Abstract
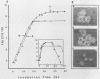
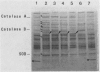
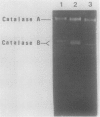
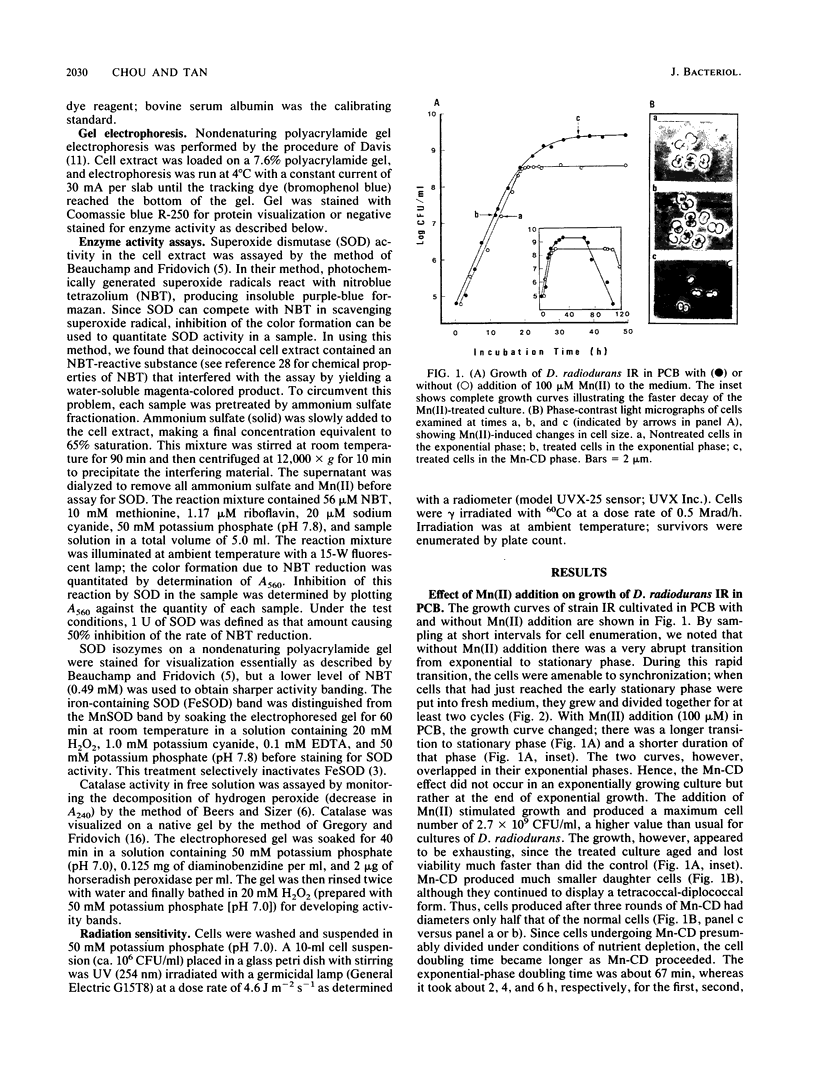
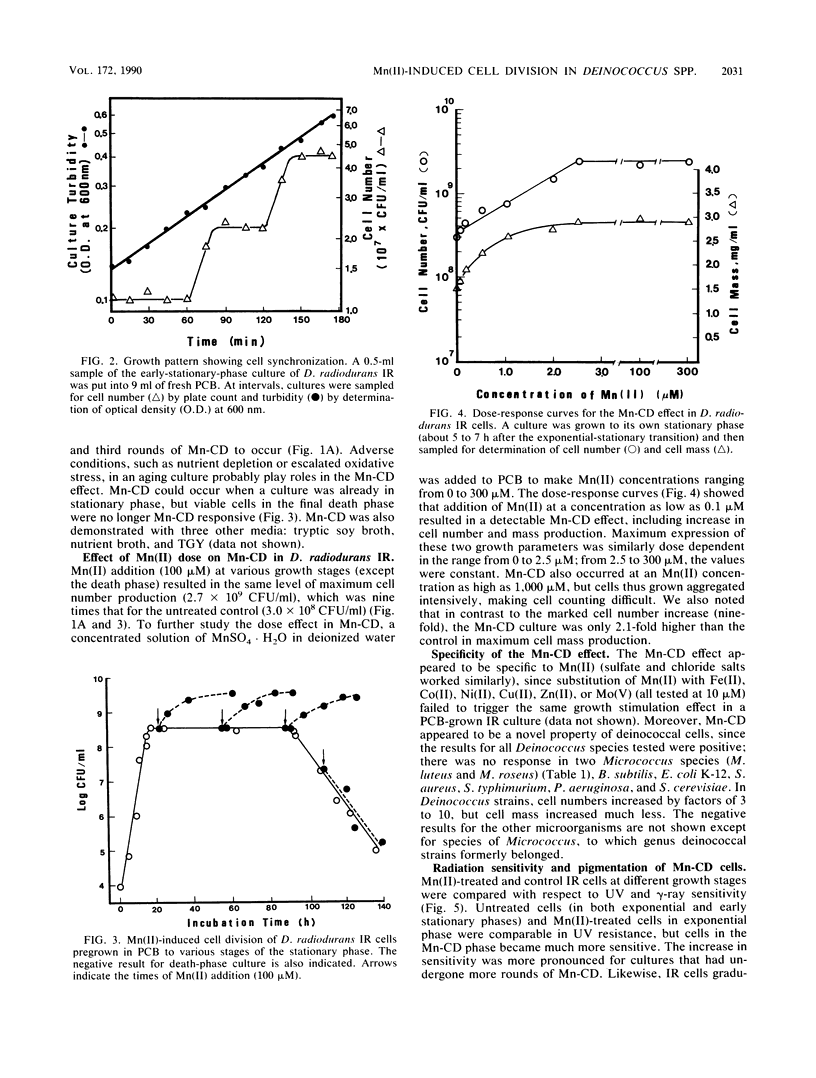
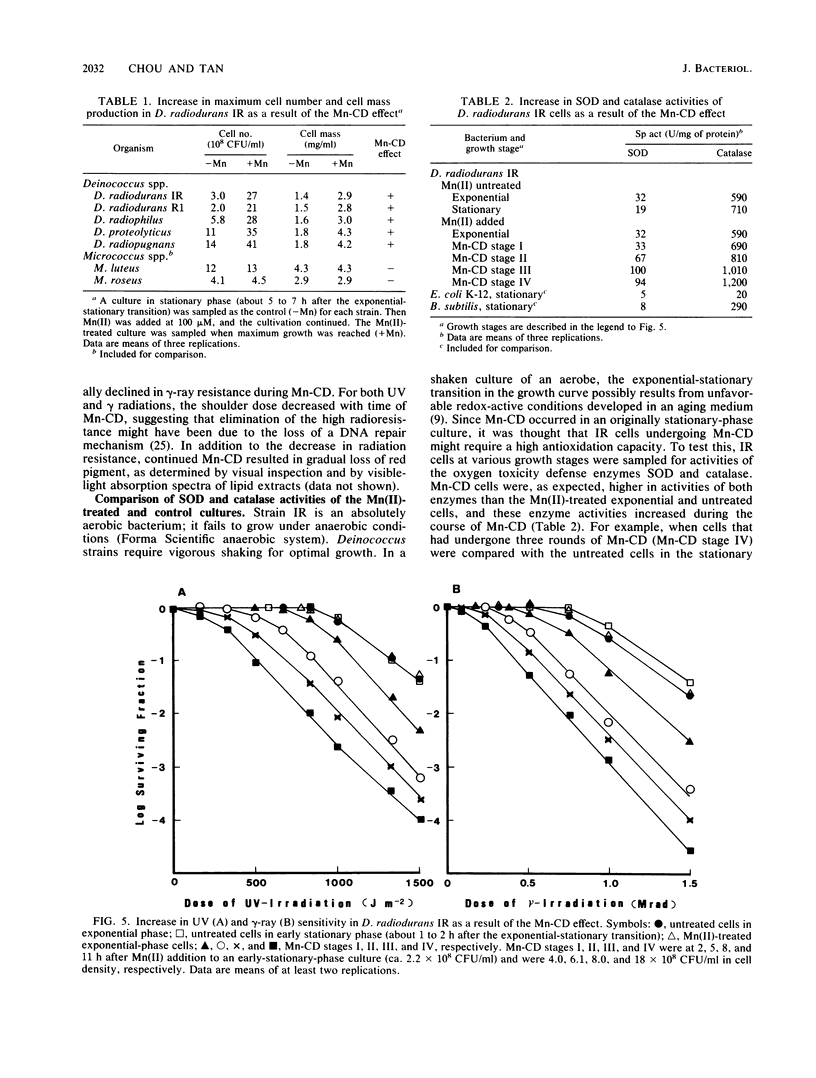
Addition of Mn(II) at 2.5 microM or higher to stationary-phase cultures of Deinococcus radiodurans IR was found to trigger at least three rounds of cell division. This Mn(II)-induced cell division (Mn-CD) did not occur when the culture was in the exponential or death phase. The Mn-CD effect produced daughter cells proportionally reduced in size, pigmentation, and radioresistance but proportionally increased in activity and amount of the oxygen toxicity defense enzymes superoxide dismutase and catalase. In addition, the concentration of an Mn-CD-induced protein was found to remain high throughout the entire Mn-CD phase. It was also found that an untreated culture exhibited a growth curve characterized by a very rapid exponential-stationary transition and that cells which had just reached the early stationary phase were synchronous. Our results suggest the presence of an Mn(II)-sensitive mechanism for controlling cell division. The Mn-CD effect appears to be specific to the cation Mn(II) and the radioresistant bacteria, deinococci.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Kuntz G. P., Evans H. H., Swift T. J. Preferential interaction of manganous ions with the guanine moiety in nucleosides, dinucleoside monophosphates, and deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4368–4374. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asada K., Yoshikawa K., Takahashi M., Maeda Y., Enmanji K. Superoxide dismutases from a blue-green alga, Plectonema boryanum. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2801–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister W., Barth M., Hegerl R., Guckenberger R., Hahn M., Saxton W. O. Three-dimensional structure of the regular surface layer (HPI layer) of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISINGER J., FAWAZ-ESTRUP F., SHULMAN R. G. BINDING OF MN2+ TO NUCLEIC ACIDS. J Chem Phys. 1965 Jan 1;42:43–53. doi: 10.1063/1.1695717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Moseley B. E. Identification and initial characterisation of a pyrimidine dimer UV endonuclease (UV endonuclease beta) from Deinococcus radiodurans; a DNA-repair enzyme that requires manganese ions. Mutat Res. 1985 May;145(3):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Moseley B. E. Roles of the uvsC, uvsD, uvsE, and mtcA genes in the two pyrimidine dimer excision repair pathways of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):576–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.576-583.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin B. C. Synchronization of Escherichia coli in a chemostat by periodic phosphate feeding. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):511–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory E. M., Fridovich I. Visualization of catalase on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman N., Ron E. Z. Apparent minimal size required for cell division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):80–82. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.80-82.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz P. J., Schwartzberg L. S., Bruce A. K. The in vivo association of manganese with the chromosome of Micrococcus radiodurans. Photochem Photobiol. 1976 Jan;23(1):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1976.tb06769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. The utility of superoxide dismutase in studying free radical reactions. II. The mechanism of the mediation of cytochrome c reduction by a variety of electron carriers. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1374–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase and the oxygen enhancement of radiation lethality. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):577–581. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Copland H. J. Isolation and properties of a recombination-deficient mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):422–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.422-428.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Evans D. M. Isolation and properties of strains of Micrococcus (Deinococcus) radiodurans unable to excise ultraviolet light-induced pyrimidine dimers from DNA: evidence for two excision pathways. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2437–2445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Mattingly A., Copland H. J. Sensitization to radiation by loss of recombination ability in a temperature-sensitive DNA mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans held at its restrictive temperature. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):329–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky J. A., Morita R. Y. Morphological characterization of small cells resulting from nutrient starvation of a psychrophilic marine vibrio. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):617–622. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.617-622.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkau A., Chelack W. S., Pleskach S. D. Letter: Protection of post-irradiated mice by superoxide dismutase. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1976 Mar;29(3):297–299. doi: 10.1080/09553007614550341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuni A., Czapski G. Radiation-induced damage in Escherichia coli B: the effect of superoxide radicals and molecular oxygen. Radiat Res. 1978 Dec;76(3):624–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A., DiLello D., Loudis M. C., Keller D. E., Hutner S. H. Minimal requirements in defined media for improved growth of some radio-resistant pink tetracocci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1129–1133. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1129-1133.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. T., Maxcy R. B. Simple method to demonstrate radiation-inducible radiation resistance in microbial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):88–90. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.88-90.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. T., Maxcy R. B., Thompson T. L. Paper replication method for isolation of radiation-sensitive mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.233-236.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E. AMINO ACIDS OF WALLS OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1107–1109. doi: 10.1038/2011107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]