Abstract
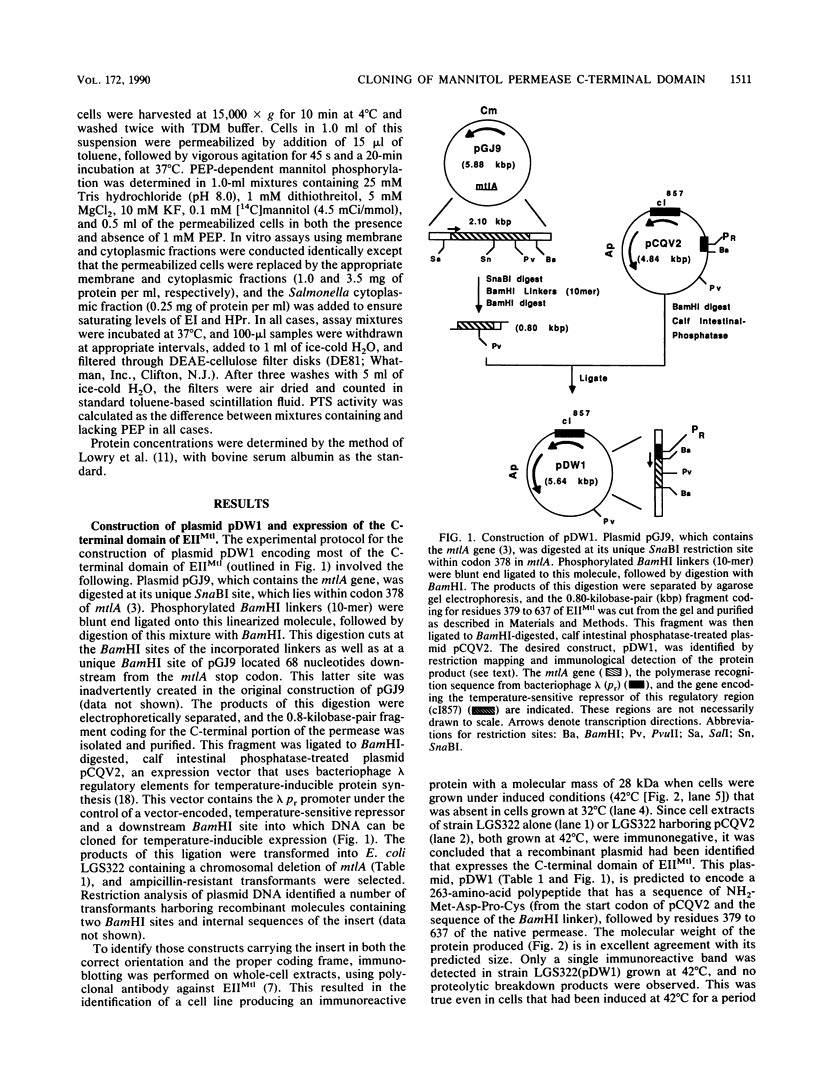
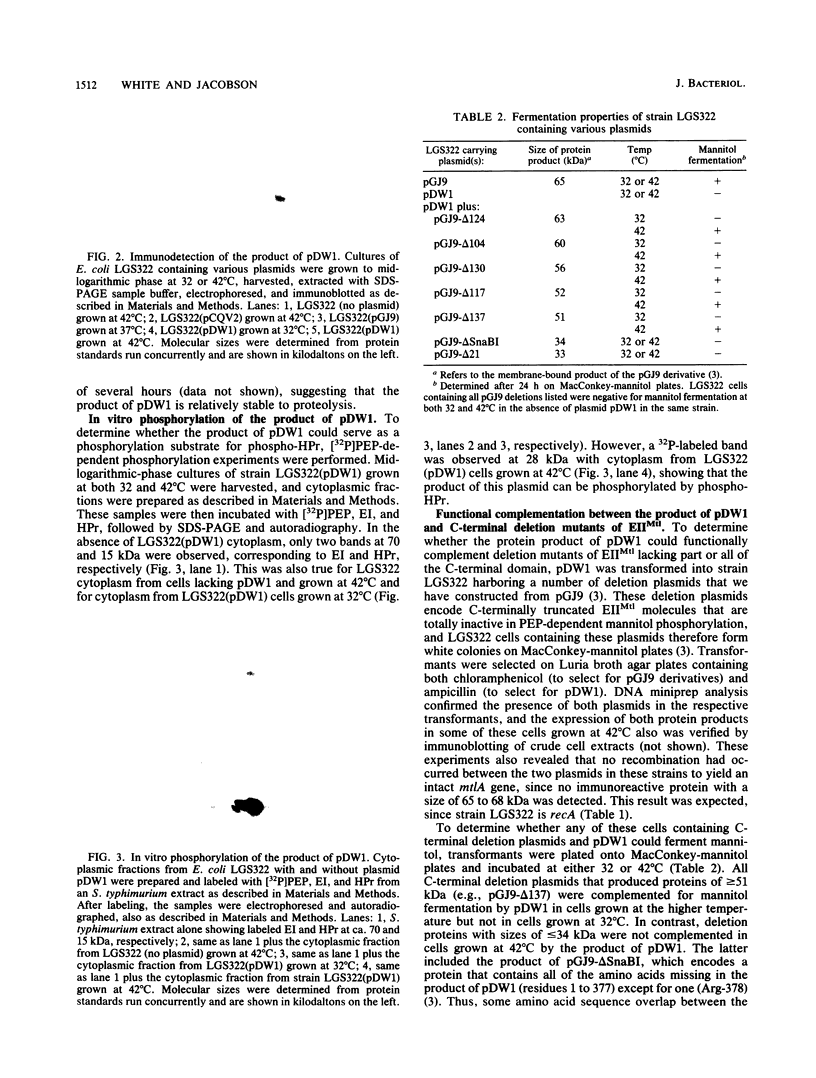
We have subcloned a portion of the Escherichia coli mtlA gene encoding the hydrophilic, C-terminal domain of the mannitol-specific enzyme II (mannitol permease; molecular mass, 68 kilodaltons [kDa]) of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent carbohydrate phosphotransferase system. This mtlA fragment, encoding residues 379 to 637 (residue 637 = C terminus), was cloned in frame into the expression vector pCQV2 immediately downstream from the lambda pr promoter of the vector, which also encodes a temperature-sensitive lambda repressor. E. coli cells carrying a chromosomal deletion in mtlA (strain LGS322) and harboring this recombinant plasmid, pDW1, expressed a 28-kDa protein cross-reacting with antipermease antibody when grown at 42 degrees C but not when grown at 32 degrees C. This protein was relatively stable and could be phosphorylated in vitro by the general phospho-carrier protein of the phosphotransferase system, phospho-HPr. Thus, this fragment of the permease, when expressed in the absence of the hydrophobic, membrane-bound N-terminal domain, can apparently fold into a conformation resembling that of the C-terminal domain of the intact permease. When transformed into LGS322 cells harboring plasmid pGJ9-delta 137, which encodes a C-terminally truncated and inactive permease (residues 1 to ca. 480; molecular mass, 51 kDa), pDW1 conferred a mannitol-positive phenotype to this strain when grown at 42 degrees C but not when grown at 32 degrees C. This strain also exhibited phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent mannitol phosphorylation activity only when grown at the higher temperature. In contrast, pDW1 could not complement a plasmid encoding the complementary N-terminal part of the permease (residues 1 to 377). The pathway of phosphorylation of mannitol by the combined protein products of pGJ9-delta 137 and pDPW1 was also investigated by using N-ethylmaleimide to inactivate the second phosphorylation sites of these permease fragments (proposed to be Cys-384). These results are discussed with respect to the domain structure of the permease and its mechanism of transport and phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF

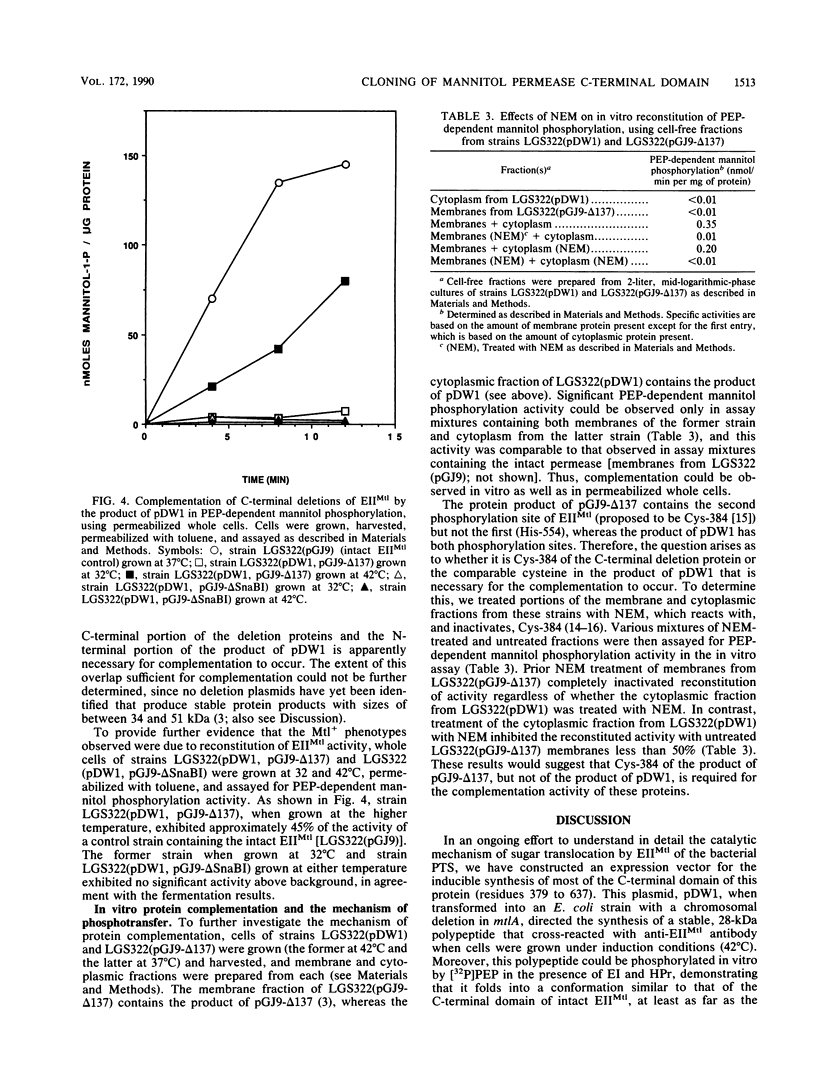
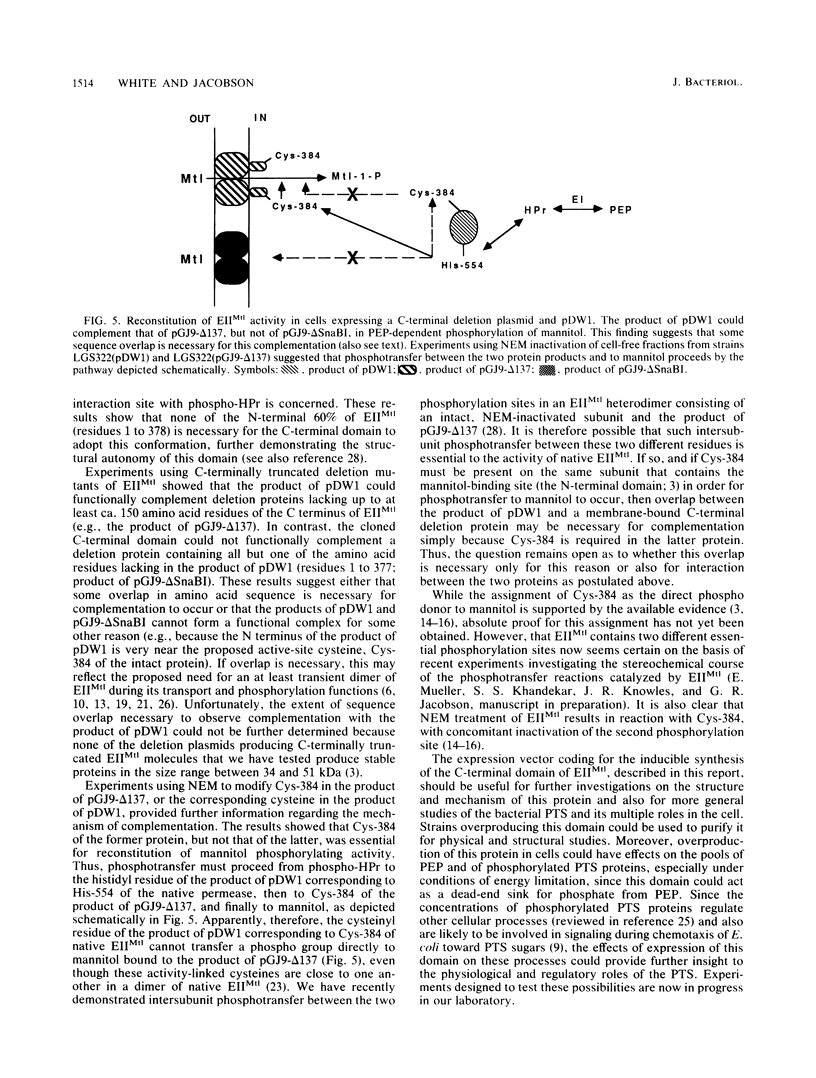

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begley G. S., Hansen D. E., Jacobson G. R., Knowles J. R. Stereochemical course of the reactions catalyzed by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate:glucose phosphotransferase system. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5552–5556. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisafi P. L., Scholle A., Sugiyama J., Briggs C., Jacobson G. R., Lengeler J. W. Deletion mutants of the Escherichia coli K-12 mannitol permease: dissection of transport-phosphorylation, phospho-exchange, and mannitol-binding activities. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2719–2727. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2719-2727.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Lee C. A., Saier M. H., Jr Purification of the mannitol-specific enzyme II of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Stephan M. M. Structural and functional domains of the mannitol-specific enzyme II of the E. coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;5(1-2):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandekar S. S., Jacobson G. R. Evidence for two distinct conformations of the Escherichia coli mannitol permease that are important for its transport and phosphorylation functions. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):207–216. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Jacobson G. R., Saier M. H., Jr Plasmid-directed synthesis of enzymes required for D-mannitol transport and utilization in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7336–7340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Saier M. H., Jr Mannitol-specific enzyme II of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. III. The nucleotide sequence of the permease gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10761–10767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler J. W., Vogler A. P. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial chemotaxis towards PTS-carbohydrates. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;5(1-2):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. E., Saier M. H., Jr Mannitol-specific enzyme II of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. II. Reconstitution of vectorial transphosphorylation in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10757–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., Ellory J. C., Robillard G. T. Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: association state of membrane-bound mannitol-specific enzyme II demonstrated by inactivation. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6689–6696. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., Robillard G. T. Enzyme IIMtl of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: identification of the activity-linked cysteine on the mannitol carrier. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5515–5519. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., Robillard G. T. S-phosphocysteine and phosphohistidine are intermediates in the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent mannitol transport catalyzed by Escherichia coli EIIMtl. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5835–5839. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pas H. H., ten Hoeve-Duurkens R. H., Robillard G. T. Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: mannitol-specific EII contains two phosphoryl binding sites per monomer and one high-affinity mannitol binding site per dimer. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5520–5525. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):232–269. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.232-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. A vector that uses phage signals for efficient synthesis of proteins in Escherichia coli. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T., Blaauw M. Enzyme II of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: protein-protein and protein-phospholipid interactions. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5796–5803. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T., Lolkema J. S. Enzymes II of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar transport systems: a review of their structure and mechanism of sugar transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):493–519. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossien F. F., Blaauw M., Robillard G. T. Kinetics and subunit interaction of the mannitol-specific enzyme II of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4934–4939. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossien F. F., Brink J., Robillard G. T. A simple procedure for the synthesis of [32P]phosphoenolpyruvate via the pyruvate kinase exchange reaction at equilibrium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 4;760(1):185–187. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossien F. F., van Es-Spiekman W., Robillard G. T. Dimeric enzyme IImtl of the E. coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. Cross-linking studies with bifunctional sulfhydryl reagents. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 17;196(2):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Protein phosphorylation and allosteric control of inducer exclusion and catabolite repression by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):109–120. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.109-120.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan M. M., Jacobson G. R. Membrane disposition of the Escherichia coli mannitol permease: identification of membrane-bound and cytoplasmic domains. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8230–8234. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan M. M., Jacobson G. R. Subunit interactions of the Escherichia coli mannitol permease: correlation with enzymic activities. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4046–4051. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan M. M., Khandekar S. S., Jacobson G. R. Hydrophilic C-terminal domain of the Escherichia coli mannitol permease: phosphorylation, functional independence, and evidence for intersubunit phosphotransfer. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7941–7946. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]