Abstract
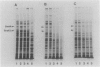
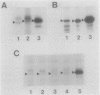
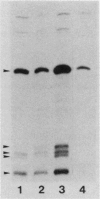
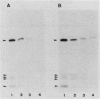
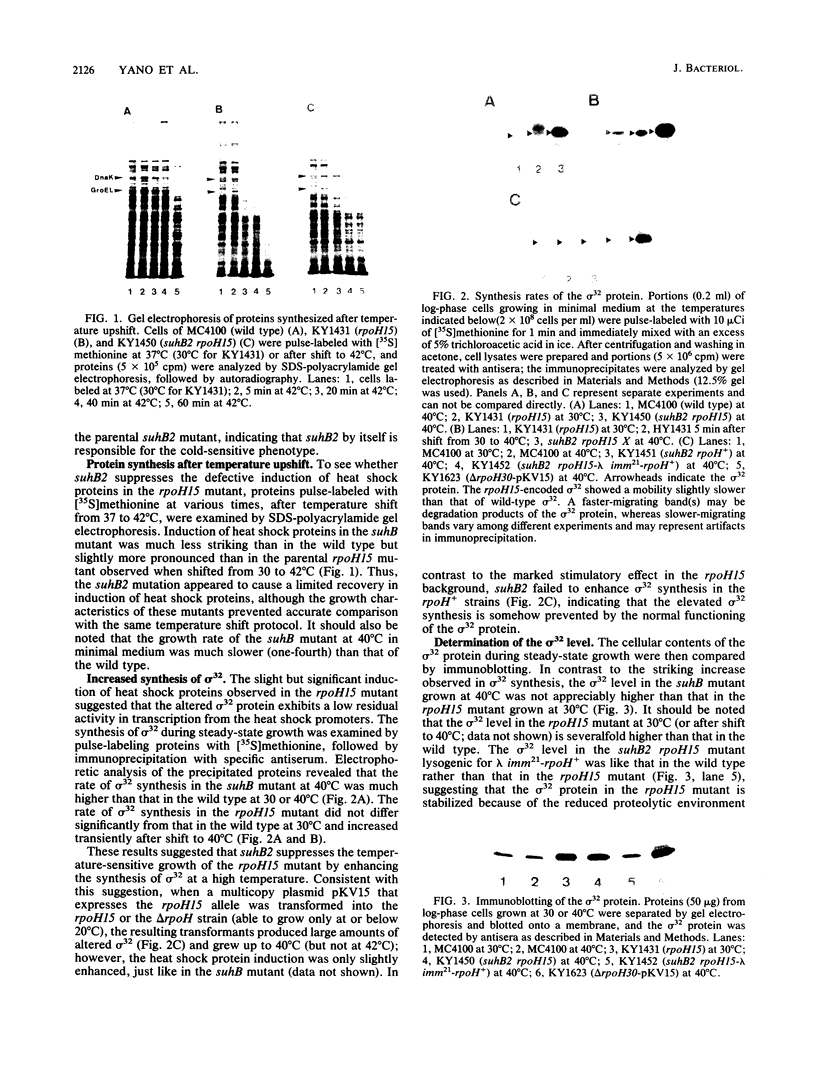
The rpoH15 mutant cannot grow at or above 34 degrees C, because it produces an altered sigma 32 protein that is largely deficient in the transcription of the heat shock genes. Extragenic suppressor mutations (suhB) located at 55 min on the Escherichia coli chromosome endowed the mutant cell with the ability to grow at 40 degrees C and the inability to grow at 25 degrees C. One such mutation (suhB2), studied in detail, markedly enhanced the rate of sigma 32 synthesis and the rpoH mRNA level during steady-state growth at 37 to 40 degrees C but little affected the cellular content of sigma 32 or the induction of heat shock proteins. In the isogenic rpoH+ strain, neither sigma 32 synthesis nor the rpoH mRNA level was enhanced by the suhB suppressor. Furthermore, expression of the rpoH-lacZ gene fusion, but not the operon fusion, was much higher in the suhB mutant than in the wild type or the suhB rpoH+ strain, indicating that suhB affects rpoH expression primarily at the level of translation. suhB probably acts to increase sigma 32 synthesis by affecting the regulatory circuit of rpoH expression or by modulating certain parameters in protein synthesis. Consistent with these findings, overproduction of the mutant (rpoH15) sigma 32 by multicopy plasmid enabled the rpoH15 or delta rpoH (deletion) mutant to grow at up to 40 degrees C. Plasmids containing an E. coli DNA segment of 1.0 kilobase could complement the cold-sensitive phenotype of the suhB2 mutant. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that the segment contained an open reading frame encoding a protein of 29,128 daltons.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. A., Grossman A. D., Gross C. A. A gene regulating the heat shock response in Escherichia coli also affects proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6779–6783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkareva E. S., Lissin N. M., Girshovich A. S. Transient association of newly synthesized unfolded proteins with the heat-shock GroEL protein. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):254–257. doi: 10.1038/336254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Vaughn V., Walter W. A., Neidhardt F. C., Gross C. A. Regulation of the promoters and transcripts of rpoH, the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Ishihama A. Heat-shock induction of RNA polymerase sigma-32 synthesis in Escherichia coli: transcriptional control and a multiple promoter system. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):10–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00337752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Casson L. P., Goldberg A. L. Heat shock regulatory gene htpR influences rates of protein degradation and expression of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6647–6651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Akiyama Y., Yura T., Shiba K. Diverse effects of the MalE-LacZ hybrid protein on Escherichia coli cell physiology. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):201–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.201-204.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Yura T. Heat shock protein GroE of Escherichia coli: key protective roles against thermal stress. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):874–882. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Yura T., Ueguchi C., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Effects of mutations in heat-shock genes groES and groEL on protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3517–3521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Aiba H. Evidence for negative control of cya transcription by cAMP and cAMP receptor protein in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14838–14843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T. Mutation that suppresses the protein export defect of the secY mutation and causes cold-sensitive growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):696–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.696-701.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T. Suppressors of the secY24 mutation: identification and characterization of additional ssy genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):849–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.849-856.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelly S., Coleman T., Fu C. F., Brot N., Weissbach H. Correlation between the 32-kDa sigma factor levels and in vitro expression of Escherichia coli heat shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8365–8369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of sigma 32. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):348–351. doi: 10.1038/329348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., Erickson J., Sharma S., Georgopoulos C. Heat shock regulatory gene rpoH mRNA level increases after heat shock in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1155–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1155-1158.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Ito K., Yura T. Isolation and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants defective in heat-shock induction of proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00332716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Kusukawa N., Yura T. Suppression of rpoH (htpR) mutations of Escherichia coli: heat shock response in suhA revertants. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4128–4134. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4128-4134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Genetic control of heat-shock protein synthesis and its bearing on growth and thermal resistance in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Temperature-induced synthesis of specific proteins in Escherichia coli: evidence for transcriptional control. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.843-851.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Imai M., Yura T. The use of operon fusions in studies of the heat-shock response: effects of altered sigma 32 on heat-shock promoter function in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00331486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Yura T. Suppression of the Escherichia coli rpoH opal mutation by ribosomes lacking S15 protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1712–1717. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1712-1717.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Tobe T., Ito K., Osawa T. Heat shock regulatory gene (htpR) of Escherichia coli is required for growth at high temperature but is dispensable at low temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6803–6807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. N., Kusukawa N., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A., Yura T. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants that lack the heat shock sigma factor sigma 32. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3640–3649. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3640-3649.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]