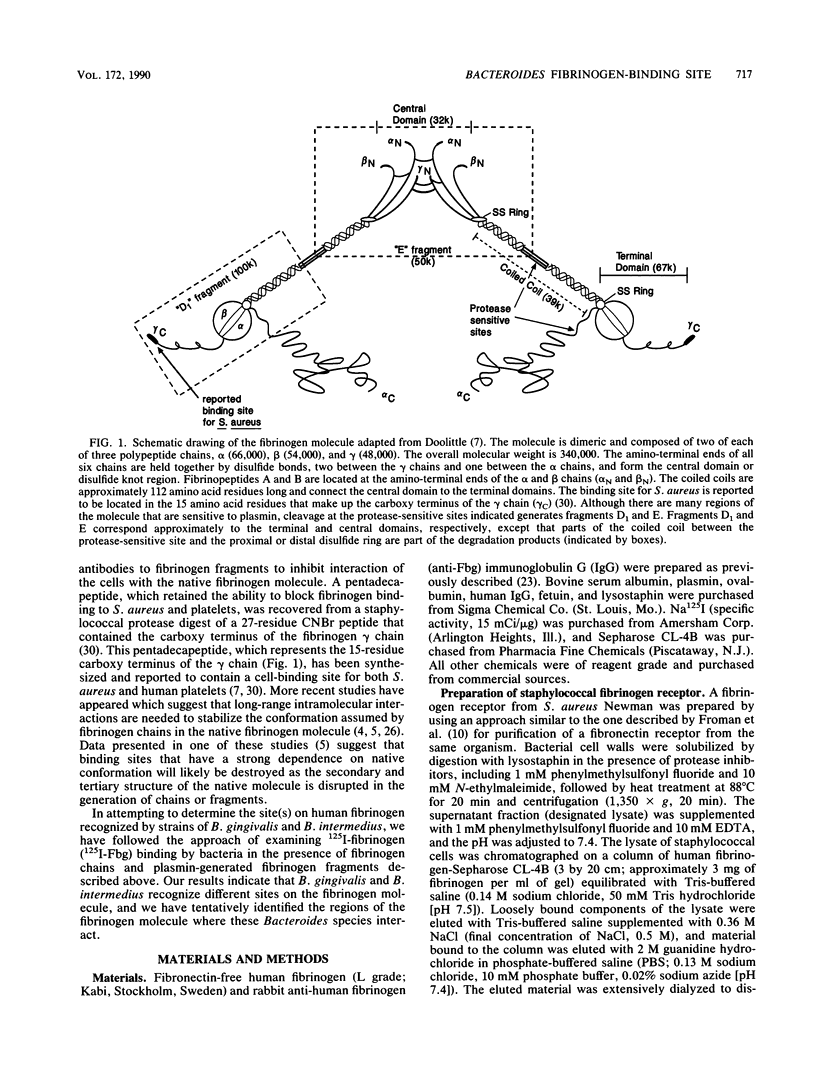
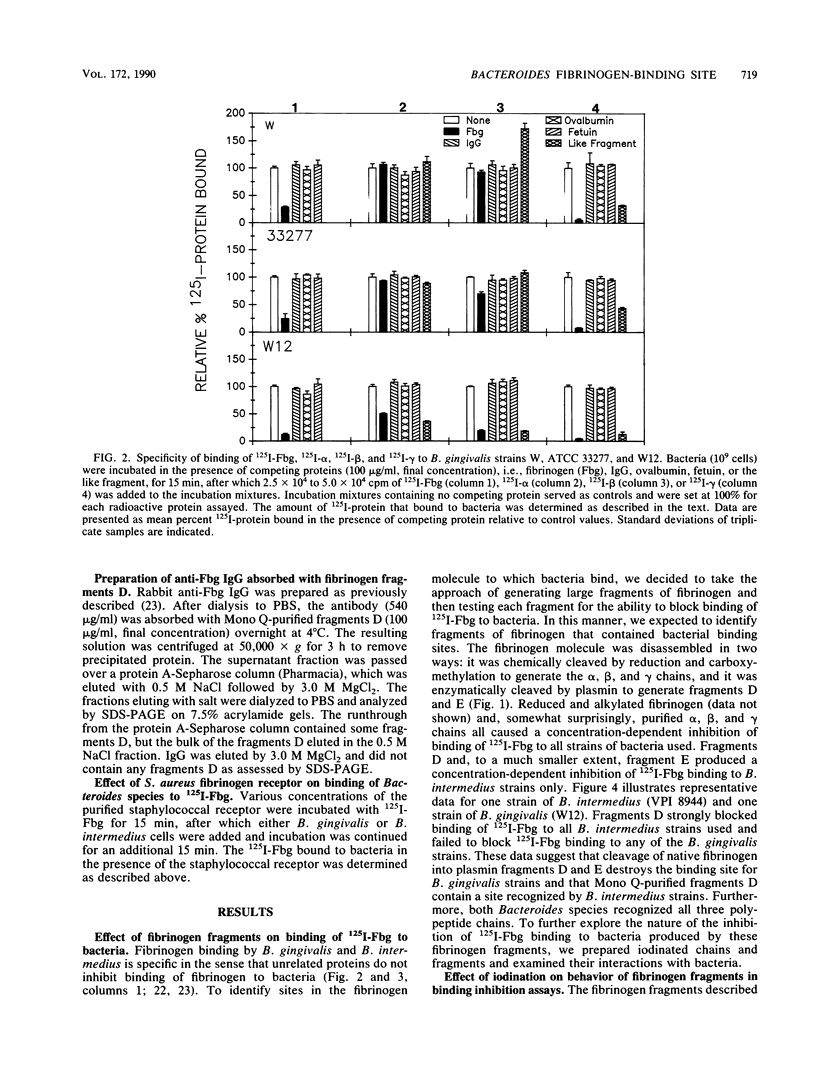
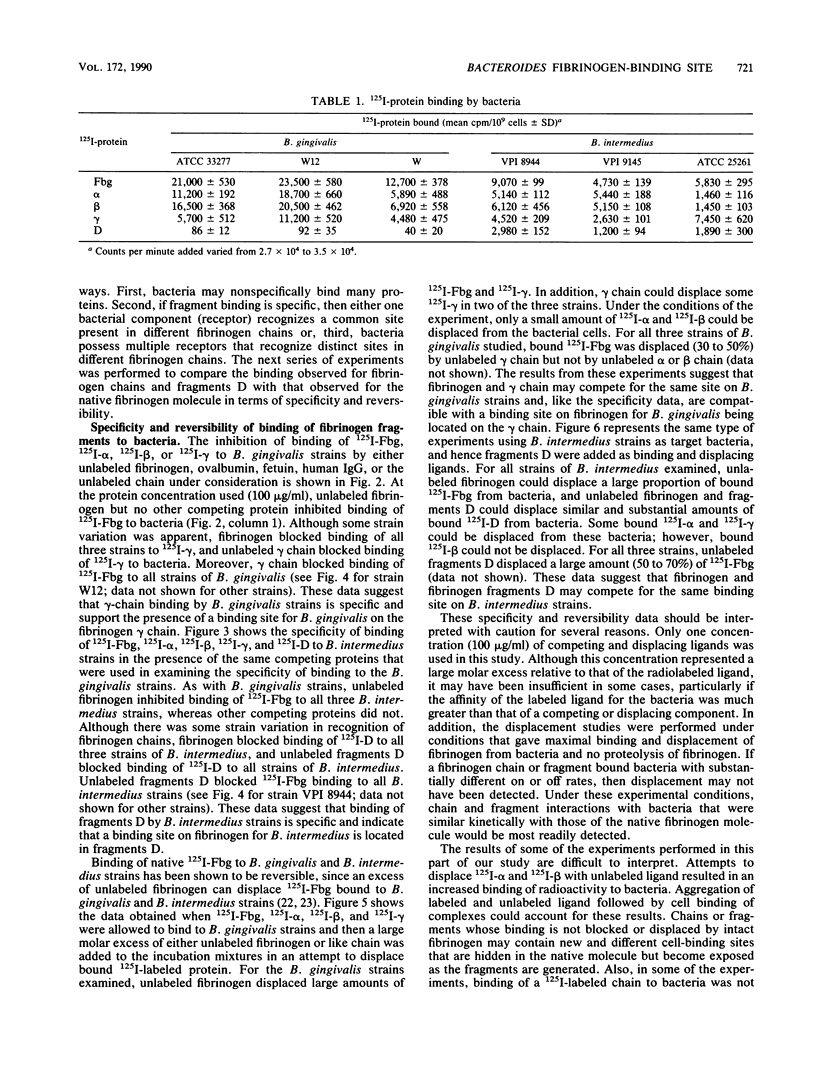
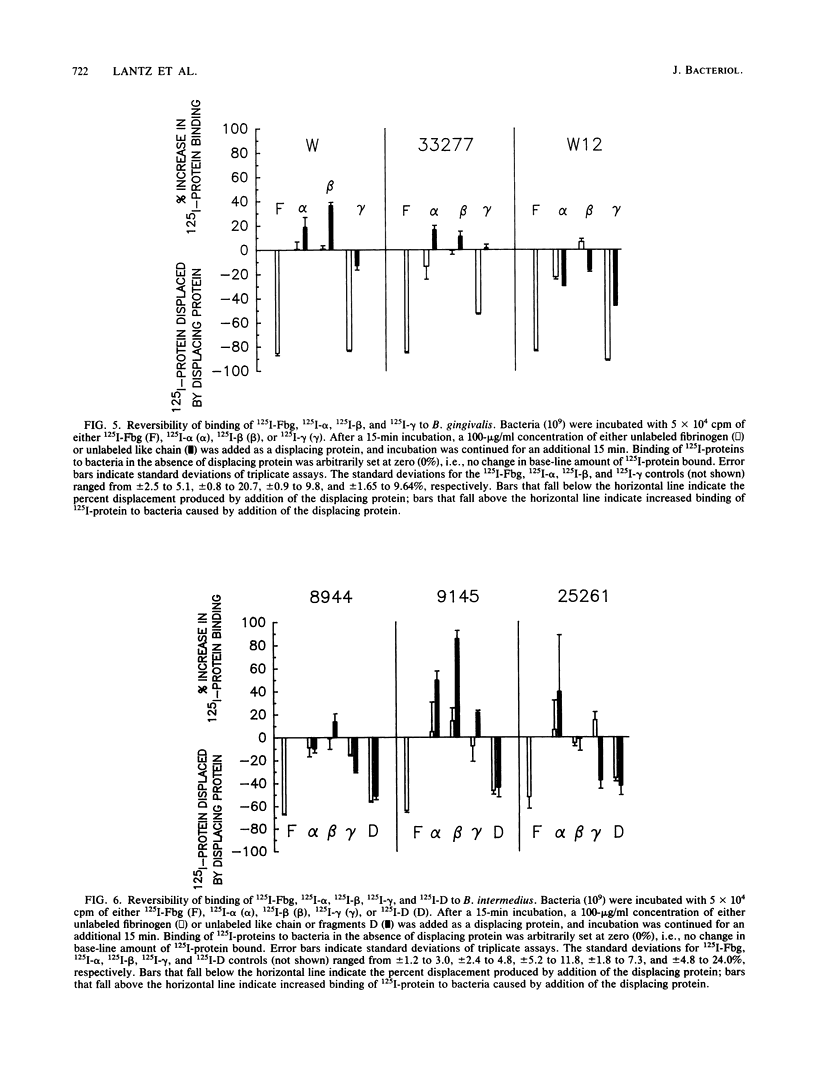
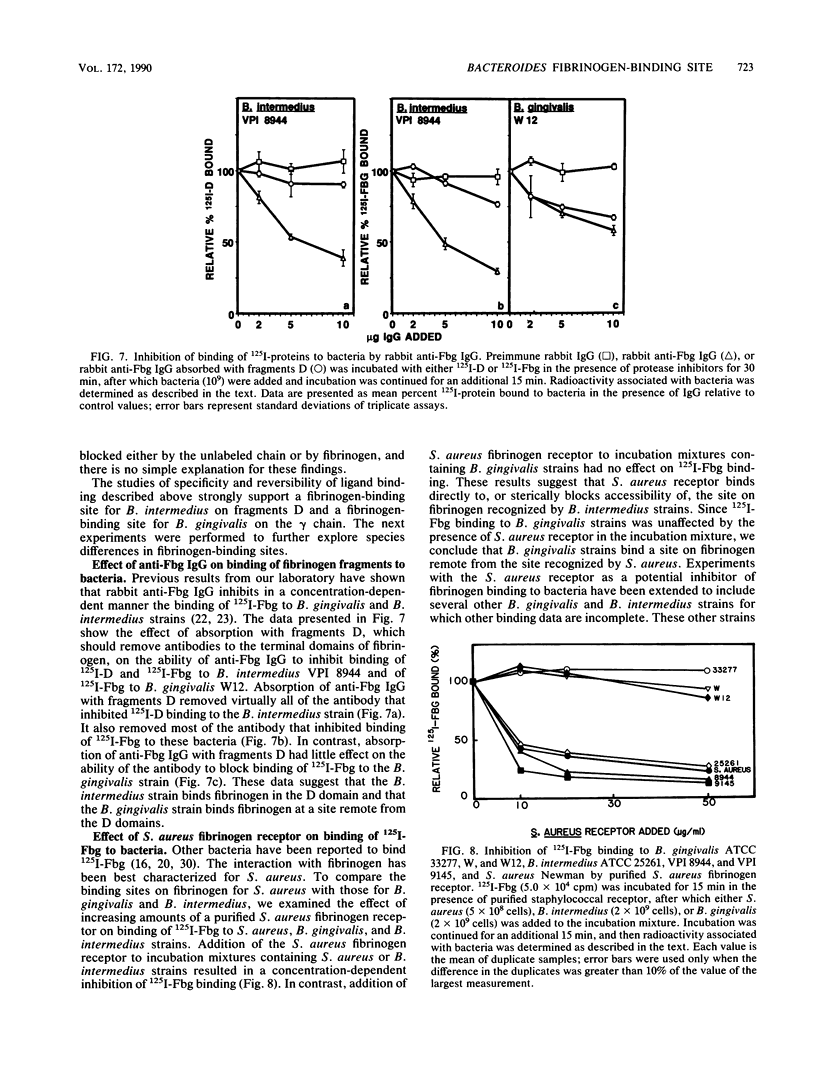
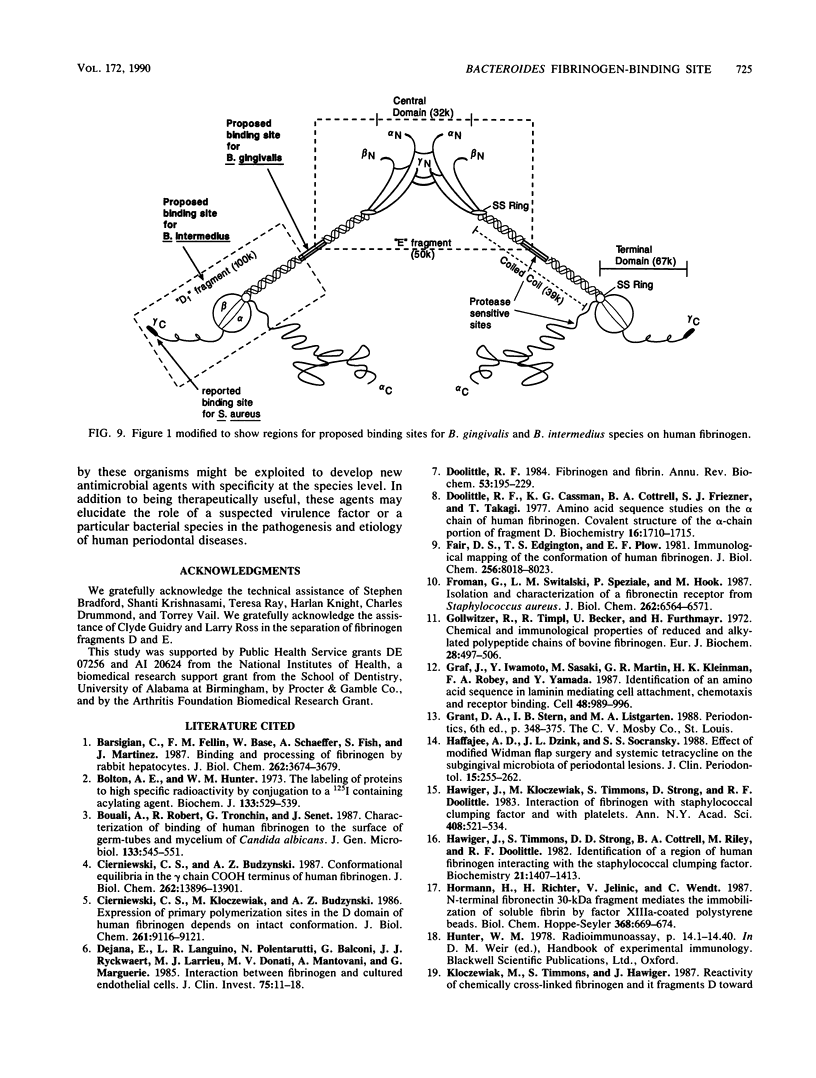
Abstract
Bacteroides (Porphyromonas) gingivalis and Bacteroides (Porphyromonas) intermedius have been implicated in the etiology of human periodontal diseases. These organisms are able to bind and degrade human fibrinogen, and these interactions may play a role in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. In attempts to map the bacterial binding sites along the fibrinogen molecule, we have found that strains of B. gingivalis and B. intermedius, respectively, recognize spatially distant and distinct sites on the fibrinogen molecule. Isolated reduced and alkylated alpha-, beta-, and gamma-fibrinogen chains inhibited binding of 125I-fibrinogen to both Bacteroides species in a concentration-dependent manner. Plasmin fragments D and to some extent fragment E, however, produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of 125I-fibrinogen binding to B. intermedius strains but did not affect binding of 125I-fibrinogen to B. gingivalis strains. Radiolabeled fibrinogen chains and fragments were compared with 125I-fibrinogen with respect to specificity and reversibility of binding to bacteria. According to these criteria, gamma chain most closely resembled the native fibrinogen molecule in behavior toward B. gingivalis strains and fragments D most closely resembled fibrinogen in behavior toward B. intermedius strains. The ability of anti-human fibrinogen immunoglobulin G (IgG) to inhibit binding of 125I-fibrinogen to B. intermedius strains was greatly reduced by absorbing the IgG with fragments D. Absorbing the IgG with fragments D had no effect on the ability of the antibody to inhibit binding of 125I-fibrinogen to B. gingivalis strains. A purified staphylococcal fibrinogen-binding protein blocked binding of 125I-fibrinogen to B. intermedius strains but not to B. gingivalis strains.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsigian C., Fellin F. M., Base W., Schaeffer A., Fish S., Martinez J. Binding and processing of fibrinogen by rabbit hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3674–3679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouali A., Robert R., Tronchin G., Senet J. M. Characterization of binding of human fibrinogen to the surface of germ-tubes and mycelium of candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):545–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cierniewski C. S., Budzynski A. Z. Conformational equilibria in the gamma chain COOH terminus of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13896–13901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cierniewski C. S., Kloczewiak M., Budzynski A. Z. Expression of primary polymerization sites in the D domain of human fibrinogen depends on intact conformation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9116–9121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Languino L. R., Polentarutti N., Balconi G., Ryckewaert J. J., Larrieu M. J., Donati M. B., Mantovani A., Marguerie G. Interaction between fibrinogen and cultured endothelial cells. Induction of migration and specific binding. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):11–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI111661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Cassman K. G., Cottrell B. A., Friezner S. J., Takagi T. Amino acid sequence studies on the alpha chain of human fibrinogen. Covalent structure of the alpha-chain portion of fragment D. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1710–1715. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:195–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D. S., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Immunochemical mapping of the conformation of human fibrinogen. The gamma 95-264 segment in inaccessible to antibody in native fibrinogen but progressively exposed by plasmic cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8018–8023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M. Isolation and characterization of a fibronectin receptor from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6564–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollwitzer R., Timpl R., Becker U., Furthmayr H. Chemical and immunological properties of reduced and alkylated polypeptide chains of bovine fibrinogen. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 4;28(4):497–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis, and receptor binding. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffajee A. D., Dzink J. L., Socransky S. S. Effect of modified Widman flap surgery and systemic tetracycline on the subgingival microbiota of periodontal lesions. J Clin Periodontol. 1988 Apr;15(4):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb01579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Strong D., Doolittle R. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with staphylococcal clumping factor and with platelets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:521–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Timmons S., Strong D. D., Cottrell B. A., Riley M., Doolittle R. F. Identification of a region of human fibrinogen interacting with staphylococcal clumping factor. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1407–1413. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörmann H., Richter H., Jelinić V., Wendt C. N-terminal fibronectin 30-kDa fragment mediates the immobilization of soluble fibrin by factor XIIIa-coated polystyrene beads. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Jun;368(6):669–674. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Hawiger J. Reactivity of chemically cross-linked fibrinogen and its fragments D toward the staphylococcal clumping receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6152–6156. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Schönbeck C., Myhre E. Fibrinogen binding structures in beta-hemolytic streptococci group A, C, and G. Comparisons with receptors for IgG and aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Oct;87(5):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam S. C., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Andrieux A., Ryckwaert J. J., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Evidence that arginyl-glycyl-aspartate peptides and fibrinogen gamma chain peptides share a common binding site on platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):947–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M. S., Rowland R. W., Switalski L. M., Hök M. Interactions of Bacteroides gingivalis with fibrinogen. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):654–658. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.654-658.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M. S., Switalski L. M., Kornman K. S., Hök M. Bacteroides intermedius binds fibrinogen. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.623-628.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoeuf R. D., Raja R. H., Fuller G. M., Weigel P. H. Human fibrinogen specifically binds hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12586–12592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Holt S. C. Biology of asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides species. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):134–152. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.134-152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. A., Meinwald Y. C., Scheraga H. A. Immunochemical determination of conformational equilibria for fragments of the B beta chain of fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):882–887. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A. Interaction of soluble fibroblast surface antigen with fribrinogen and fibrin. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):497–501. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathakis N. E., Mosesson M. W., Chen A. B., Galanakis D. K. Cryoprecipitation of fibrin-fibrinogen complexes induced by the cold-insoluble globulin of plasma. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1211–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong D. D., Laudano A. P., Hawiger J., Doolittle R. F. Isolation, characterization, and synthesis of peptides from human fibrinogen that block the staphylococcal clumping reaction and construction of a synthetic clumping particle. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1414–1420. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Bacteriology of human experimental gingivitis: effect of plaque age. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):821–829. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.821-829.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Socransky S. S., Goodson J. M. Microbiota of periodontal pockets losing crestal alveolar bone. J Periodontal Res. 1984 May;19(3):279–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb00819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence of the beta chain of human fibrinogen: homology with the gamma chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Reynolds H., Fisher J. G., Shlossman M., Dunford R., Genco R. J. Microbiological and immunological studies of adult periodontitis in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. 1988 Jan;59(1):23–31. doi: 10.1902/jop.1988.59.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



