Abstract
The metY-nusA-infB operon of Escherichia coli encodes functions involved in both transcription and translation. Previous studies have identified a single promoter, P0, that directs transcription of the entire operon. We have identified a second promoter, P-1, that also is positioned to transcribe the complete operon. P-1 is located 50 base pairs upstream of and oriented in the same direction as P0. Sequences associated with P-1 have features suggestive of regulatory elements. P-1 differs from any previously described naturally occurring E. coli promoter by having -35 and -10 sequences that perfectly match the procaryotic promoter consensus hexamer sequences, although the spacing between the two elements is 1 base pair more than optimal. We demonstrate that P-1 is active in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auble D. T., deHaseth P. L. Promoter recognition by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Influence of DNA structure in the spacer separating the -10 and -35 regions. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer B. F., Kar E. G., Elford R. M., Holmes W. M. Sequence determinants for promoter strength in the leuV operon of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988;63(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Lupski J. R. Plasmids for the selection and analysis of prokaryotic promoters. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:54–68. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenatiempo Y., Deville F., Brot N., Weissbach H. In vitro expression of the Escherichia coli nusA-infB operon. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Imperiale M. J., Adhya S. L. RNA 3' end formation in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:453–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
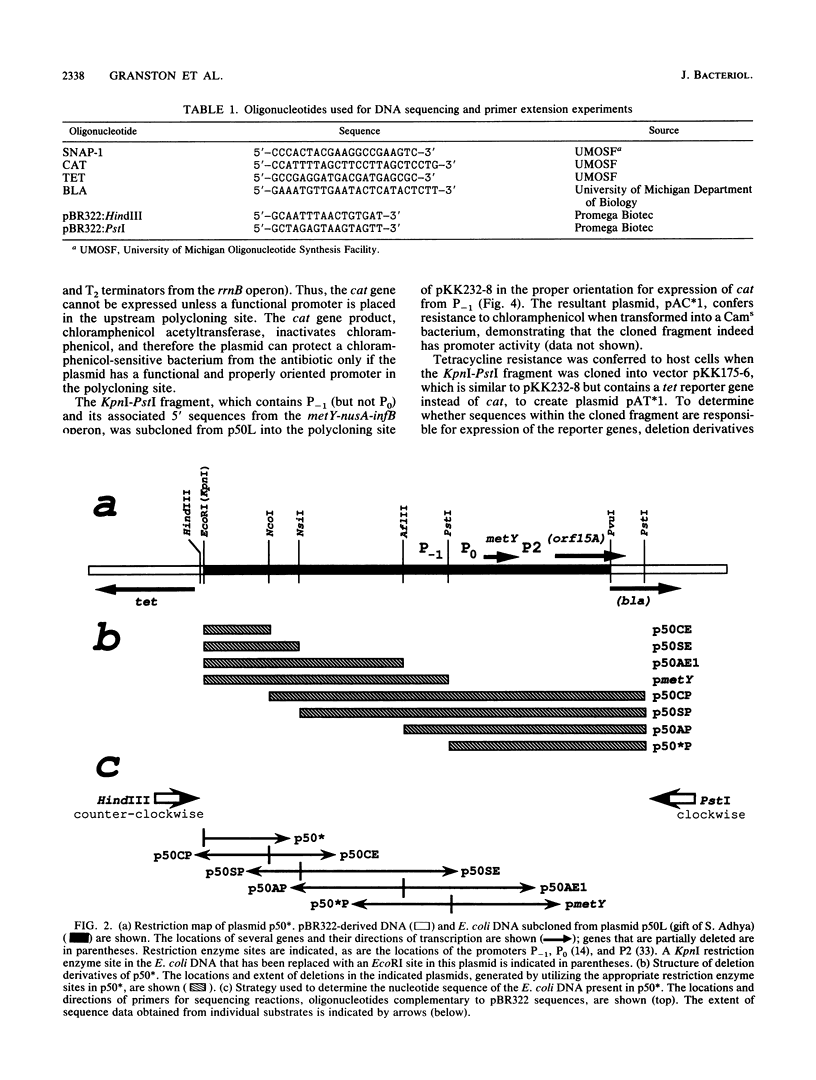
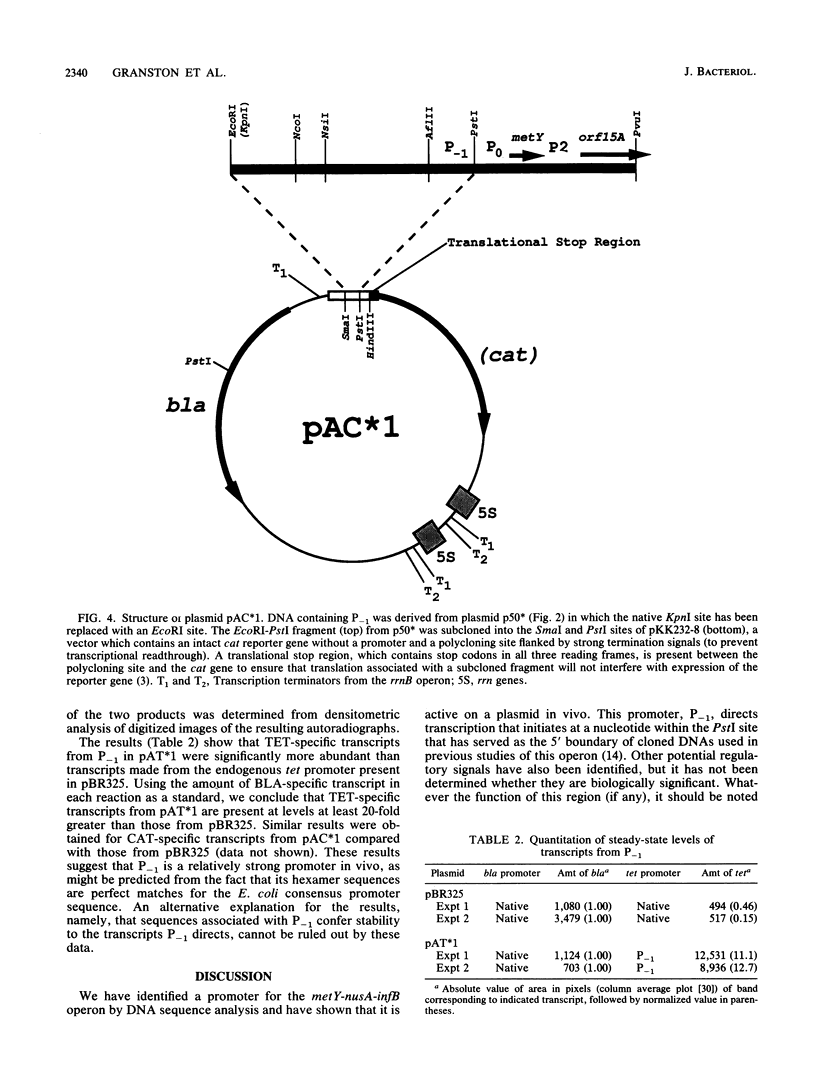
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A., Honda A., Nagasawa-Fujimori H., Glass R. E., Maekawa T., Imamoto F. Multivalent regulation of the nusA operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):185–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00333573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Ihara M., Maekawa T., Nakamura Y., Uchida H., Imamoto F. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned nusA gene and its flanking region of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3333–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kuroki K., Imamoto F. tRNAMetf2 gene in the leader region of the nusA operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):409–413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. G., VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Induction of proteins in response to low temperature in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2092–2095. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2092-2095.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus R., Bujard H. PL of coliphage lambda: an alternative solution for an efficient promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2919–2923. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Genetically separable functional elements mediate the optimal expression and stringent regulation of a bacterial tRNA gene. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim D. B., Oppenheim J. D., Eckhardt T., Maas W. K. Nucleotide sequence of the argR gene of Escherichia coli K-12 and isolation of its product, the arginine repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6697–6701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Friedman D. I. An E. coli gene product required for lambda site-specific recombination. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Ward D. F. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning with BamHI and Sau3A. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Brosius J., McClure W. R. Characterization in vitro of the effect of spacer length on the activity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase at the TAC promoter. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3529–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase T., Ishii S., Imamoto F. Differential transcriptional control of the two tRNA(fMet) genes of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Mizusawa S. In vivo evidence that the nusA and infB genes of E. coli are part of the same multi-gene operon which encodes at least four proteins. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):527–532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Mitchell L. G., Merril C. R., Rasband W. S. Use of image analysis to quantitate changes in form of mitochondrial DNA after x-irradiation. Appl Theor Electrophor. 1989;1(3):163–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge J. A., Deville F., Sacerdot C., Petersen H. U., Cenatiempo Y., Cozzone A., Grunberg-Manago M., Hershey J. W. Two translational initiation sites in the infB gene are used to express initiation factor IF2 alpha and IF2 beta in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):223–229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
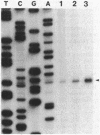
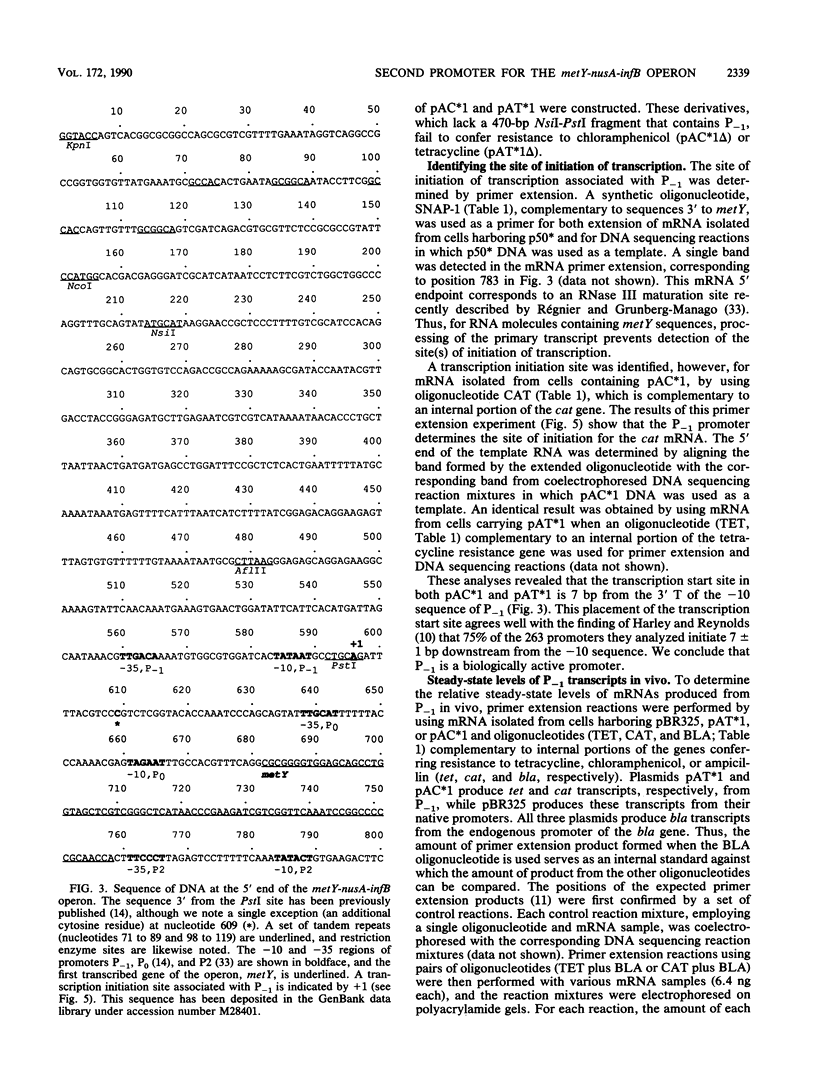
- Régnier P., Grunberg-Manago M. Cleavage by RNase III in the transcripts of the met Y-nus-A-infB operon of Escherichia coli releases the tRNA and initiates the decay of the downstream mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier P., Grunberg-Manago M., Portier C. Nucleotide sequence of the pnp gene of Escherichia coli encoding polynucleotide phosphorylase. Homology of the primary structure of the protein with the RNA-binding domain of ribosomal protein S1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier P., Portier C. Initiation, attenuation and RNase III processing of transcripts from the Escherichia coli operon encoding ribosomal protein S15 and polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacerdot C., Dessen P., Hershey J. W., Plumbridge J. A., Grunberg-Manago M. Sequence of the initiation factor IF2 gene: unusual protein features and homologies with elongation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7787–7791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. F., Regnier P., Cummings H. S., Grunberg-Manago M., Hershey J. W. The existence of two genes between infB and rpsO in the Escherichia coli genome: DNA sequencing and S1 nuclease mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10803–10816. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmientos P., Sylvester J. E., Contente S., Cashel M. Differential stringent control of the tandem E. coli ribosomal RNA promoters from the rrnA operon expressed in vivo in multicopy plasmids. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1337–1346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer A. T., Carver D. L., Bigelow B., Baron L. S., Friedman D. I. lambda N antitermination system: functional analysis of phage interactions with the host NusA protein. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):679–690. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Sierra F. Alternative promoters in developmental gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:237–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA binding by proteins. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1182–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.2842864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M. Altered translation initiation factor 2 in the cold-sensitive ssyG mutant affects protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3001–3006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Promoter sequence for stringent control of bacterial ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):973–976. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.973-976.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]