Abstract
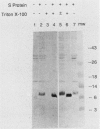
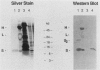
Western blot (immunoblot) analysis of cell extracts from induced bacteriophage lambda lysogens probed with S-protein-specific antibody (raised against an S--beta-galactosidase fusion protein) demonstrated that the bacteriophage lambda S protein begins to appear 10 min after phage induction and is localized to the inner membrane at all times during the lytic cycle. Between 100 and 1,000 molecules of S protein per cell were present at the time of phage-induced lysis. Western blots of chemically cross-linked membranes from induced lysogens showed a ladder of bands at 18, 24, 32, and 42 kilodaltons (the S-protein monomer ran at 8 kilodaltons) that reacted with anti-S-protein antibody. Thus, the S protein appears to reside in the inner membrane as a multimer, and the molecular weights of the cross-linked species are consistent with those of S-protein homopolymers. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant dimers were also detected when S protein was purified by immunoprecipitation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman E., Altman R. K., Garrett J. M., Grimaila R. J., Young R. S gene product: identification and membrane localization of a lysis control protein. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1130–1137. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1130-1137.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman E., Young K., Garrett J., Altman R., Young R. Subcellular localization of lethal lysis proteins of bacteriophages lambda and phiX174. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1008-1011.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Lipinska B., Taylor A. The R gene product of bacteriophage lambda is the murein transglycosylase. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):111–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00271205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieńkowska-Szewczyk K., Taylor A. Murein transglycosylase from phage lambda lysate. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct;615(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. W., Hogness D. S. The lysozyme of bacteriophage lambda. I. Purification and molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):1968–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. W., Hogness D. S. The lysozyme of bacteriophage lambda. II. Amino acid and end group analysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):1976–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Linke R. P., Lubitz W. Evidence for membrane-bound oligomerization of bacteriophage phi X174 lysis protein-E. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4552–4558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Nam K., Hartz D., Gold L., Young R. Dual translational initiation sites control function of the lambda S gene. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3501–3510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. H., Rolfe B. G. Evidence for a dual control of the initiation of host-cell lysis caused by phage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 5;139(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00267990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Briggs M. M., Smith R. J. Cleavable bifunctional reagents for studying near neighbor relationships among mitochondrial inner membrane complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:630–642. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., SUZUKI G. QUANTITATIVE STUDY OF ENDOLYSIN SYNTHESIS DURING REPRODUCTION OF LAMBDA PHAGES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.187-194.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. M., Young R. Lethal action of bacteriophage lambda S gene. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):886–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.886-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J., Fusselman R., Hise J., Chiou L., Smith-Grillo D., Schulz J., Young R. Cell lysis by induction of cloned lambda lysis genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):326–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00269678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Rapid purification of a cloned gene product by genetic fusion and site-specific proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4692–4696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goessens W. H., Driessen A. J., Wilschut J., van Duin J. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal 25 residues of phage MS2 coded lysis protein dissipates the protonmotive force in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles by generating hydrophilic pores. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):867–873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Arnheim N., Sternglanz R. Bacteriophage T7 lysozyme is an N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7247–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji T. H. Bifunctional reagents. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:580–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Kasamatsu H. On the electrotransfer of polypeptides from gels to nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;128(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Studier F. W. T7 lysozyme inhibits transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Müller H. Synthesis and processing of in vitro and in vivo precursors of the vacuolar yeast enzyme carboxypeptidase Y. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11962–11965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam K., Bläsi U., Zagotta M. T., Young R. Conservation of a dual-start motif in P22 lysis gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.204-211.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab R., Neal G., Garrett J., Grimaila R., Fusselman R., Young R. Mutational analysis of bacteriophage lambda lysis gene S. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1035-1042.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab R., Neal G., Sohaskey C., Smith J., Young R. Dominance in lambda S mutations and evidence for translational control. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Siminovitch L. Lysis defective mutants of bacteriophage lambda: genetics and physiology of S cistron mutants. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):607–622. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Siminovitch L. Lysis defective mutants of bacteriophage lambda: on the role of the S function in lysis. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):623–637. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennell D., Poteete A. R. Phage P22 lysis genes: nucleotide sequences and functional relationships with T4 and lambda genes. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., McClees J. S. Active transport of calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5042–5046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Examination of the protein composition of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.882-889.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Epp C., Pearson M. L., Reeve J. N. Aberrant regulation of synthesis and degradation of viral proteins in coliphage lambda-infected UV-irradiated cells and in minicells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3254–3265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3254-3265.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steers E., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Pollard H. B. The purification of beta-galactosidase from Escherichia coli by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk B., Kozloff L. M. A method for the efficient blotting of strongly basic proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 1;150(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90528-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Effect of the lambda S gene product on properties of the Escherichia coli inner membrane. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1403–1410. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1403-1410.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Okabe A. A second function of the S gene of bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1091-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R., Way J., Way S., Yin J., Syvanen M. Transposition mutagenesis of bacteriophage lambda: a new gene affecting cell lysis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):307–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]