Abstract
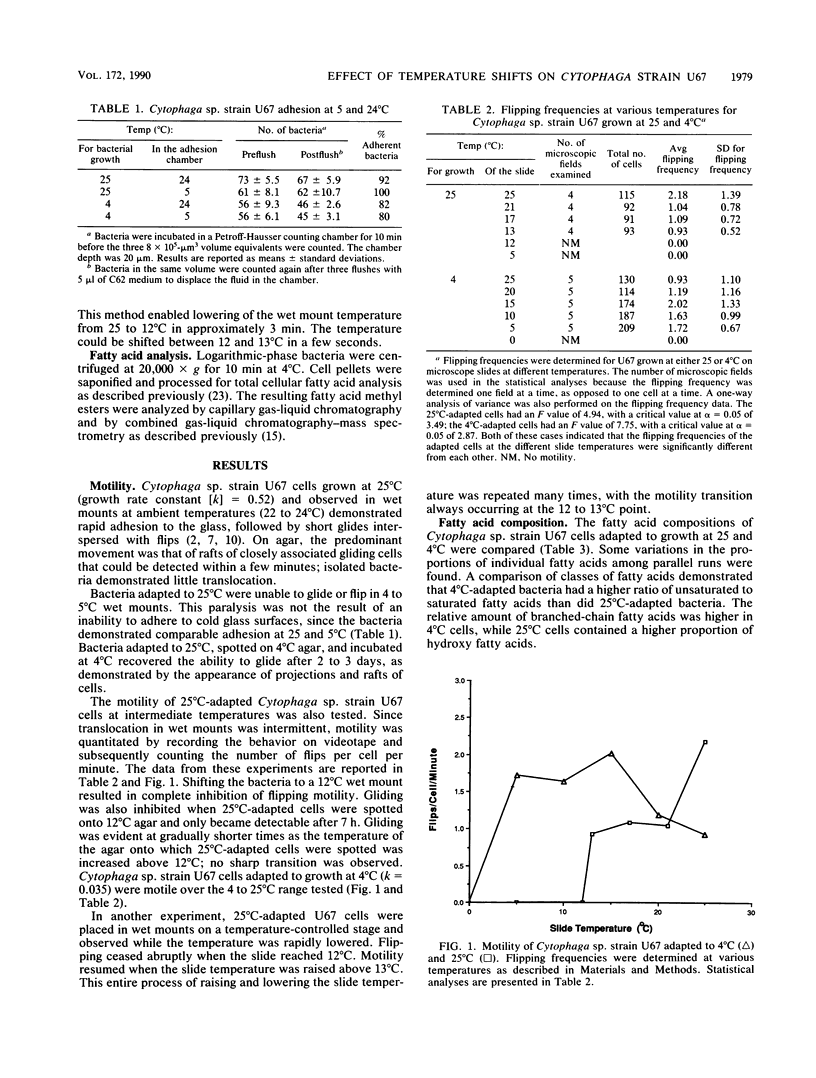
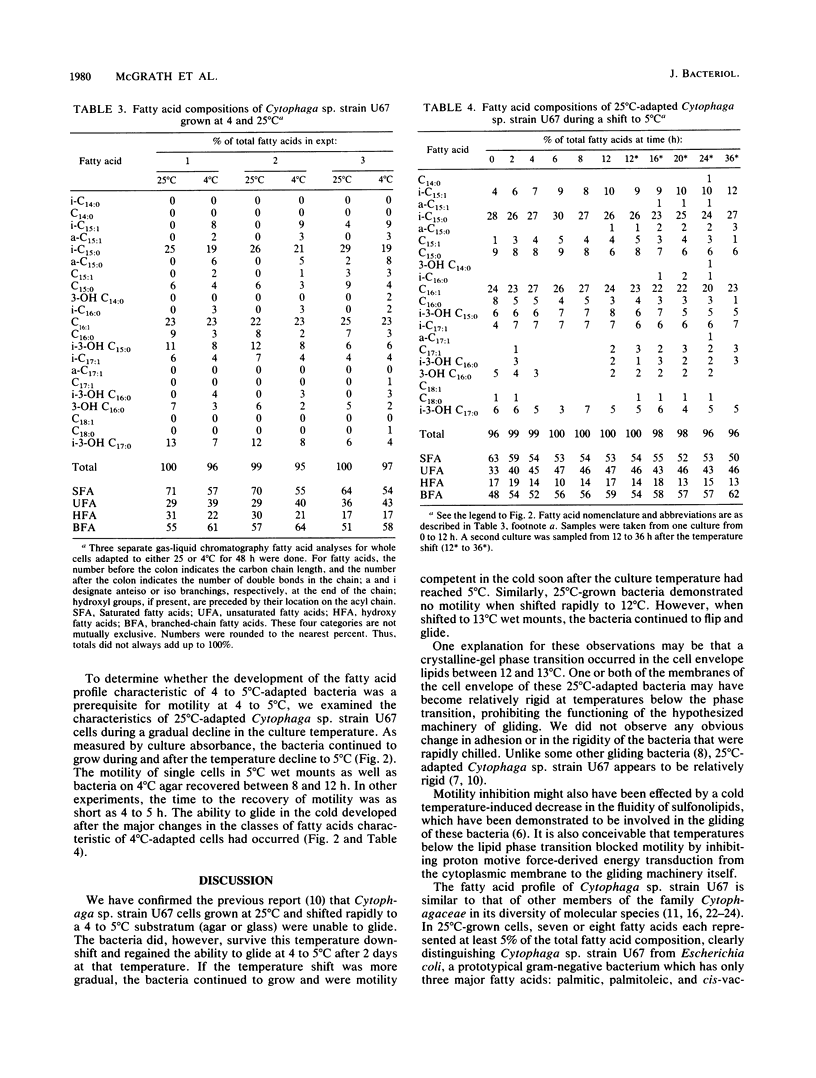
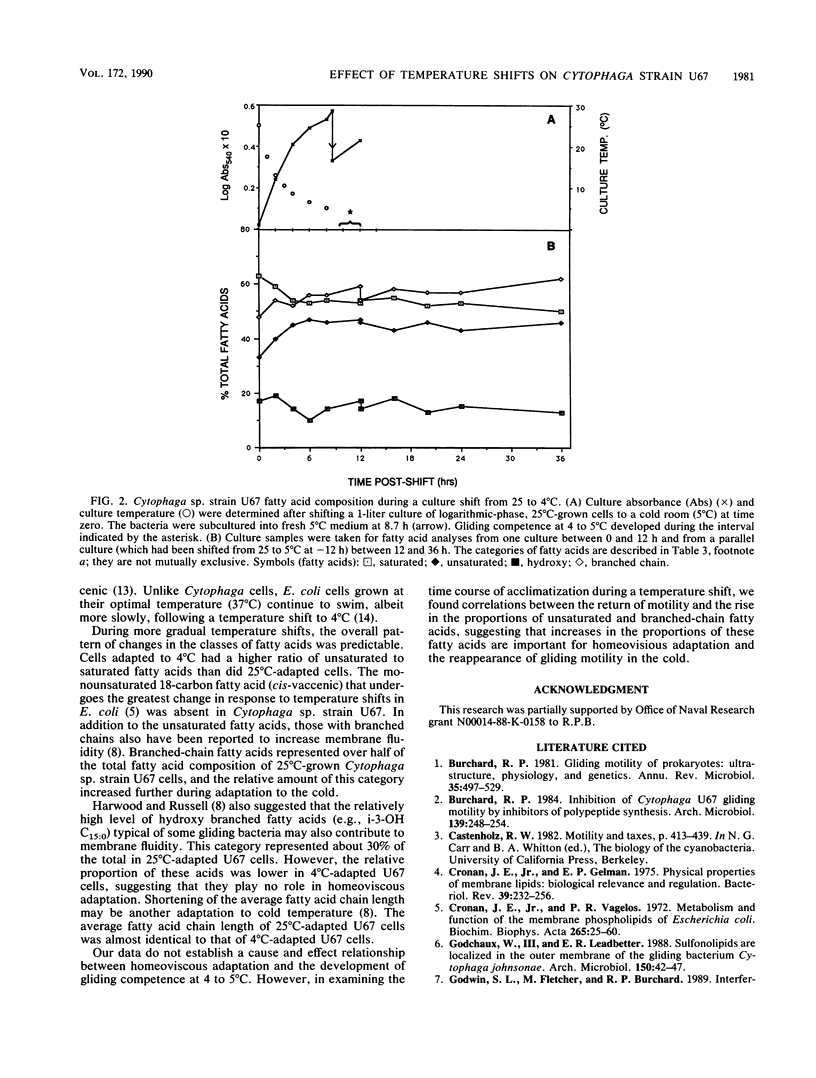
Gliding motility and flipping of 25 degrees C-adapted Cytophaga sp. strain U67 were inhibited when the bacteria were shifted to a less than or equal to 12 degrees C environment; motility was not blocked by a shift to 13 degrees C. Bacteria adapted to 4 degrees C were motile over the entire 4 to 25 degrees C temperature range tested. U67 adhesion to the substratum appeared to be unaffected by temperature shifts. Bacteria adapted to 4 degrees C had higher proportions of unsaturated and branched-chain fatty acids than did those grown at 25 degrees C. When 25 degrees C-adapted bacteria were subjected to a gradual temperature decline, the time of reappearance of gliding competence at 4 to 5 degrees C was correlated with these changes in fatty acid composition.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burchard R. P. Gliding motility of prokaryotes: ultrastructure, physiology, and genetics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:497–529. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr, Gelmann E. P. Physical properties of membrane lipids: biological relevance and regulation. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):232–256. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.232-256.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Vagelos P. R. Metabolism and function of the membrane phospholipids of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):25–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Bacterial surface translocation: a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):478–503. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.478-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus I. R., Berg H. C. Gliding motility of Cytophaga sp. strain U67. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):384–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.384-398.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebert C. A., Hood M. A., Deck F. H., Bishop K., Flaherty D. K. Isolation and characterization of a new Cytophaga species implicated in a work-related lung disease. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):936–943. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.936-943.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane fluidity and chemotaxis: effects of temperature and membrane lipid composition on the swimming behavior of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):183–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Lambert-Fair M. A. Location of double bonds in monounsaturated fatty acids of Campylobacter cryaerophila with dimethyl disulfide derivatives and combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1467–1470. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1467-1470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbach H. Taxonomy of the gliding bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:339–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. F., Lewin R. A. Characterization of gliding motility in Flexibacter polymorphus. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;11(1):46–63. doi: 10.1002/cm.970110106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M. Homeoviscous adaptation--a homeostatic process that regulates the viscosity of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):522–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. W. Cis-11-hexadecenoic acid from Cytophaga hutchinsonii lipids. Lipids. 1969 Jan;4(1):15–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02531788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



