Abstract
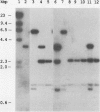
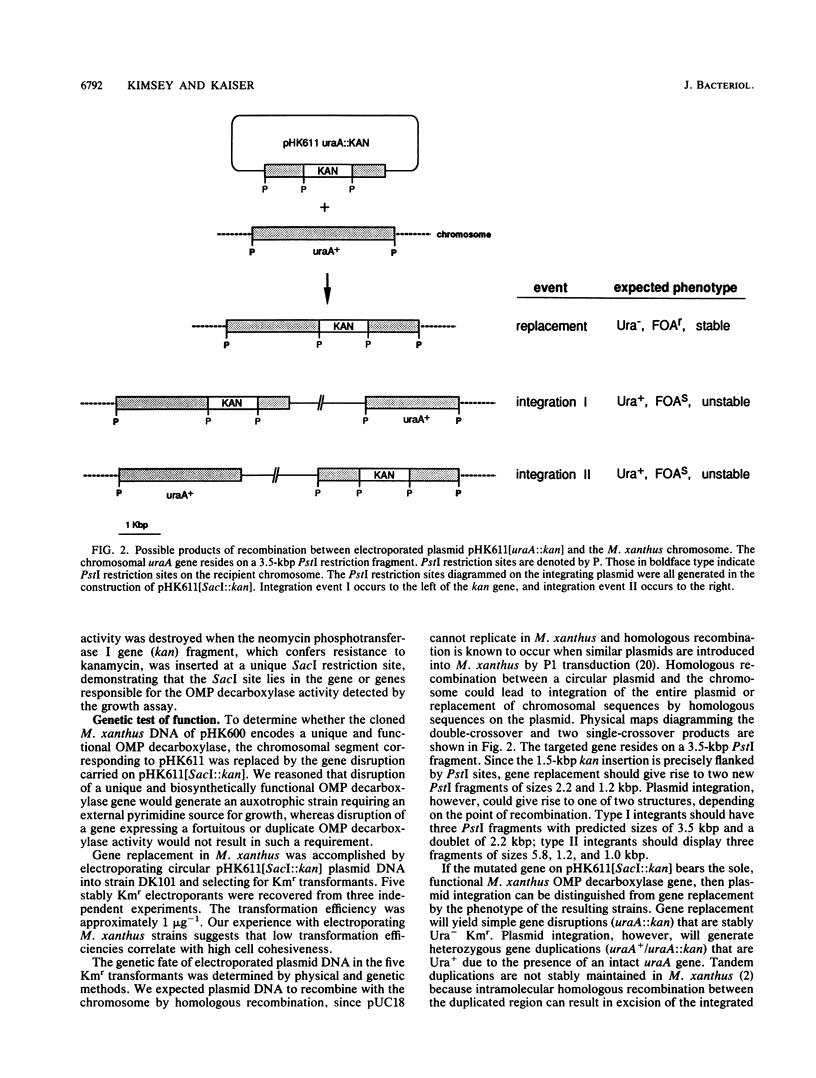
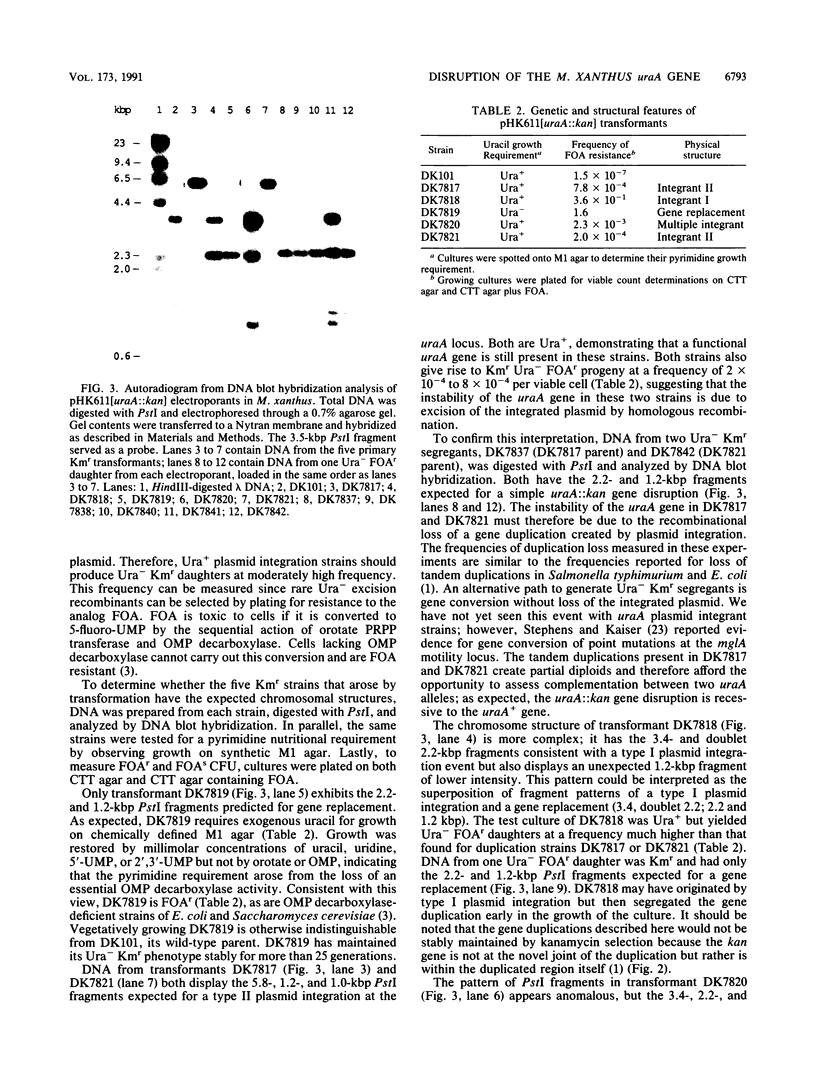
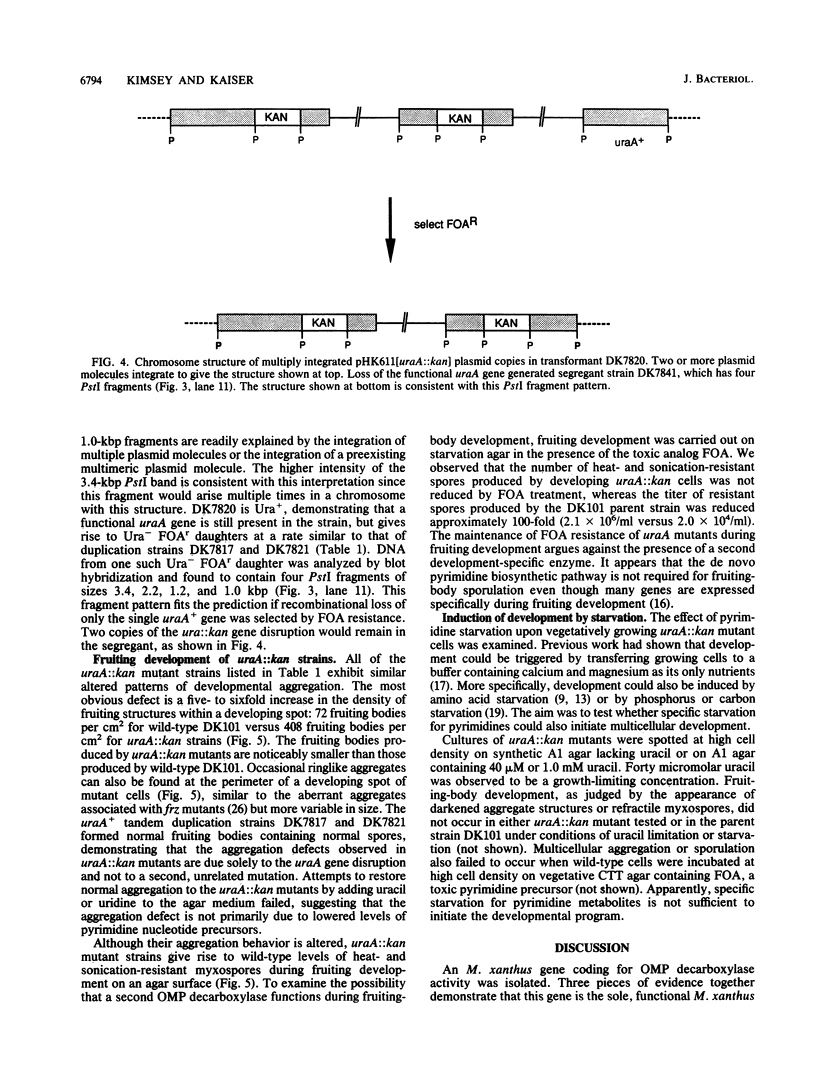
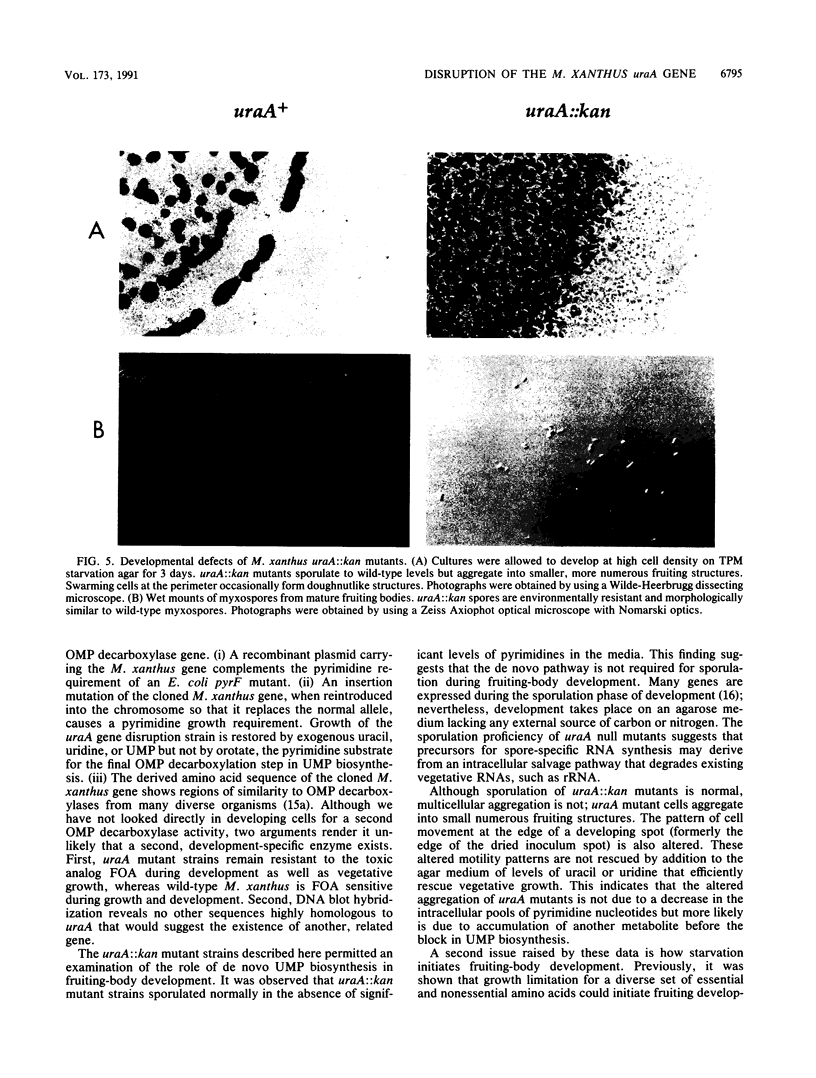
The Myxococcus xanthus gene coding for orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP) decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.23) was cloned. The M. xanthus uraA gene efficiently complemented an Escherichia coli OMP decarboxylase mutant, permitting it to grow in the absence of uracil. Electroporation of M. xanthus with a circular plasmid carrying a selectable uraA::kan gene disruption resulted in homologous recombination at the chromosomal uraA locus. Chromosomal integration of the gene disruption plasmid created heterozygous (uraA+/uraA::kan) tandem duplications. These tandem duplications were unstable and segregated auxotrophic uraA::kan daughters at frequencies of 2 x 10(-4) to 8 x 10(-4) per viable cell. Rare uraA::kan segregants were easily obtained by selecting for resistance to the toxic analog 5-fluoroorotic acid. Our experiments suggest that the cloned uraA gene could facilitate the use of gene duplications in the genetic analysis of M. xanthus development. The uraA mutants could utilize uracil, uridine, or uridine 5'-phosphate for growth, indicating that M. xanthus has pyrimidine salvage pathways. During multicellular development, uraA::kan gene disruption mutants sporulated to wild-type levels but formed smaller and more numerous aggregates than did their uraA+ parent, regardless of whether uracil was added to the medium. Pyrimidine deprivation of uraA mutants, under conditions that otherwise supported vegetative growth, failed to induce fruiting-body development or sporulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem genetic duplications in phage and bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:473–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery L., Kaiser D. In situ transposon replacement and isolation of a spontaneous tandem genetic duplication. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):99–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00330896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. NUTRITIONAL REGU.ATION OF MORPHOGENESIS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:67–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.67-72.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure M., Kalekine M., Boy-Marcotte E., Jacquet M. Developmental control of the expression of the dihydroorotate dehydrogenase and UMP synthase genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Differ. 1988 Jan;22(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(88)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Zahler S. A. Nutritional induction and suppression of fruiting in Myxococcus xanthus FBa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1018-1023.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Control of multicellular development: Dictyostelium and Myxococcus. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:539–566. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Fruiting body morphogenesis in submerged cultures of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.458-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., KORNBERG A., SIMMS E. S. Enzymatic synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides; orotidine-5'-phosphate and uridine-5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jul;215(1):403–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Coliphage P1-mediated transduction of cloned DNA from Escherichia coli to Myxococcus xanthus: use for complementation and recombinational analyses. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):317–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.317-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R. "Frizzy" mutants: a new class of aggregation-defective developmental mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1430–1437. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1430-1437.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D., Rosenberg E. Division cycle of Myxococcus xanthus. II. Kinetics of stable and unstable ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.801-810.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]