Abstract
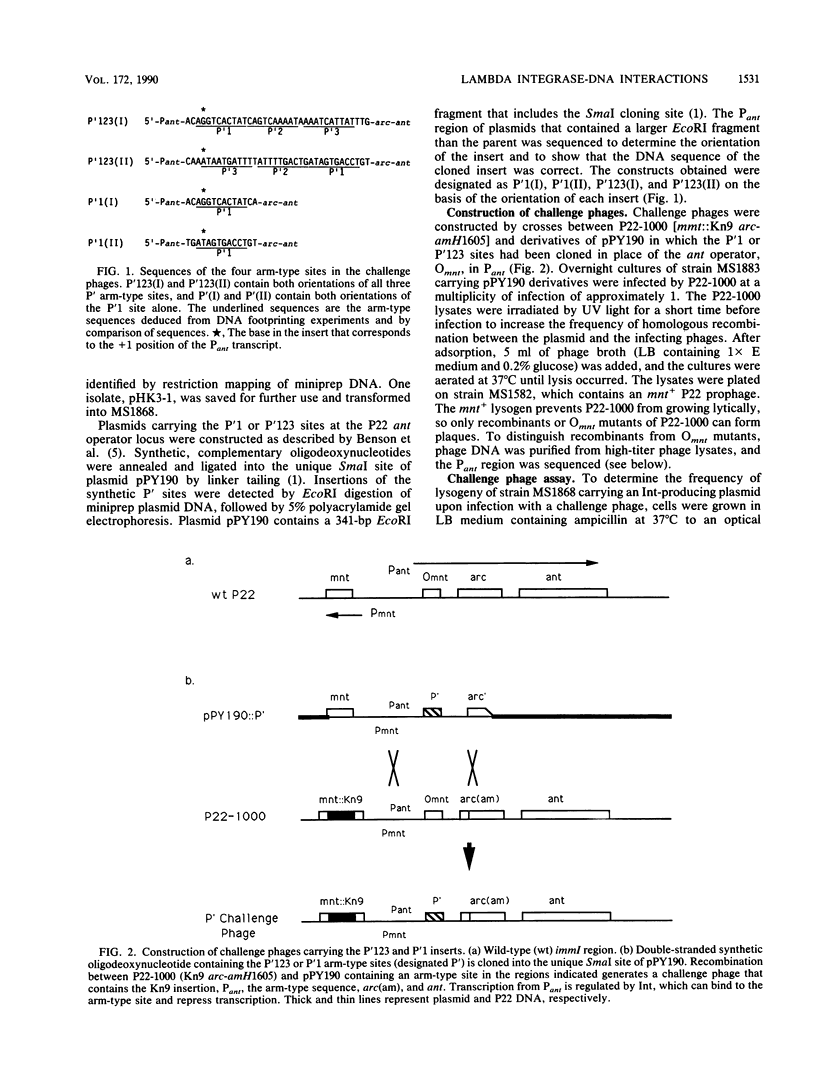
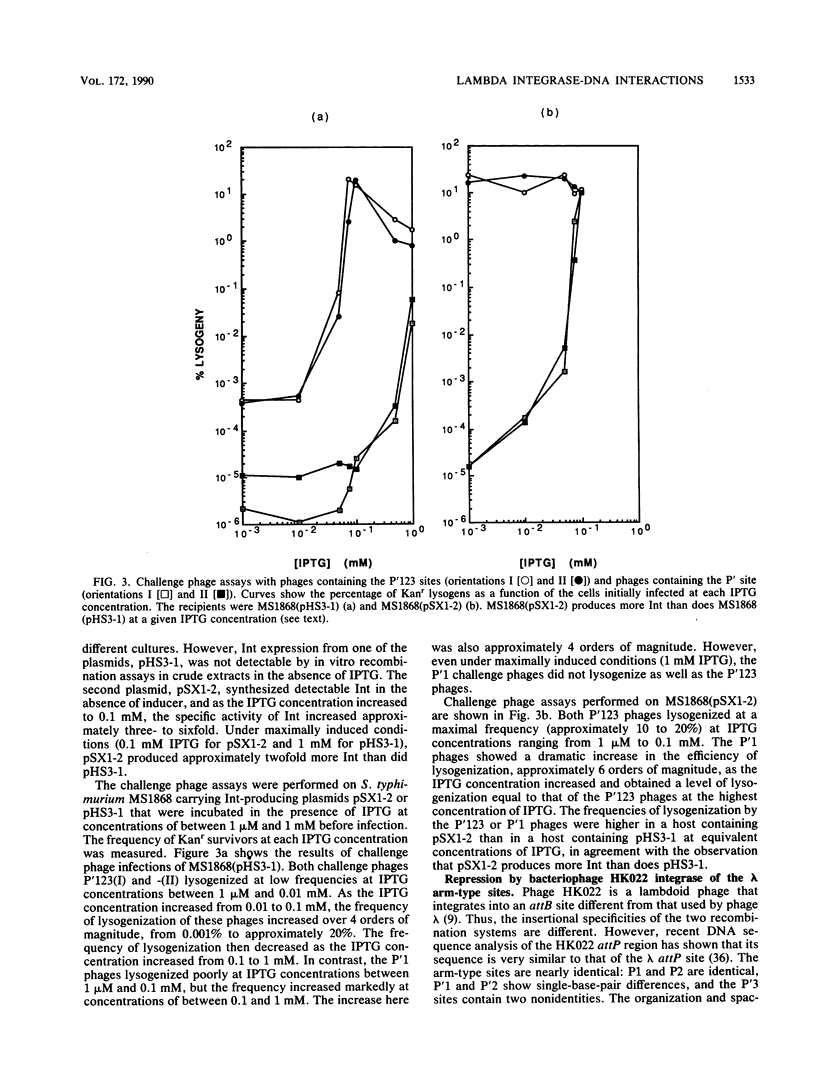
The bacteriophage P22-based challenge phage system was used to study lambda integrase (Int) protein binding to its arm-type recognition sequences in the bacteriophage lambda attachment site. Challenge phages were constructed that carried inserts containing either the contiguous P'123 arm-type sites or the single P'1 site within the P22 phage promoter, Pant, which is required for expression of antirepressor. If Int protein binds to these sequences in vivo, it represses transcription from Pant. We found that Int repressed Pant in phages carrying the P'123 sites more efficiently than those carrying only the P'1 site, suggesting that the protein binds cooperatively at the three adjacent sites. The Int protein from a related lambdoid phage, HK022, also repressed transcription by binding to the same arm-type sites. Mutations in the P'123 or P'1 sites that impair Int binding were isolated by selecting mutant phages that express antirepressor in the presence of Int. DNA sequence analyses showed that most of the mutants in the challenge phages carrying the P'123 sites contained multiple changes and that two mutants contained only single-base-pair changes at positions that are completely conserved among all arm-type sites. Thirty-five mutants were isolated and analyzed from phages containing only the P'1 site. Most mutants contained single-nucleotide changes, and mutations were isolated at 8 of the 10 positions of the site, suggesting that most if not all base pairs in the conserved recognition sequence are involved in Int binding.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass S., Sugiono P., Arvidson D. N., Gunsalus R. P., Youderian P. DNA specificity determinants of Escherichia coli tryptophan repressor binding. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):565–572. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. E., Hesse S. D., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. Mutational analysis of integrase arm-type binding sites of bacteriophage lambda. Integration and excision involve distinct interactions of integrase with arm-type sites. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):513–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson N., Sugiono P., Bass S., Mendelman L. V., Youderian P. General selection for specific DNA-binding activities. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson N., Sugiono P., Youderian P. DNA sequence determinants of lambda repressor binding in vivo. Genetics. 1988 Jan;118(1):21–29. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Lu C., Williams R. C., Echols H. Site-specific DNA condensation and pairing mediated by the int protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5837–5841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Wickner S., Auerbach J., Echols H. Role of the Xis protein of bacteriophage lambda in a specific reactive complex at the attR prophage attachment site. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon T. S., Dhillon E. K., Lai A. N. Genetic recombination between phage HK022, lambda, and phi 80. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):198–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Systematic method for the detection of potential lambda Cro-like DNA-binding regions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. A genetic analysis of the att-int-xis region of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):97–120. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña D., Gardella T., Susskind M. M. The effects of mutations in the ant promoter of phage P22 depend on context. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):319–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. The lambda phage att site: functional limits and interaction with Int protein. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):85–91. doi: 10.1038/285085a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. T., Youderian P., Simon M. I. Phase variation in Salmonella: analysis of Hin recombinase and hix recombination site interaction in vivo. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):937–948. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination proceeds with a defined order of strand exchanges. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Gustafson B. J., Nash H. A. Purification and properties of Int-h, a variant protein involved in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12724–12732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton B., Prasad P. V., Jayaram M., Youderian P. Mutations that improve the binding of yeast FLP recombinase to its substrate. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):393–400. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Mozola M. A., Friedman D. I. int-h: An int mutation of phage lambda that enhances site-specific recombination. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Pargellis C. A., Hasan N. M., Bushman E. W., Landy A. Autonomous DNA binding domains of lambda integrase recognize two different sequence families. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Purification and properties of the bacteriophage lambda Int protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:210–216. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Walker G. C. Identification of plasmid (pKM101)-coded proteins involved in mutagenesis and UV resistance. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):278–281. doi: 10.1038/300278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. Synapsis of attachment sites during lambda integrative recombination involves capture of a naked DNA by a protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90526-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. The interaction of recombination proteins with supercoiled DNA: defining the role of supercoiling in lambda integrative recombination. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Bacteriophage lambda int protein recognizes two classes of sequence in the phage att site: characterization of arm-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Patterns of lambda Int recognition in the regions of strand exchange. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., de Vargas L. M., Skinner S. E., Landy A. Protein-protein interactions in a higher-order structure direct lambda site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):481–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Chung S., Abraham J., Echols H. Directional control of site-specific recombination by bacteriophage lambda. Evidence that a binding site for Int protein far from the crossover point is required for integrative but not excisive recombination. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil E., Dolev S., Oberto J., Kislev N., Ramaiah N., Weisberg R. A. Determinants of site-specific recombination in the lambdoid coliphage HK022. An evolutionary change in specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):695–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissler J. Integration-negative (int) mutants of phage lambda. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):189–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



