Abstract
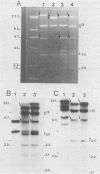
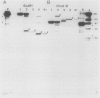
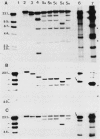
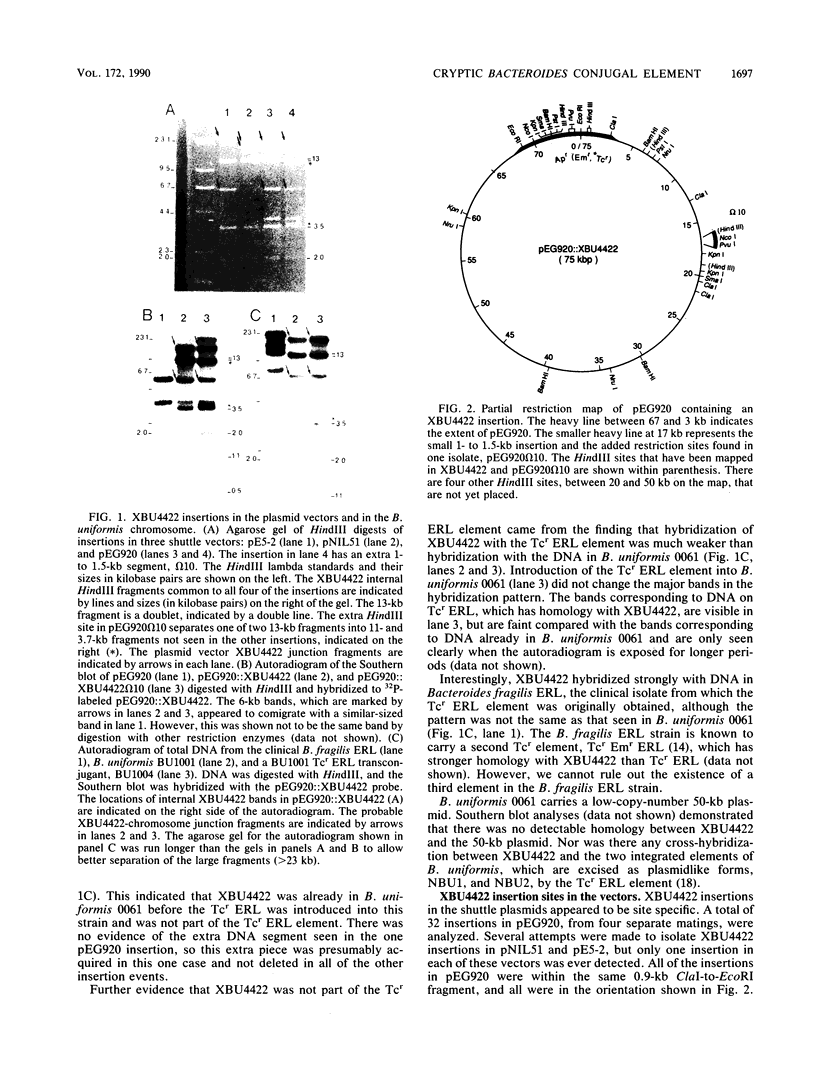
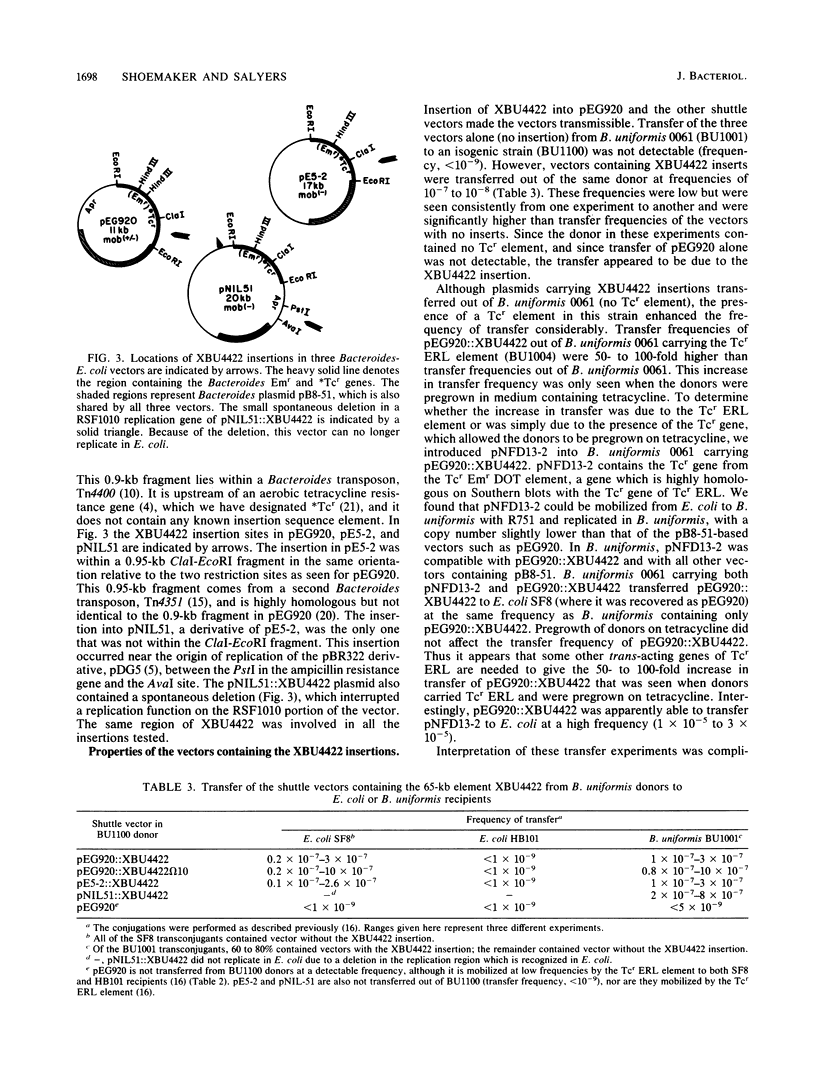
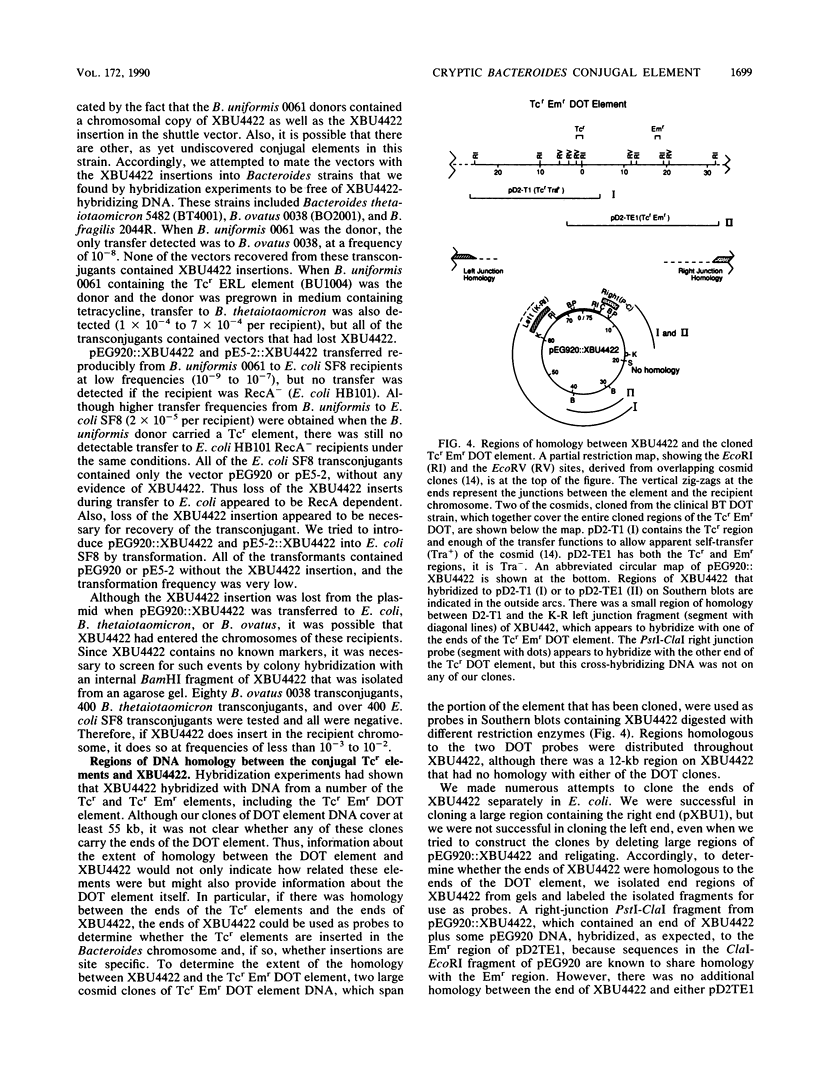
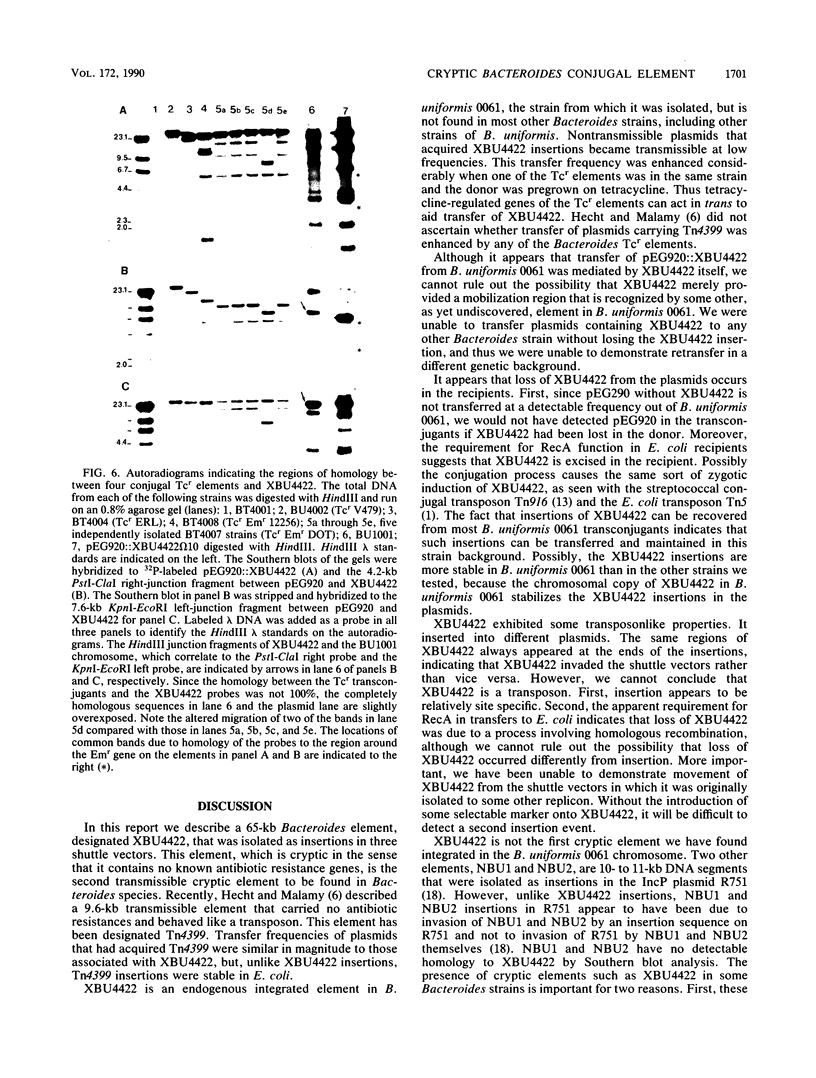
A 65-kilobase-pair element, XBU4422, which has some transposonlike characteristics but carries no known antibiotic resistance genes, has been isolated from Bacteroides uniformis 0061. XBU4422 was trapped on Bacteroides-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors during experiments in which one of the conjugal Bacteroides tetracycline resistance (Tcr) elements was being used to mobilize the shuttle vectors to Bacteroides recipients. Results of Southern hybridization experiments showed that XBU4422 is normally integrated in the B. uniformis 0061 chromosome and is found only in some strains. Insertion of XBU4422 in the shuttle vectors was site specific and orientation specific. Nonmobilizable vectors that had acquired XBU4422 became transmissible and could be transferred to Bacteroides or E. coli recipients. In B. uniformis transconjugants, the XBU4422 insertion in the vectors was usually intact, but XBU4422 was always lost in matings with E. coli, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, or B. ovatus. The loss of XBU4422 did not visibly alter the vector; in the case of E. coli, the loss of the insertion appeared to be RecA dependent. Although XBU4422 carried no antibiotic resistances, it shared regions of homology with six conjugal Bacteroides Tcr elements; this homology was strongest with the ends of XBU4422. Using a strain of B. thetaiotaomicron that contains no XBU4422-hybridizing sequences, we showed that the ends of XBU4422 were probably reacting with the ends of the Tcr elements. These results provide the first direct evidence that the Tcr elements, like XBU4422, are integrated in the chromosome and that insertion of the least some Tcr elements, such as TcrEmr DOT, is relatively site specific.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg D. E., Egner C., Lowe J. B. Mechanism of F factor-enhanced excision of transposon Tn5. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Hasegawa P., Davis C. E. Plasmid transfer from Escherichia coli to Bacteroides fragilis: differential expression of antibiotic resistance phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7203–7206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Jr, Hasegawa P., Davis C. E. Expression in Escherichia coli of cryptic tetracycline resistance genes from bacteroides R plasmids. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht D. W., Malamy M. H. Tn4399, a conjugal mobilizing transposon of Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3603–3608. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3603-3608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odelson D. A., Rasmussen J. L., Smith C. J., Macrina F. L. Extrachromosomal systems and gene transmission in anaerobic bacteria. Plasmid. 1987 Mar;17(2):87–109. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Tally F. P., Malamy M. H. Tn4400, a compound transposon isolated from Bacteroides fragilis, functions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1248-1255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Shoemaker N. B., Guthrie E. P. Recent advances in Bacteroides genetics. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(1):49–71. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senghas E., Jones J. M., Yamamoto M., Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. Genetic organization of the bacterial conjugative transposon Tn916. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):245–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.245-249.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Barber R. D., Salyers A. A. Cloning and characterization of a Bacteroides conjugal tetracycline-erythromycin resistance element by using a shuttle cosmid vector. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1294–1302. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1294-1302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Getty C., Gardner J. F., Salyers A. A. Tn4351 transposes in Bacteroides spp. and mediates the integration of plasmid R751 into the Bacteroides chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):929–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.929-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Getty C., Guthrie E. P., Salyers A. A. Regions in Bacteroides plasmids pBFTM10 and pB8-51 that allow Escherichia coli-Bacteroides shuttle vectors to be mobilized by IncP plasmids and by a conjugative Bacteroides tetracycline resistance element. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):959–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.959-965.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guthrie E. P., Salyers A. A., Gardner J. F. Evidence that the clindamycin-erythromycin resistance gene of Bacteroides plasmid pBF4 is on a transposable element. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):626–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.626-632.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Salyers A. A. Tetracycline-dependent appearance of plasmidlike forms in Bacteroides uniformis 0061 mediated by conjugal Bacteroides tetracycline resistance elements. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1651–1657. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1651-1657.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J. Development and use of cloning systems for Bacteroides fragilis: cloning of a plasmid-encoded clindamycin resistance determinant. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.294-301.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Gonda M. A. Comparison of the transposon-like structures encoding clindamycin resistance in Bacteroides R-plasmids. Plasmid. 1985 May;13(3):182–192. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer B. S., Salyers A. A. Characterization of a novel tetracycline resistance that functions only in aerobically grown Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1423–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1423-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine P. J., Shoemaker N. B., Salyers A. A. Mobilization of Bacteroides plasmids by Bacteroides conjugal elements. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1319-1324.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Kaytes P. S. Amplification, storage, and replication of libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:407–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]