Abstract
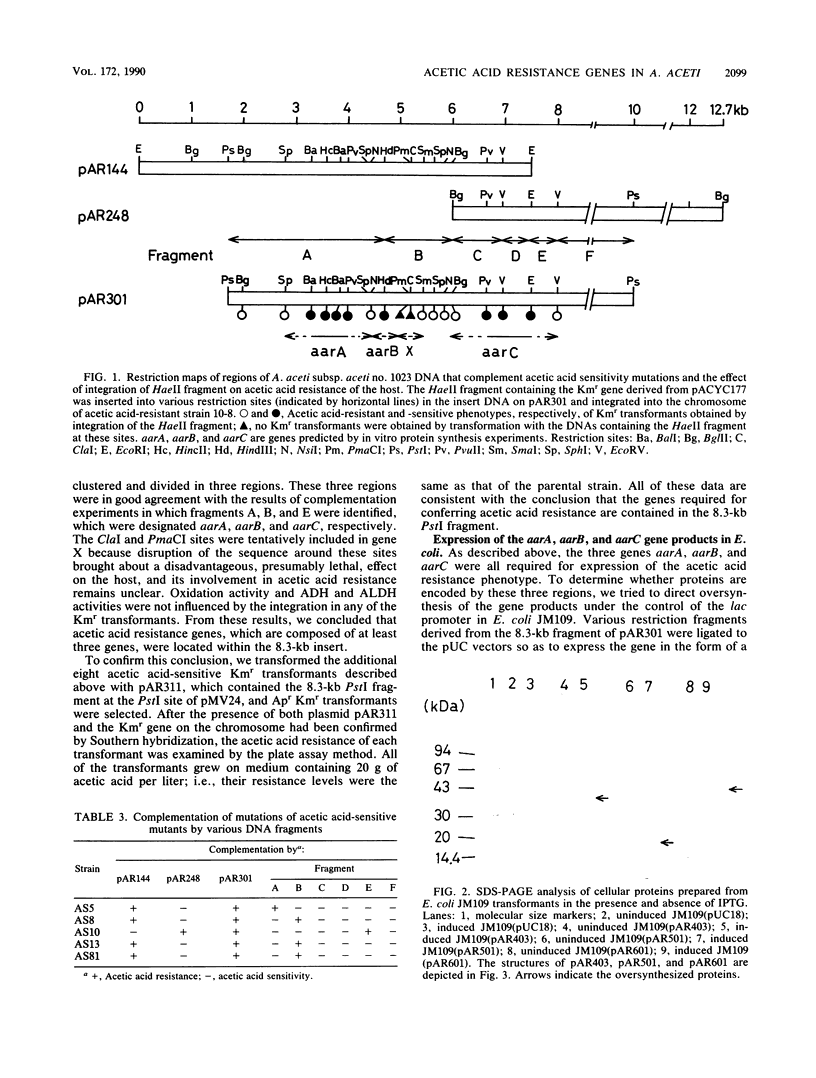
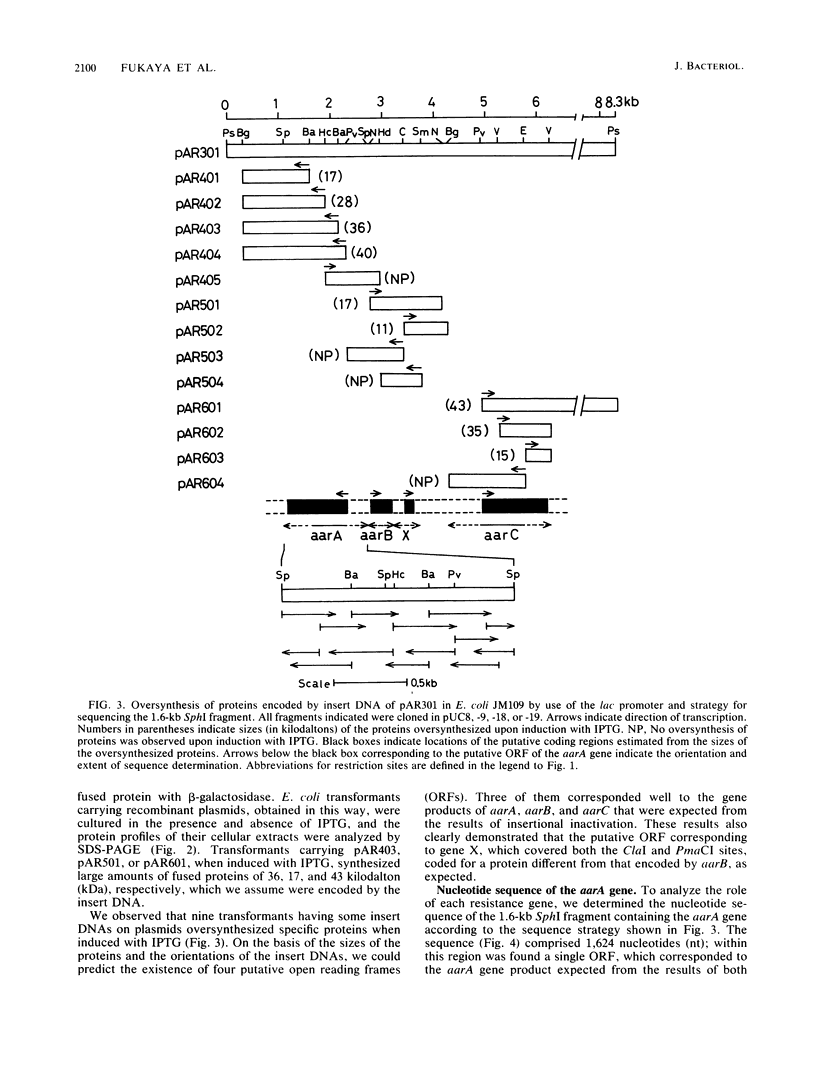
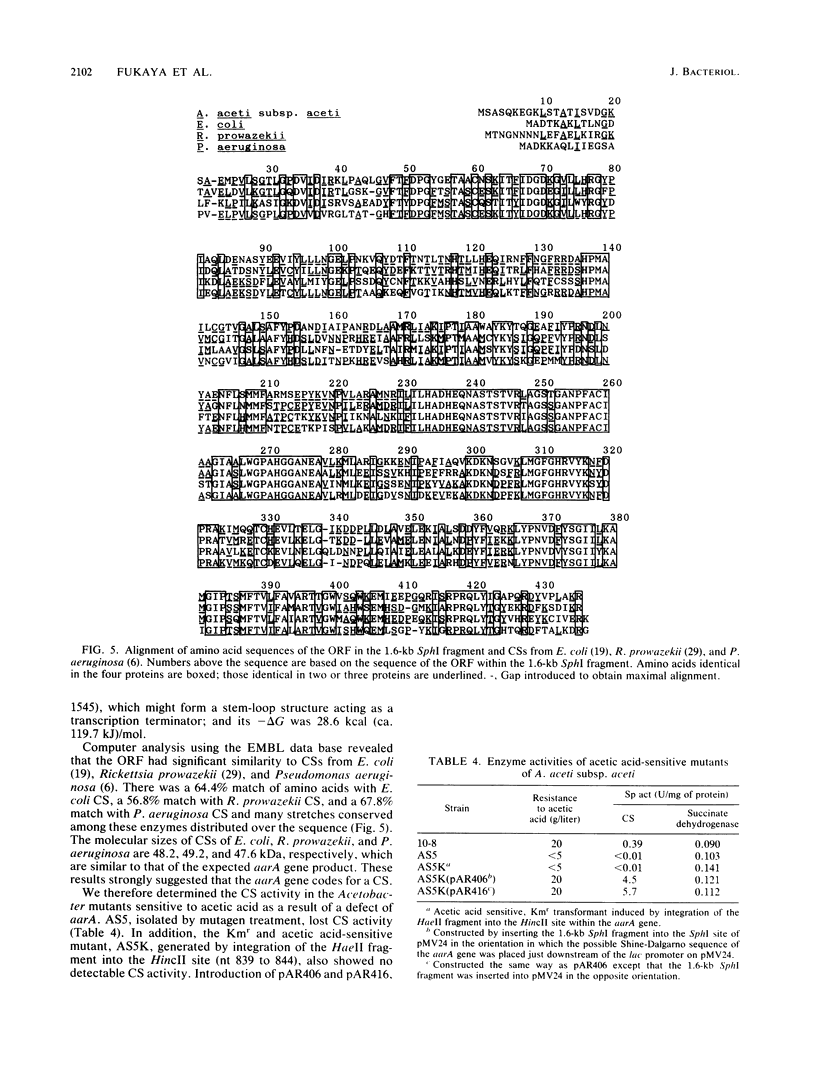
Five acetic acid-sensitive mutants of Acetobacter aceti subsp. aceti no. 1023 were isolated by mutagenesis with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Three recombinant plasmids that complemented the mutations were isolated from a gene bank of the chromosome DNA of the parental strain constructed in Escherichia coli by using cosmid vector pMVC1. One of these plasmids (pAR1611), carrying about a 30-kilobase-pair (kb) fragment that conferred acetic acid resistance to all five mutants, was further analyzed. Subcloning experiments indicated that a 8.3-kb fragment was sufficient to complement all five mutations. To identify the mutation loci and genes involved in acetic acid resistance, insertional inactivation was performed by insertion of the kanamycin resistance gene derived from E. coli plasmid pACYC177 into the cloned 8.3-kb fragment and successive integration into the chromosome of the parental strain. The results suggested that three genes, designated aarA, aarB, and aarC, were responsible for expression of acetic acid resistance. Gene products of these genes were detected by means of overproduction in E. coli by use of the lac promoter. The amino acid sequence of the aarA gene product deduced from the nucleotide sequence was significantly similar to those of the citrate synthases (CSs) of E. coli and other bacteria. The A. aceti mutants defective in the aarA gene were found to lack CS activity, which was restored by introduction of a plasmid containing the aarA gene. A mutation in the CS gene of E. coli was also complemented by the aarA gene. These results indicate that aarA is the CS gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald L. J., Molgat G. F., Duckworth H. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene for NADH-sensitive citrate synthase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5542–5550. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5542-5550.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukaya M., Tayama K., Tamaki T., Tagami H., Okumura H., Kawamura Y., Beppu T. Cloning of the Membrane-Bound Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Gene of Acetobacter polyoxogenes and Improvement of Acetic Acid Production by Use of the Cloned Gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):171–176. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.171-176.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Atkinson W. H., Sikorski R. S., Winkler H. H. Expression of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):412–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.412-416.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Williamson L. R., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3564-3572.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]