Abstract
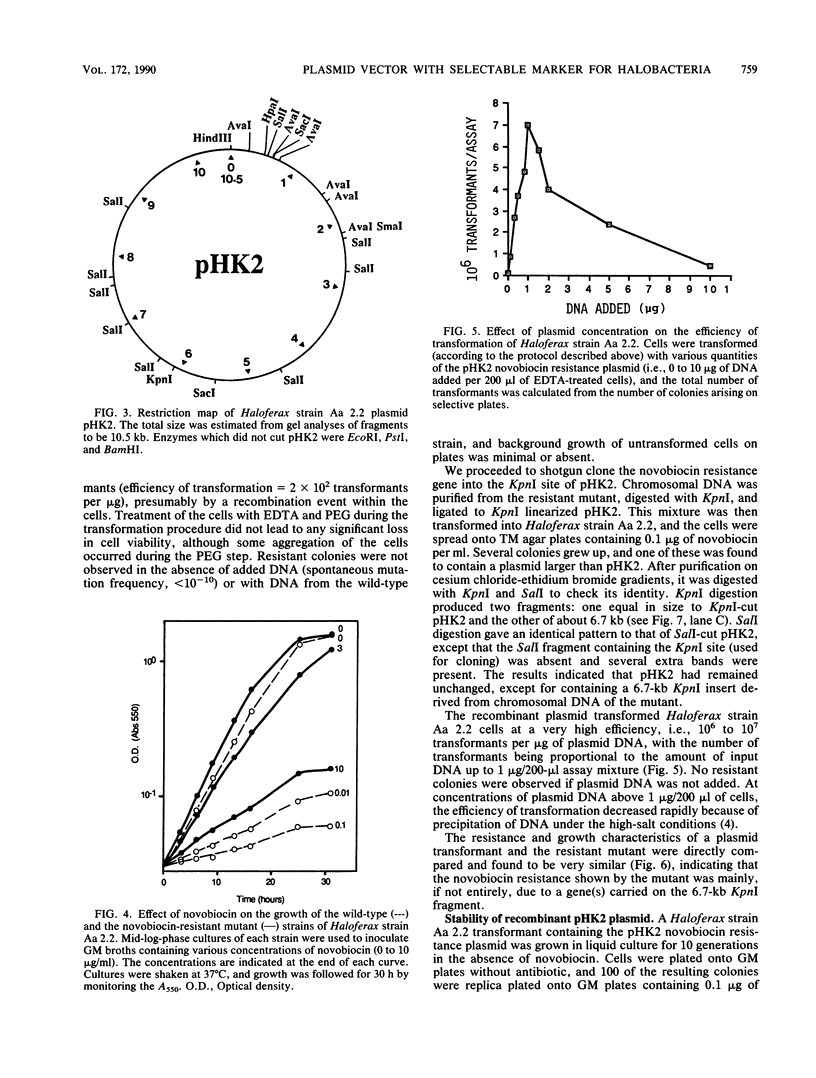
A mutant resistant to the gyrase inhibitor novobiocin was selected from a halophilic archaebacterium belonging to the genus Haloferax. Chromosomal DNA from this mutant was able to transform wild-type cells to novobiocin resistance, and these transformants formed visible colonies in 3 to 4 days on selective plates. The resistance gene was isolated on a 6.7-kilobase DNA KpnI fragment, which was inserted into a cryptic multicopy plasmid (pHK2) derived from the same host strain. The recombinant plasmid transformed wild-type cells at a high efficiency (greater than 10(6)/micrograms), was stably maintained, and could readily be reisolated from transformants. It could also transform Halobacterium volcanii and appears to be a useful system for genetic analysis in halophilic archaebacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertani G., Baresi L. Genetic transformation in the methanogen Methanococcus voltae PS. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2730–2738. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2730-2738.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlebois R. L., Lam W. L., Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Characterization of pHV2 from Halobacterium volcanii and its use in demonstrating transformation of an archaebacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8530–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Lam W. L., Charlebois R. L., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. Transformation methods for halophilic archaebacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):148–152. doi: 10.1139/m89-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBorde D. C., Naeve C. W., Herlocher M. L., Maassab H. F. Resolution of a common RNA sequencing ambiguity by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Anal Biochem. 1986 Sep;157(2):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90626-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
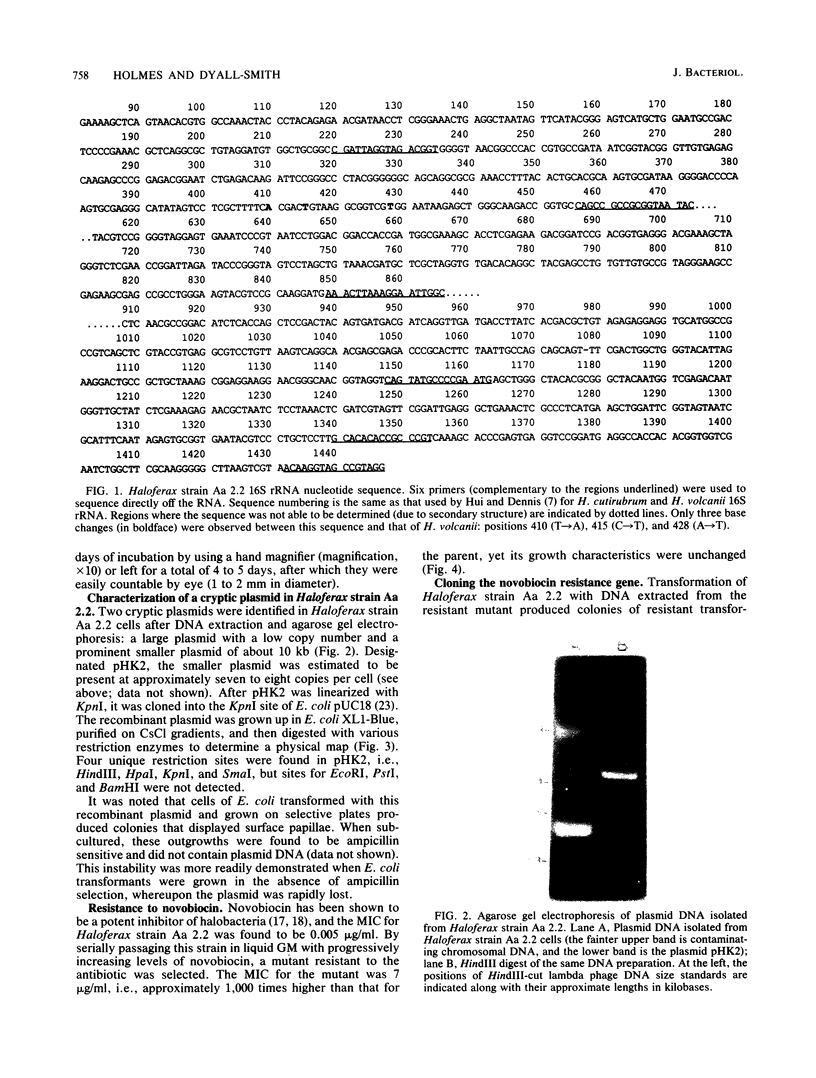
- Hui I., Dennis P. P. Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene clusters in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Werczberger R. Genetic transfer in Halobacterium volcanii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):461–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.461-462.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeve C. W., Hinshaw V. S., Webster R. G. Mutations in the hemagglutinin receptor-binding site can change the biological properties of an influenza virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):567–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.567-569.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterlund M., Luthman H., Nilsson S. V., Magnusson G. Ethidium-bromide-inhibited restriction endonucleases cleave one strand of circular DNA. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson N. H., Pauling C. Evidence for two restriction-modification systems in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):783–784. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.783-784.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):375–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.375-381.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M., Baldacci G., de Recondo A. M., Forterre P. Novobiocin induces positive supercoiling of small plasmids from halophilic archaebacteria in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1379–1391. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M., Possot O., Elie C., Sibold L., Forterre P. Coumarin and quinolone action in archaebacteria: evidence for the presence of a DNA gyrase-like enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):946–953. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.946-953.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Olsen G. J. Archaebacterial phylogeny: perspectives on the urkingdoms. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]