Abstract
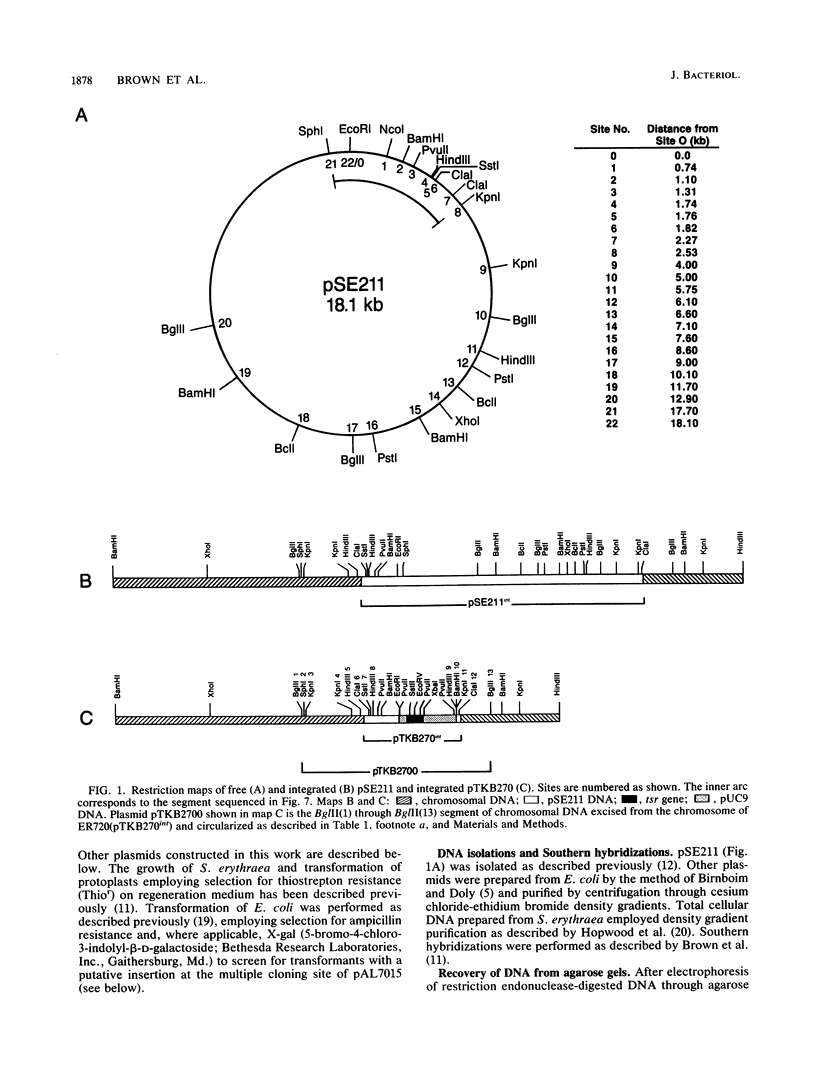
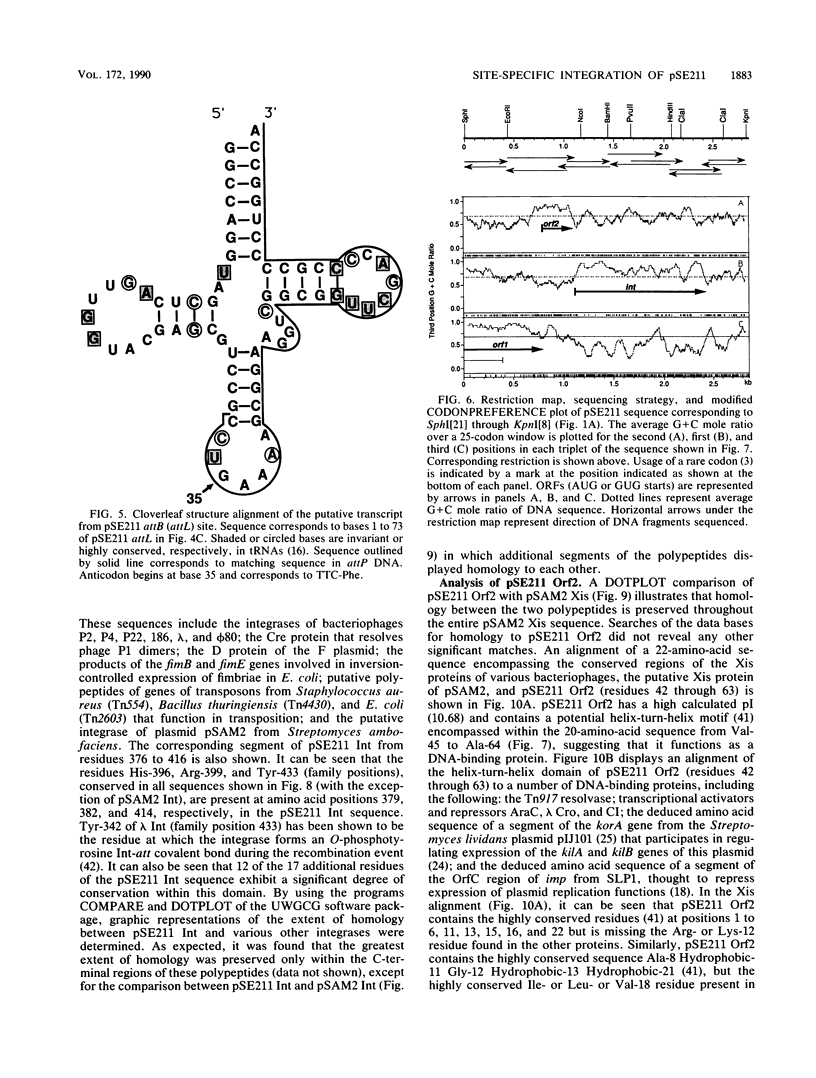
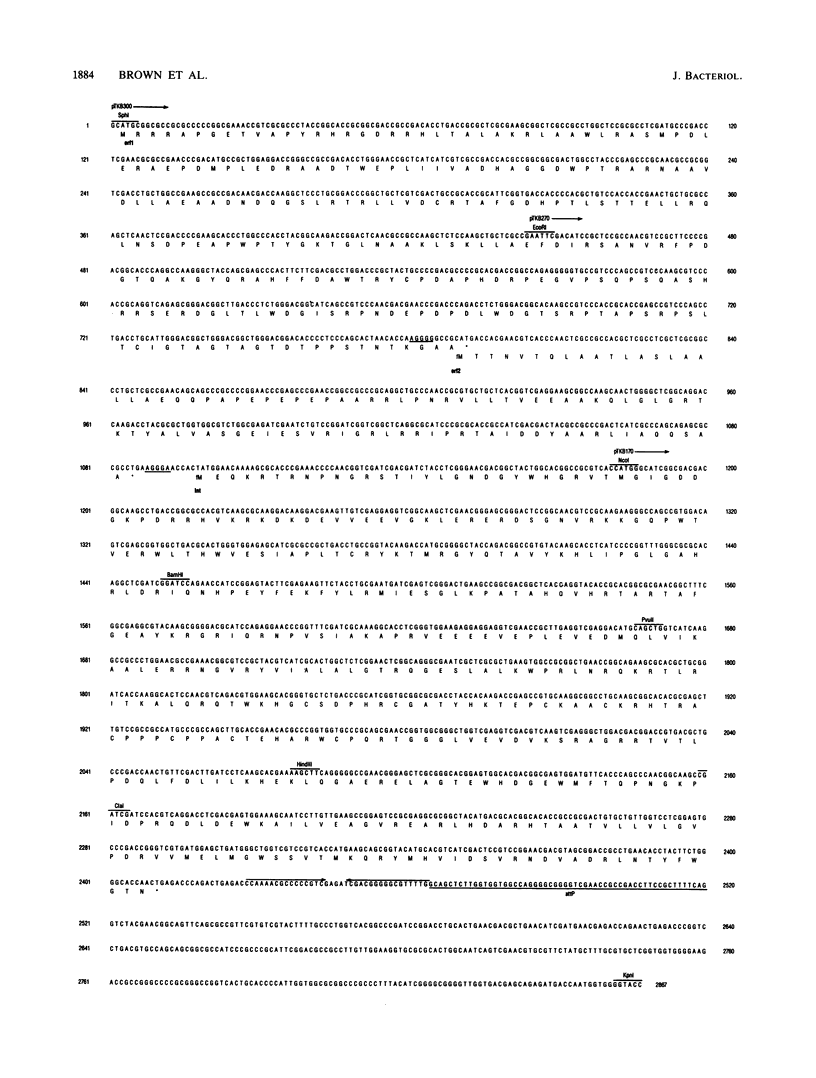
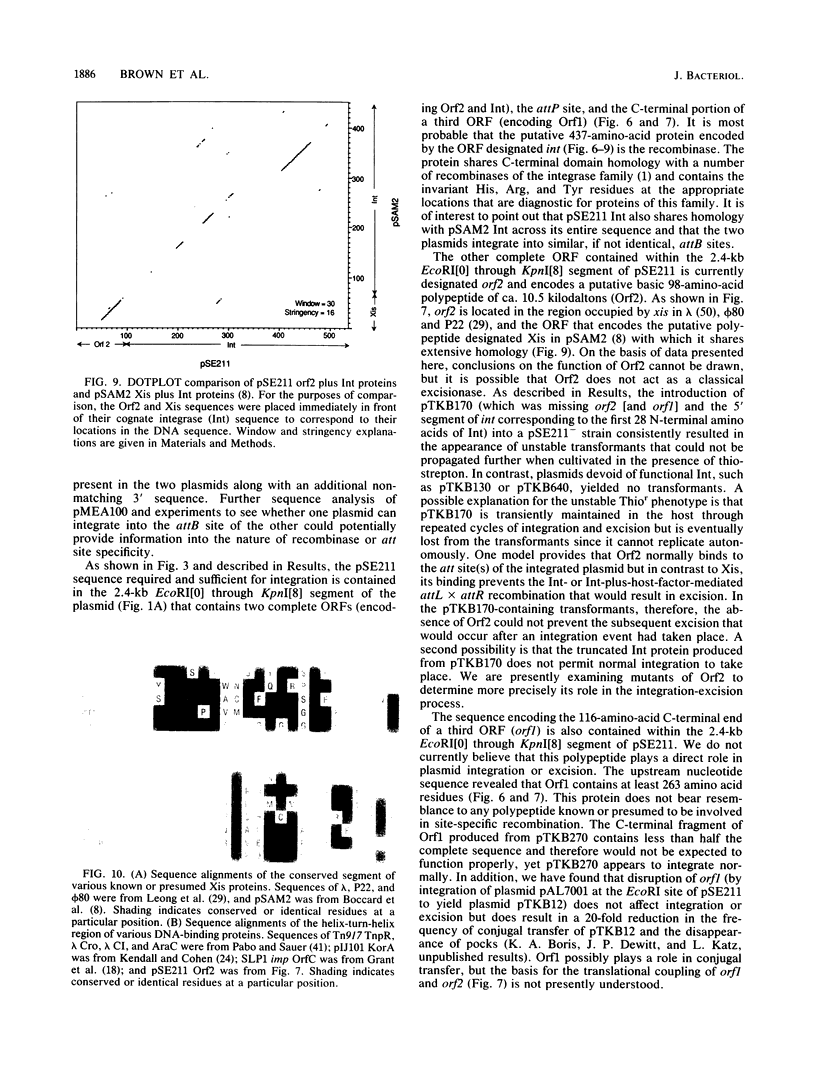
The 18.1-kilobase plasmid pSE211 integrates into the chromosome of Saccharopolyspora erythraea at a specific attB site. Restriction analysis of the integrated plasmid, pSE211int, and adjacent chromosomal sequences allowed identification of attP, the plasmid attachment site. Nucleotide sequencing of attP, attB, attL, and attR revealed a 57-base-pair sequence common to all sites with no duplications of adjacent plasmid or chromosomal sequences in the integrated state, indicating that integration takes place through conservative, reciprocal strand exchange. An analysis of the sequences indicated the presence of a putative gene for Phe-tRNA at attB which is preserved at attL after integration has occurred. A comparison of the attB site for a number of actinomycete plasmids is presented. Integration at attB was also observed when a 2.4-kilobase segment of pSE211 containing attP and the adjacent plasmid sequence was used to transform a pSE211- host. Nucleotide sequencing of this segment revealed the presence of two complete open reading frames (ORFs) and a segment of a third ORF. The ORF adjacent to attP encodes a putative polypeptide 437 amino acids in length that shows similarity, at its C-terminal domain, to sequences of site-specific recombinases of the integrase family. The adjacent ORF encodes a putative 98-amino-acid basic polypeptide that contains a helix-turn-helix motif at its N terminus which corresponds to domains in the Xis proteins of a number of bacteriophages. A proposal for the function of this polypeptide is presented. The deduced amino acid sequence of the third ORF did not reveal similarities to polypeptide sequences in the current data banks.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):265–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00331128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Kieser T., Cohen S. N., Hopwood D. A. Excision of chromosomal DNA sequences from Streptomyces coelicolor forms a novel family of plasmids detectable in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):230–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00272910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccard F., Smokvina T., Pernodet J. L., Friedmann A., Guérineau M. Structural analysis of loci involved in pSAM2 site-specific integration in Streptomyces. Plasmid. 1989 Jan;21(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccard F., Smokvina T., Pernodet J. L., Friedmann A., Guérineau M. The integrated conjugative plasmid pSAM2 of Streptomyces ambofaciens is related to temperate bacteriophages. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):973–980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. P., Chiang S. J., Tuan J. S., Katz L. Site-specific integration in Saccharopolyspora erythraea and multisite integration in Streptomyces lividans of actinomycete plasmid pSE101. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2287–2295. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2287-2295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Bar-Nir D., Goedeke M. E., Parag Y. The integrated and free states of Streptomyces griseus plasmid pSG1. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt J. P. Evidence for a sex factor in Streptomyces erythreus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):969–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.969-971.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r55–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. R., Lee S. C., Kendall K., Cohen S. N. Identification and characterization of a locus inhibiting extrachromosomal maintenance of the Streptomyces plasmid SLP1. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):324–331. doi: 10.1007/BF02464900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Hintermann G., Kieser T., Wright H. M. Integrated DNA sequences in three streptomycetes form related autonomous plasmids after transfer to Streptomyces lividans. Plasmid. 1984 Jan;11(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J. Plasmids, recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2257–2269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Thompson C. J., Hopwood D. A. Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2703–2714. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 and correlation of the sequence with genetic properties. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4634–4651. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4634-4651.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Plasmid transfer in Streptomyces lividans: identification of a kil-kor system associated with the transfer region of pIJ101. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4177–4183. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4177-4183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhstoss S., Richardson M. A., Rao R. N. Site-specific integration in Streptomyces ambofaciens: localization of integration functions in S. ambofaciens plasmid pSAM2. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.16-23.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Omer C. A., Brasch M. A., Cohen S. N. Analysis of recombination occurring at SLP1 att sites. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5806–5813. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5806-5813.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Nunes-Düby S. E., Oser A. B., Lesser C. F., Youderian P., Susskind M. M., Landy A. Structural and regulatory divergence among site-specific recombination genes of lambdoid phage. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 20;189(4):603–616. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madon J., Moretti P., Hütter R. Site-specific integration and excision of pMEA100 in Nocardia mediterranei. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00329651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretti P., Hintermann G., Hütter R. Isolation and characterization of an extrachromosomal element from Nocardia mediterranei. Plasmid. 1985 Sep;14(2):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Cohen S. N. Plasmid formation in Streptomyces: excision and integration of the SLP1 replicon at a specific chromosomal site. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):429–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00436190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Cohen S. N. Structural analysis of plasmid and chromosomal loci involved in site-specific excision and integration of the SLP1 element of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.999-1006.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Stein D., Cohen S. N. Site-specific insertion of biologically functional adventitious genes into the Streptomyces lividans chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2174–2184. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2174-2184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernodet J. L., Simonet J. M., Guérineau M. Plasmids in different strains of Streptomyces ambofaciens: free and integrated form of plasmid pSAM2. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00328697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson L. S., 3rd, Kahn M. L. Integration of satellite bacteriophage P4 in Escherichia coli. DNA sequences of the phage and host regions involved in site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Yeats S. Transfer RNA genes frequently serve as integration sites for prokaryotic genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1907–1914. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., RajBhandary U. L. Transfer RNA: molecular structure, sequence, and properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:805–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosio M., Madoń J., Hütter R. Excision of pIJ408 from the chromosome of Streptomyces glaucescens and its transfer into Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00330580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. DNA cloning in Streptomyces: resistance genes from antibiotic-producing species. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):525–527. doi: 10.1038/286525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Scholl R., Browse J., Somerville C. Double stranded DNA sequencing as a choice for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1220–1220. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]