Abstract
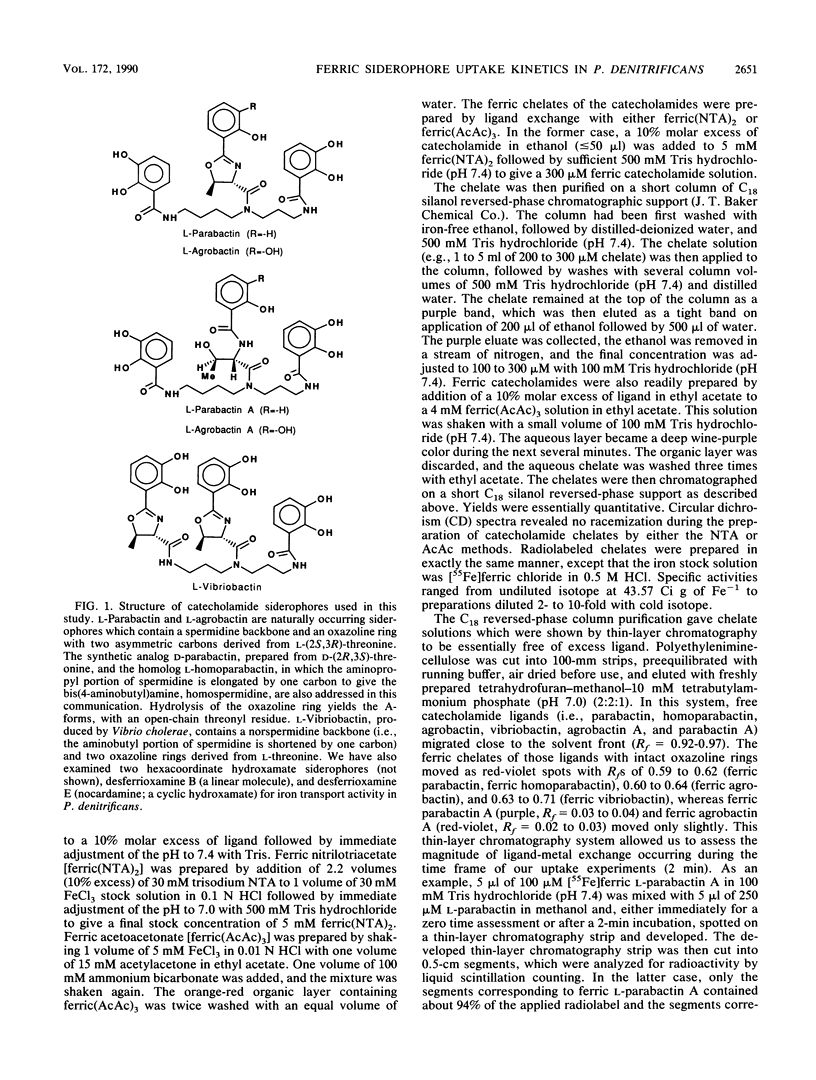
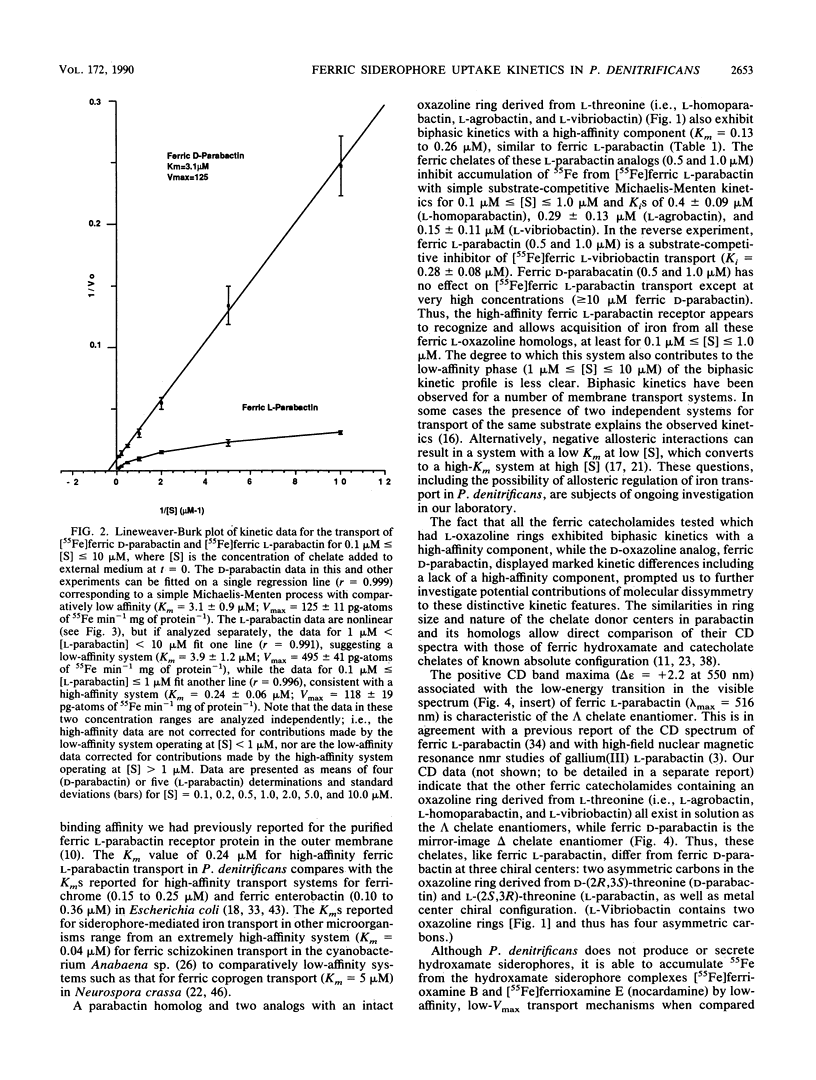
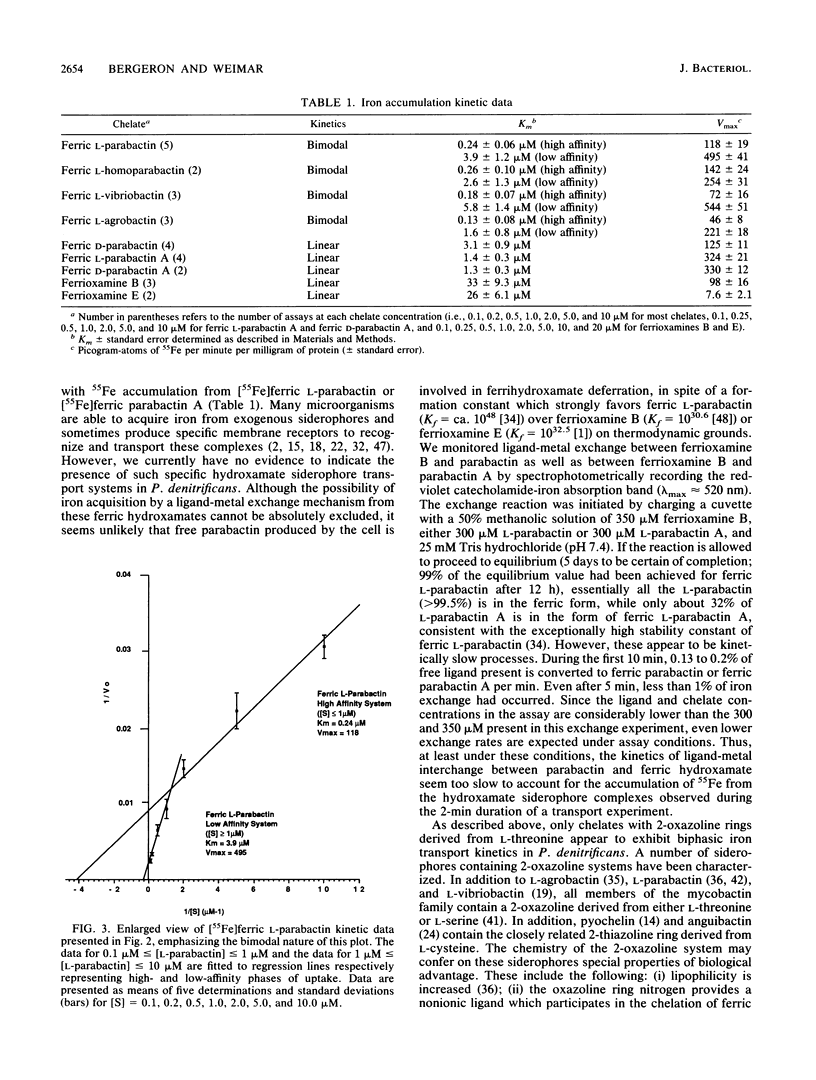
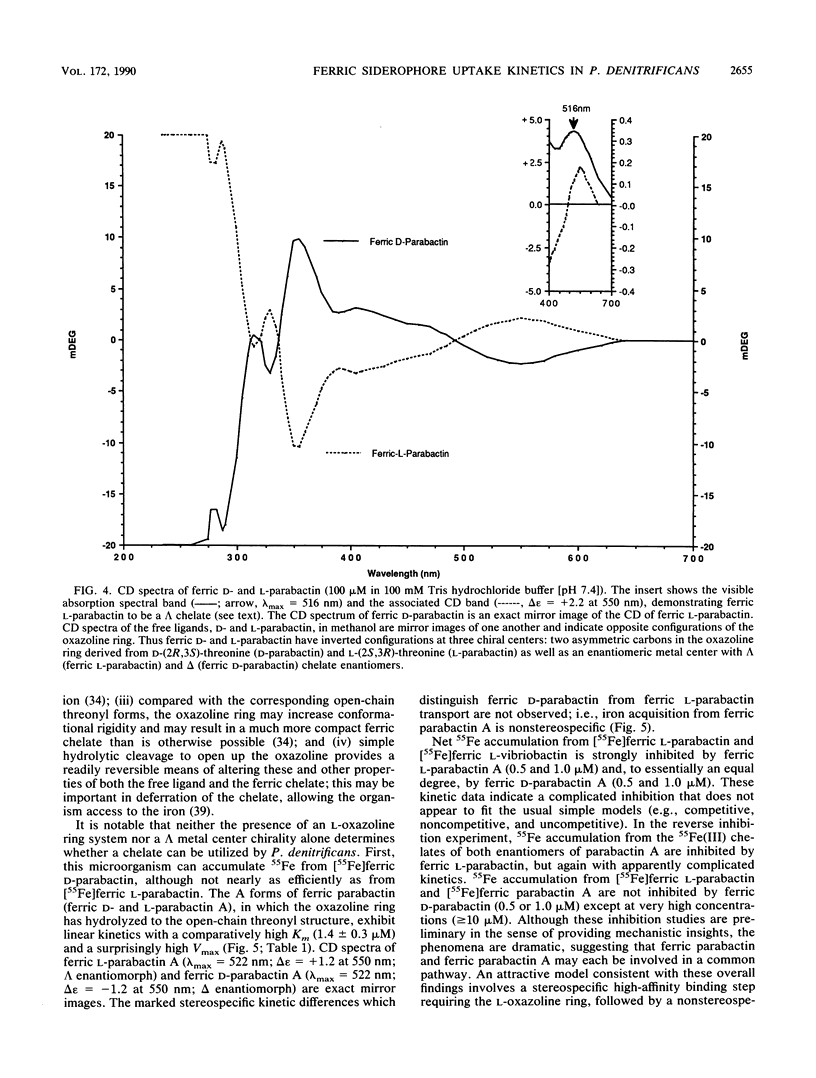
The kinetics of iron accumulation by iron-starved Paracoccus denitrificans during the first 2 min of exposure to 55Fe-labeled ferric siderophore chelates is described. Iron is acquired from the ferric chelate of the natural siderophore L-parabactin in a process exhibiting biphastic kinetics by Lineweaver-Burk analysis. The kinetic data for 1 microM less than [Fe L-parabactin] less than 10 microM fit a regression line which suggests a low-affinity system (Km = 3.9 +/- 1.2 microM, Vmax = 494 pg-atoms of 55Fe min-1 mg of protein-1), whereas the data for 0.1 microM less than or equal to [Fe L-parabactin] less than or equal to 1 microM fit another line consistent with a high-affinity system (Km = 0.24 +/- 0.06 microM, Vmax = 108 pg-atoms of 55Fe min-1 mg of protein-1). The Km of the high-affinity uptake is comparable to the binding affinity we had previously reported for the purified ferric L-parabactin receptor protein in the outer membrane. In marked contrast, ferric D-parabactin data fit a single regression line corresponding to a simple Michaelis-Menten process with comparatively low affinity (Km = 3.1 +/- 0.9 microM, Vmax = 125 pg-atoms of 55Fe min-1 mg of protein-1). Other catecholamide siderophores with an intact oxazoline ring derived from L-threonine (L-homoparabactin, L-agrobactin, and L-vibriobactin) also exhibit biphasic kinetics with a high-affinity component similar to ferric L-parabactin. Circular dichroism confirmed that these ferric chelates, like ferric L-parabactin, exist as the lambda enantiomers. The A forms ferric parabactin (ferrin D- and L-parabactin A), in which the oxazoline ring is hydrolyzed to the open-chain threonyl structure, exhibit linear kinetics with a comparatively high Km (1.4 +/- 0.3 microM) and high Vmax (324 pg-atoms of 55Fe min-1 of protein-1). Furthermore, the marked stereospecificity seen between ferric D- and L-parabactins is absent; i.e., iron acquisition from ferric parabactin A is non stereospecific. The mechanistic implications of these findings in relation to a stereospecific high-affinity binding followed by a nonstereospecific postreceptor processing is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arceneaux J. E., Davis W. B., Downer D. N., Haydon A. H., Byers B. R. Fate of labeled hydroxamates during iron transport from hydroxamate-ion chelates. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):919–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.919-927.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
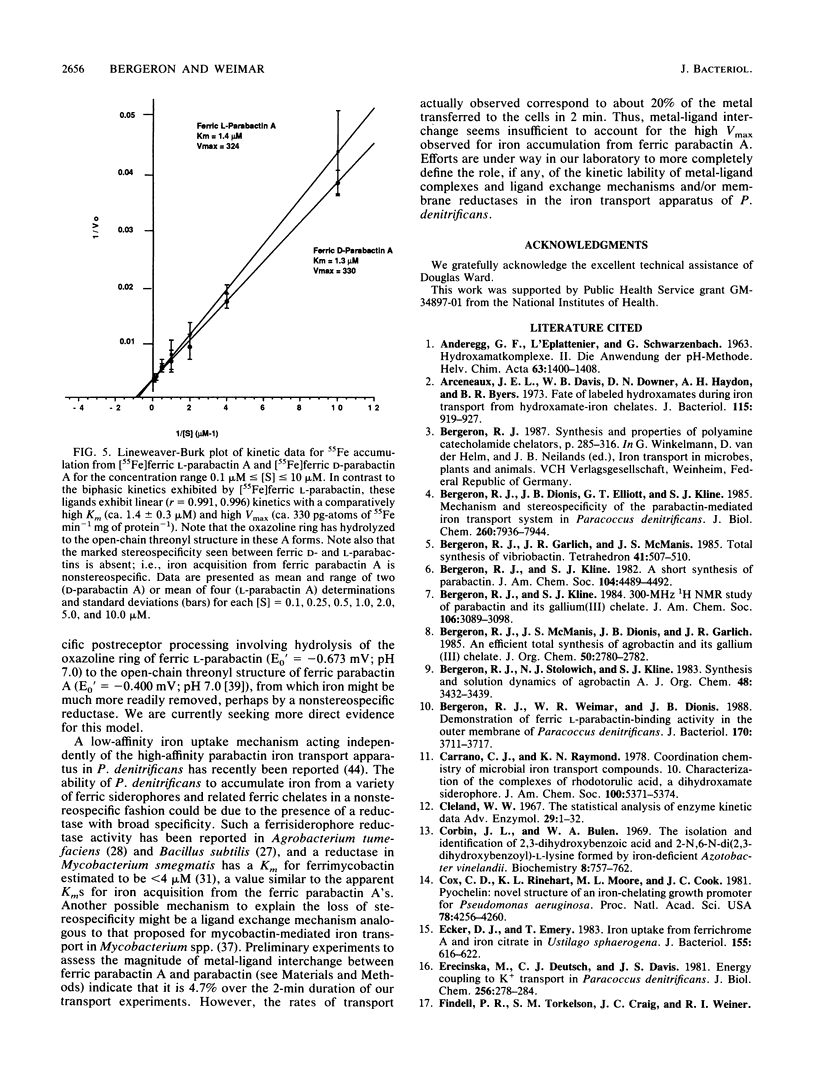
- Bergeron R. J., Dionis J. B., Elliott G. T., Kline S. J. Mechanism and stereospecificity of the parabactin-mediated iron-transport system in Paracoccus denitrificans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7936–7944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron R. J., Weimar W. R., Dionis J. B. Demonstration of ferric L-parabactin-binding activity in the outer membrane of Paracoccus denitrificans. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3711–3717. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3711-3717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. L., Bulen W. A. The isolation and identification of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and 2-N,6-N-di-92,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)-L-lysine formed by iron-deficient Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):757–762. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Moore M. L., Cook J. C., Jr Pyochelin: novel structure of an iron-chelating growth promoter for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4256–4260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Emery T. Iron uptake from ferrichrome A and iron citrate in Ustilago sphaerogena. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):616–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.616-622.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Deutsch C. J., Davis J. S. Energy coupling to K+ transport in Paracoccus denitrificans. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):278–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. The inducible citrate-dependent iron transport system in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. L., Sigel S. P., Payne S. M., Neilands J. B. Vibriobactin, a siderophore from Vibrio cholerae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):383–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Busza A. L., Pierce E. J., Rees W. D. Evidence for negative cooperativity in human erythrocyte sugar transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 21;649(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huschka H., Naegeli H. U., Leuenberger-Ryf H., Keller-Schierlein W., Winkelmann G. Evidence for a common siderophore transport system but different siderophore receptors in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):715–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.715-721.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isied S. S., Kuo G., Raymond K. N. Coordination isomers of biological iron transport compounds. V. The preparation and chirality of the chromium(III) enterobactin complex and model tris(catechol)chromium(III) analogues. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Mar 31;98(7):1763–1767. doi: 10.1021/ja00423a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers P. J., Sanders-Loehr J. Active transport of ferric schizokinen in Anabaena sp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.288-294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Gaines C. G., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Ferrisiderophore reductase activity in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):771–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.771-774.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Gaines C. G., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Non-hydrolytic release of iron from ferrienterobactin analogs by extracts of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Raymond K. N. Specificity and mechanism of ferrioxamine-mediated iron transport in Streptomyces pilosus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):304–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.304-312.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrin R. S., Neilands J. B. Ferrichrome transport in inner membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2339–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong S. A., Peterson T., Neilands J. B. Agrobactin, a siderophore from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1860–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge C., Patel P. V., Mundy J. Iron transport in Mycobacterium smegmatis: the location of mycobactin by electron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jul;128(7):1559–1565. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-7-1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. Transport of iron into bacterial cells. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:388–394. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow G. A. Mycobactins: iron-chelating growth factors from mycobacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):99–125. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.99-125.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait G. H. The identification and biosynthesis of siderochromes formed by Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):191–204. doi: 10.1042/bj1460191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Newton A. An additional step in the transport of iron defined by the tonB locus of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2147–2151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann G. Metabolic products of microorganisms. 132. Uptake of iron by Neurospora crassa. 3. Iron transport studies with ferrichrome-type compounds. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Jun 7;98(1):39–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



