Abstract
Erwinia amylovora 1430 was shown to be sensitive to Mu G(-) particles. Infection resulted either in lytic development or in lysogenic derivatives with insertion of the Mu genome at many sites in the bacterial chromosome. We used the Mu d1Bx::Tn9 (lac Apr Cmr) derivative, called Mu dX, to identify mutants affected in pathogenicity and in their ability to induce a hypersensitive reaction (HR) on tobacco plants. Inoculation of 1,400 lysogenic derivatives on apple root calli led to the identification of 12 mutants in three classes: (i) class 1 mutants were nonpathogenic and unable to induce an HR on tobacco plants; (ii) class 2 mutants were nonpathogenic but retained the ability to induce an HR; and (iii) class 3 mutants showed attenuated virulence. Of the 12 mutants, 8 had a single insertion of the Mu dX prophage. For class 1 and 2 mutants, reversion to pathogenicity was concomitant with the loss of the Mu dX prophage. Furthermore, revertants from the class 1 mutants also recovered the ability to induce an HR on tobacco plants. Five of the six class 3 mutants were impaired in exopolysaccharide production. No changes of the envelope structure (lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane proteins) were correlated with differences in pathogenicity. One class 3 mutant did not produce any functional siderophore, suggesting that iron uptake could be involved in pathogenicity.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andro T., Chambost J. P., Kotoujansky A., Cattaneo J., Bertheau Y., Barras F., Van Gijsegem F., Coleno A. Mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi defective in secretion of pectinase and cellulase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1199-1203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ayers S. B., Goodman R. N. Extracellular Polysaccharide of Erwinia amylovora: a Correlation with Virulence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):659–666. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.659-666.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Howe M. M., Gross C. A. Mu dX, a derivative of Mu d1 (lac Apr) which makes stable lacZ fusions at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):970–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.970-974.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Van Gijsegem F., Barberis P. A., Arlat M., Zischek C. Pseudomonas solanacearum genes controlling both pathogenicity on tomato and hypersensitivity on tobacco are clustered. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5626–5632. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5626-5632.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I. Reversal of mutator phage Mu integration. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Taylor A. L. Influence of insertions on packaging of host sequences covalently linked to bacteriophage Mu DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4399–4403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coplin D. L., Frederick R. D., Majerczak D. R., Haas E. S. Molecular cloning of virulence genes from Erwinia stewartii. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):619–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.619-623.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppels D. A. Generation and Characterization of Tn5 Insertion Mutations in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):323–327. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.323-327.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drigues P., Demery-Lafforgue D., Trigalet A., Dupin P., Samain D., Asselineau J. Comparative studies of lipopolysaccharide and exopolysaccharide from a virulent strain of Pseudomonas solanacearum and from three avirulent mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):504–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.504-509.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enard C., Diolez A., Expert D. Systemic virulence of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937 requires a functional iron assimilation system. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2419–2426. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2419-2426.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Expert D., Toussaint A. Bacteriocin-resistant mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi: possible involvement of iron acquisition in phytopathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):221–227. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.221-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. N., Huang J. S., Huang P. Y. Host-Specific Phytotoxic Polysaccharide from Apple Tissue Infected by Erwinia amylovora. Science. 1974 Mar 15;183(4129):1081–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4129.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [The reciprocal antagonistic properties among the Erwinia. Discussion of the taxonomic position of this genus]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1961 Jul 31;253:913–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
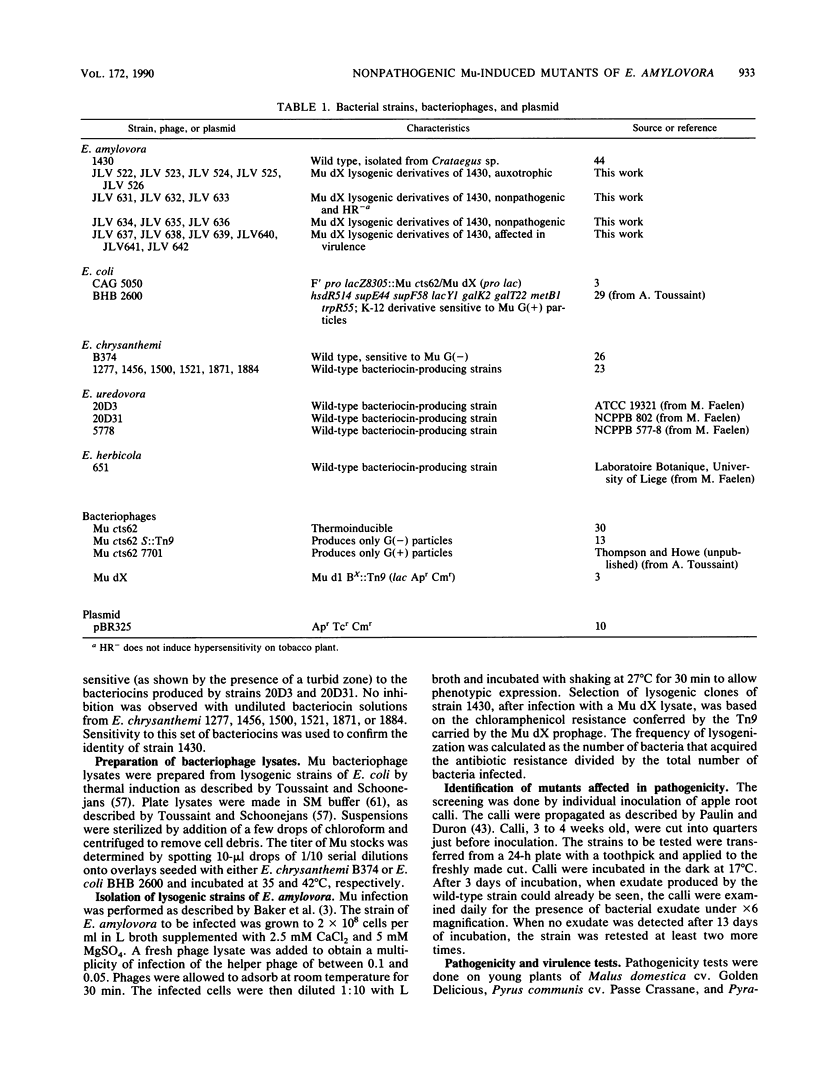
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M. Prophage deletion mapping of bacteriophage Mu-1. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Schuurink R., Denny T. P., Atkinson M. M., Baker C. J., Yucel I., Hutcheson S. W., Collmer A. Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae gene cluster that enables Pseudomonas fluorescens to elicit the hypersensitive response in tobacco plants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4748–4756. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4748-4756.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz L. C., Zimm B. H. Size of DNA determined by viscoelastic measurements: results on bacteriophages, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):779–800. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren P. B., Peet R. C., Panopoulos N. J. Gene cluster of Pseudomonas syringae pv. "phaseolicola" controls pathogenicity of bean plants and hypersensitivity of nonhost plants. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):512–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.512-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonejans E., Expert D., Toussaint A. Characterization and virulence properties of Erwinia chrysanthemi lipopolysaccharide-defective, phi EC2-resistant mutants. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4011–4017. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4011-4017.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon V., Schumann W. In vivo formation of gene fusions in Pseudomonas putida and construction of versatile broad-host-range vectors for direct subcloning of Mu d1 and Mu d2 fusions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1649–1654. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1649-1654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A., Schoonejans E. Production and modification of Mu (G-) phage particles in E. coli K12 and Erwinia. Genet Res. 1983 Apr;41(2):145–154. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300021182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Molecular cloning of Mu d(bla lacZ) transcriptional and translational fusions. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2026–2030. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2026-2030.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley M. H., Hunter N., Cantrell M. A., Hendrick C., Keegstra K., Sequeira L. Lipopolysaccharide Composition of the Wilt Pathogen, Pseudomonas solanacearum: CORRELATION WITH THE HYPERSENSITIVE RESPONSE IN TOBACCO. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):557–559. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Cramer S., Giphart-Gassler M. Invertible DNA determines host specificity of bacteriophage mu. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):218–222. doi: 10.1038/286218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]