Abstract
We have cloned from Bacillus subtilis a novel protease gene (nprB) encoding a neutral protease by using a shotgun cloning approach. The gene product was determined to have a molecular mass of 60 kDa. It has a typical signal peptide-like sequence at the N-terminal region. The expression of nprB can be stimulated by using a B. subtilis strain, WB30, carrying a sacU(h)h mutation. Expression of this protease gene results in production of a 37-kDa protease in the culture medium. The first five amino acid residues from the N terminus of the mature protease were determined to be Ala-Ala-Gly-Thr-Gly. This indicates that the protease is synthesized in a preproenzyme form. The purified protease has a pH optimum of around 6.6, and its activity can be inhibited by EDTA, 1,10-phenanthroline (a zinc-specific chelator), and dithiothreitol. It retained 65% of its activity after treatment at 65 degrees C for 20 min. Sequence comparison indicates that the mature form of this protease has 66% homology with the two thermostable neutral proteases from B. thermoproteolyticus and B. stearothermophilus. It also shares 65, 61, and 56% homology with the thermolabile neutral proteases from B. cereus, B. amyloliquefaciens, and B. subtilis, respectively. The zinc-binding site and the catalytic residues are all conserved among these proteases. Sequence homology extends into the "propeptide" region. The nprB gene was mapped between metC and glyB and was not required for growth or sporulation.
Full text
PDF





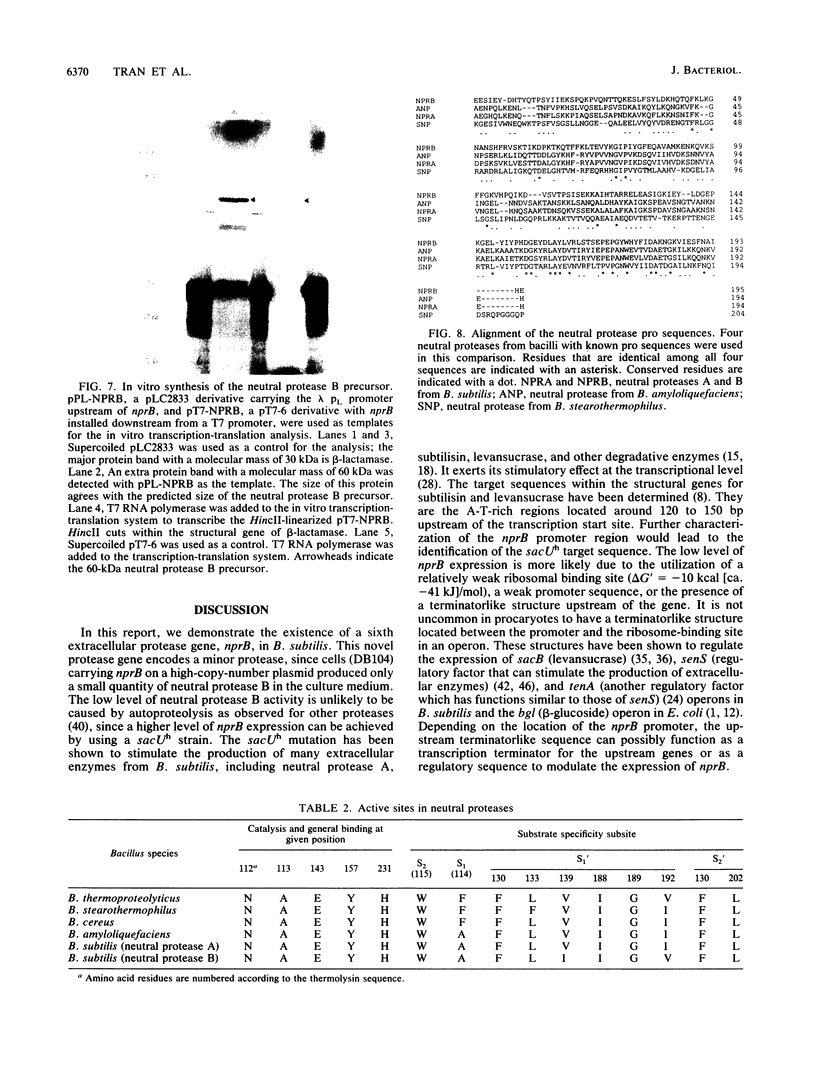


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amster-Choder O., Wright A. Regulation of activity of a transcriptional anti-terminator in E. coli by phosphorylation in vivo. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):540–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2200123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS T. L., FELBER J. P., VALLEE B. L. Metallocarboxpeptidases: mechanism of inhibition by chelating agents, mercaptans, and metal ions. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:899–905. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedonder R. A., Lepesant J. A., Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Billault A., Steinmetz M., Kunst F. Construction of a kit of reference strains for rapid genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis 168. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):989–993. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.989-993.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J., Keay L., Garrett L. R., Cirulis N., Moseley M. H., Wildi B. S. Bacillus cereus neutral protease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;251(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Takagi M., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Molecular cloning of a thermostable neutral protease gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus in a vector plasmid and its expression in Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.831-837.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujishima A., Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature. 1972 Jul 7;238(5358):37–38. doi: 10.1038/238037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hangauer D. G., Monzingo A. F., Matthews B. W. An interactive computer graphics study of thermolysin-catalyzed peptide cleavage and inhibition by N-carboxymethyl dipeptides. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5730–5741. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Ferrari E., Perego M., Hoch J. A. Location of the targets of the hpr-97, sacU32(Hy), and sacQ36(Hy) mutations in upstream regions of the subtilisin promoter. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):296–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.296-300.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Barat M., Anagnostopoulos C. Transformation and transduction in recombination-defective mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1925-1937.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. A., Matthews B. W. Structure of thermolysin refined at 1.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 5;160(4):623–639. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90319-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Metal substitutions and inhibition of thermolysin: spectra of the cobalt enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4601–4607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houman F., Diaz-Torres M. R., Wright A. Transcriptional antitermination in the bgl operon of E. coli is modulated by a specific RNA binding protein. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90392-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Takagi H., Inouye M. Requirement of pro-sequence for the production of active subtilisin E in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7859–7864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.442-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst F., Pascal M., Lepesant-Kejzlarova J., Lepesant J. A., Billault A., Dedonder R. Pleiotropic mutations affecting sporulation conditions and the syntheses of extracellular enzymes in Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1481–1489. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton T. J., Doi R. H. The stability of messenger ribonucleic acid during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3189–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant J. A., Kunst F., Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Dedonder R. Chromosomal location of mutations affecting sucrose metabolism in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(2):135–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00267084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y. Thermostable protease from thermophilic bacteria. II. Studies on the stability of the protease. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):509–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang A. S., Nathoo S., Wong S. L. Cloning and characterization of a pair of novel genes that regulate production of extracellular enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):46–54. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.46-54.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Tsao H., Fiers W. Improved plasmid vectors with a thermoinducible expression and temperature-regulated runaway replication. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche R. S., Voordouw G. The structural and functional roles of metal ions in thermolysin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978;5(1):1–23. doi: 10.3109/10409237809177138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Modulation of Bacillus subtilis levansucrase gene expression by sucrose and regulation of the steady-state mRNA level by sacU and sacQ genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):380–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.380-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silen J. L., Agard D. A. The alpha-lytic protease pro-region does not require a physical linkage to activate the protease domain in vivo. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):462–464. doi: 10.1038/341462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Ally A., Ally D., Pero J. Gene encoding a minor extracellular protease in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5557–5563. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5557-5563.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Rufo G. A., Jr, Rudolph C. F., Sullivan B. J., Theriault K. A., Pero J. Bacillopeptidase F of Bacillus subtilis: purification of the protein and cloning of the gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1470–1477. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1470-1477.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferrari E. Replacement of the Bacillus subtilis subtilisin structural gene with an In vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.411-418.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Le Coq D., Aymerich S., Gonzy-Tréboul G., Gay P. The DNA sequence of the gene for the secreted Bacillus subtilis enzyme levansucrase and its genetic control sites. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(2):220–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00425427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Thompson L. D., Rhodes C., Banner C., Nagle J., Filpula D. Genes for alkaline protease and neutral protease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens contain a large open reading frame between the regions coding for signal sequence and mature protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.811-819.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. F., Doi R. H. Complex character of senS, a novel gene regulating expression of extracellular-protein genes of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1939–1947. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1939-1947.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L. Development of an inducible and enhancible expression and secretion system in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Doi R. H. Determination of the signal peptidase cleavage site in the preprosubtilisin of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10176–10181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Price C. W., Goldfarb D. S., Doi R. H. The subtilisin E gene of Bacillus subtilis is transcribed from a sigma 37 promoter in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Wang L. F., Doi R. H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of senN, a novel 'Bacillus natto' (B. subtilis) gene that regulates expression of extracellular protein genes. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Dec;134(12):3269–3276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-12-3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X. C., Nathoo S., Pang A. S., Carne T., Wong S. L. Cloning, genetic organization, and characterization of a structural gene encoding bacillopeptidase F from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6845–6850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M. Y., Ferrari E., Henner D. J. Cloning of the neutral protease gene of Bacillus subtilis and the use of the cloned gene to create an in vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.15-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Ohta Y., Jordan F., Inouye M. Pro-sequence of subtilisin can guide the refolding of denatured subtilisin in an intermolecular process. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):483–484. doi: 10.1038/339483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]