Abstract
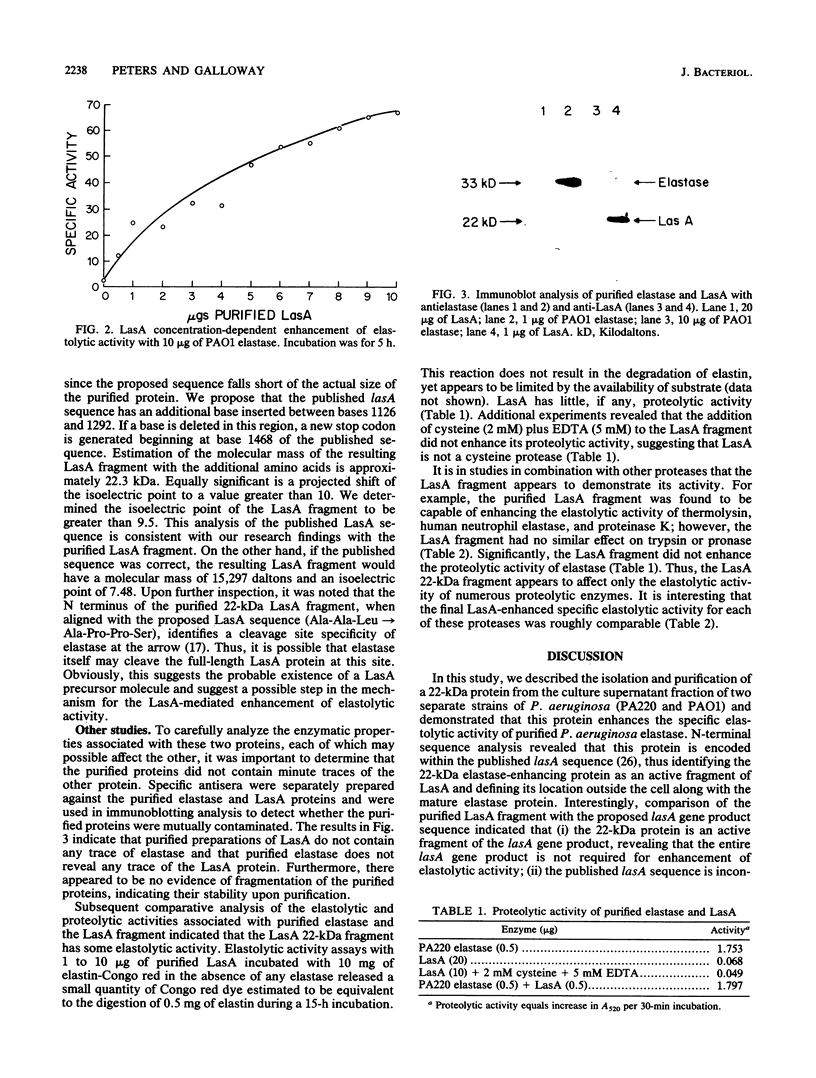
A 22-kilodalton protein purified from the culture supernatant fraction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strains PA220 and PAO1) was found to enhance the elastolytic activity of purified P. aeruginosa elastase. N-terminal sequence analysis identified the protein as a fragment of the lasA gene product (P.A. Schad and B.H. Iglewski, J. Bacteriol. 170:2784-2789, 1988). However, comparative analysis with the reported LasA sequence indicated that the purified LasA fragment is longer than the deduced sequence reported. The purified LasA fragment had minimal elastolytic and proteolytic activity and did not enhance the proteolytic activity of purified elastase, yet enhanced the elastolytic activity more than 25-fold. The LasA fragment was found to also enhance the elastolytic activities of thermolysin, human neutrophil elastase, and proteinase K. The results presented here suggest that the LasA protein interacts with the elastin substrate rather than modifying elastase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bever R. A., Iglewski B. H. Molecular characterization and nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4309–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4309-4314.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. C., Poncz L., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C., Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Dearborn D. G. Biochemical and pathologic evidence for proteolytic destruction of lung connective tissue in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):529–535. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Obernesser H. J., Botzenhart K. Extrazelluläre Toxine von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Einwirkung zweier gereinigter Proteasen auf die menschlichen Immunoglobuline IgG, IgA und sekretorisches IgA. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1981 Mar;249(1):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima J., Yamamoto S., Morihara K., Atsumi Y., Takeuchi H., Kawamoto S., Okuda K. Structural gene and complete amino acid sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO 3455 elastase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1698–1704. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1698-1704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian G. G., Moss R. L., Greaser M. Analytical isoelectric focusing using a high-voltage vertical slab polyacrylamide gel system. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):421–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Activation of an elastase precursor by the lasA gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4532–4539. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4532-4539.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and transcriptional regulation of the elastase lasA gene in mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1349–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1349-1351.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Wheeler R. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections owing to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: elastase, an IgG protease. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Sep;30(9):1118–1124. doi: 10.1139/m84-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger K. S., Bahner D. R., Warren R. L. Protease phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):55–59. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.55-59.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler E., Kennah H. E., Brown S. I. Pseudomonas protease. Purification, partial characterization, and its effect on collagen, proteoglycan, and rabbit corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Jun;16(6):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Oda K. Protease and elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inactivation of human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):188–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.188-193.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mull J. D., Callahan W. S. The role of the elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in experimental infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Dec;4(6):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Cryz S. J., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):836–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.836-842.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju K., Anwar R. A. Primary structures of bovine elastin a, b, and c deduced from the sequences of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5755–5762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saulnier J. M., Curtil F. M., Duclos M. C., Wallach J. M. Elastolytic activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 1;995(3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schad P. A., Bever R. A., Nicas T. I., Leduc F., Hanne L. F., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and characterization of elastase genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2691–2696. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2691-2696.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schad P. A., Iglewski B. H. Nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasA gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2784–2789. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2784-2789.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W. Vorkommen von Elastase bei Pseudomonas und Aeromonas. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 May;220(1):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. R., Miller K. D. Elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inactivation of complement components and complement-derived chemotactic and phagocytic factors. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.128-135.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]