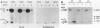Abstract
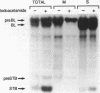
The methanol-insoluble, heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli synthesized by clinical strains or strains that harbor the cloned gene was shown to be an extracellular polypeptide. The toxin (STB) was first detected as an 8,100-Mr precursor (pre-STB) that was converted to a transiently cell-associated 5,200-Mr form. Proteolytic conversion of pre-STB to STB was shown to be inhibited by the proton motive force uncoupler carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone and did not occur in a secA background. After STB was detected as a cell-associated molecule, an extracellular form with identical electrophoretic mobility became apparent. The results suggest that there is no proteolytic processing during the mobilization of STB from the periplasm to the culture supernatant. The determined amino acid sequence of STB coincides fully with the 48 carboxy-terminal amino acids inferred from the DNA sequence. The 23 amino-terminal residues inferred from the DNA sequence were absent in the mature toxin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betley M. J., Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Genetics of bacterial enterotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:577–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. J., Bole D. G., Quay S. C., Oxender D. L. Role for membrane potential in the secretion of protein into the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5396–5400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Oudega B. Production and release of cloacin DF13 and related colicins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:183–205. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Lee E. Y., Welch R. A. Escherichia coli hemolysin is released extracellularly without cleavage of a signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):88–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.88-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Judd A. K., Schoolnik G. K. Importance of disulfide bridges in the structure and activity of Escherichia coli enterotoxin ST1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8907–8911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Lane A., Frayman F., Wilbur D., Robien W., Schoolnik G. K., Jardetzky O. Structure of the toxic domain of the Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin ST I. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7854–7866. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson L., Mahanty H. K., Kolter R. Four plasmid genes are required for colicin V synthesis, export, and immunity. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2466–2470. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2466-2470.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Hacker J., Knapp S., Then I., Wagner W., Hughes C., Juarez A. Structure, function, and regulation of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin determinant of Escherichia coli. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:791–805. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Fusion of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin and heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5201–5208. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5201-5208.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Rectification of two Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin allele sequences and lack of biological effect of changing the carboxy-terminal tyrosine to histidine. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):645–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.645-648.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán-Verduzco L. M., Fonseca R., Kupersztoch-Portnoy Y. M. Thermoactivation of a periplasmic heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):146–151. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.146-151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Export and processing analysis of a fusion between the extracellular heat-stable enterotoxin and the periplasmic B subunit of the heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):253–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Hu S. T., Swiatek P. J., Moseley S. L., Allen S. D., So M. Isolation of a novel transposon which carries the Escherichia coli enterotoxin STII gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.615-620.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Secretion of haemolysin by Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:159–181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicaud J. M., Mackman N., Gray L., Holland I. B. The C-terminal, 23 kDa peptide of E. coli haemolysin 2001 contains all the information necessary for its secretion by the haemolysin (Hly) export machinery. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80838-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo T., Kobayashi Y., Shimonishi Y., Kyogoku Y., Braun W., Go N. A conformational study of polypeptides in solution by 1H-nmr and distance geometry. Biopolymers. 1986;25 (Suppl):S123–S134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Hirst T. R., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J., Randall L. Synthesis of a precursor to the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.325-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Mazaitis A. J., Maas W. K., Rey M., Heyneker H. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for heat-stable enterotoxin II of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):269–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.269-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The ins and outs of colicins. Part I: Production, and translocation across membranes. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Oct;1(7):168–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Guzmán-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Two precursors of the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: evidence of extracellular processing. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Casadaban M. J., Shuman H. A., Beckwith J. R. Conversion of beta-galactosidase to a membrane-bound state by gene fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3423–3427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Argenzio R. A. Comparison of enterotoxic activities of heat-stable enterotoxins from class 1 and class 2 Escherichia coli of swine origin. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.245-251.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C. Protease degradation of Escherichia coli heat-stable, mouse-negative, pig-positive enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2057–2060. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2057-2060.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]