Abstract
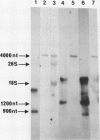
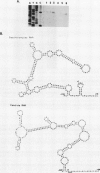
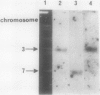
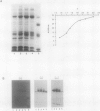
The Candida albicans PMA1 gene was isolated from a genomic library by using a hybridization probe obtained from the PMA1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The gene was localized to chromosome III of the Candida genome. An open reading frame of 2,685 nucleotides predicts an amino acid sequence of 895 amino acids that is 83% homologous at both the DNA and protein levels to its S. cerevisiae equivalent. A polyadenylated mRNA transcript of about 4,000 nucleotides contains a highly folded AU-rich leader of 242 nucleotides. The structure of the gene, codon bias, and levels of approximately 100-kDa H(+)-ATPase protein recovered in plasma membranes indicate a highly expressed gene. The plasma membrane ATPase was purified to about 90% homogeneity and appeared to be blocked at the amino terminus. Three hydrophobic membrane sector tryptic fragments from the partially digested ATPase provided internal sequence information for over 50 amino acids, which agrees with the sequence predicted by the cloned gene. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicated that the C. albicans enzyme is about 3 kDa smaller than its Saccharomyces counterpart and was consistent with a predicted Mr of 97,398. Antibodies to the S. cerevisiae whole ATPase or its carboxyl terminus bound to the C. albicans enzyme but with lower avidity. Kinetic analysis showed that the Candida and Saccharomyces ATPases respond to glucose activation-starvation in nonidentical fashions. The amino-terminal domain of the C. albicans ATPase is marked by a net deletion of 23 amino acids in comparison with the S. cerevisiae ATPase. These differences maintain net charge, occur in nonconserved regions of fungal ATPases, and are sufficient to account for the observed difference in electrophoretic mobility between the two yeast ATPases.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capieaux E., Vignais M. L., Sentenac A., Goffeau A. The yeast H+-ATPase gene is controlled by the promoter binding factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7437–7446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crislip M. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Candidiasis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1989 Mar;3(1):103–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D. Effects of the modification of transfer buffer composition and the renaturation of proteins in gels on the recognition of proteins on Western blots by monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):144–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghislain M., Schlesser A., Goffeau A. Mutation of a conserved glycine residue modifies the vanadate sensitivity of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17549–17555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. D., Peacey M. J., von Strandmann R. P. Plasma membrane proton pump inhibition and stalk cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1988 Jul;38(2):91–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager K. M., Mandala S. M., Davenport J. W., Speicher D. W., Benz E. J., Jr, Slayman C. W. Amino acid sequence of the plasma membrane ATPase of Neurospora crassa: deduction from genomic and cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7693–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Kelly J. D., Cohen E. H. Transcription terminates in yeast distal to a control sequence. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Sullivan P. A., Shepherd M. G. The kinetics and divalent cation inhibition of plasma membrane ATPase in the yeast Candida albicans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6782–6787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Surarit R., Sullivan P. A., Shepherd M. G. The isolation of plasma membrane and characterisation of the plasma membrane ATPase from the yeast Candida albicans. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):375–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H. D., Wiltfang J., Karas M., Neuhoff V., Hilschmann N. Gas-phase sequencing after electroblotting on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes assigns correct molecular weights to myoglobin molecular weight markers. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroczek R. A., Siebert E. Optimization of northern analysis by vacuum-blotting, RNA-transfer visualization, and ultraviolet fixation. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim H. M., Pène J. J. Optimal conditions for supercoil DNA sequencing with the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I large fragment. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):32–39. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A., Magee P. T. Assignment of cloned genes to the seven electrophoretically separated Candida albicans chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4721–4726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B. Functional characterization of a pyrimidine-rich element in the 5'-noncoding region of the yeast iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1045–1054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii M., Takata H., Takeguchi N. Binding site of omeprazole in hog gastric H+,K(+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):754–760. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92089-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Candida infections: an overview. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(1):1–5. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlin D. S., Brown C. L., Haber J. E. Membrane potential defect in hygromycin B-resistant pma1 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18118–18122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Serrano R. Dissection of functional domains of the yeast proton-pumping ATPase by directed mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1793–1798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Serrano R. Growth control strength and active site of yeast plasma membrane ATPase studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., de Larrinoa I. F., Serrano R. Deletion analysis of yeast plasma membrane H+-ATPase and identification of a regulatory domain at the carboxyl-terminus. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81375-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad R. Nutrient transport in Candida albicans, a pathogenic yeast. Yeast. 1987 Dec;3(4):209–221. doi: 10.1002/yea.320030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Rice D. A., Lingrel J. B. Site-directed mutagenesis of a conserved, extracellular aspartic acid residue affects the ouabain sensitivity of sheep Na,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21902–21906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabon E. C., Reuben M. A. The mechanism and structure of the gastric H,K-ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:321–344. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesser A., Ulaszewski S., Ghislain M., Goffeau A. A second transport ATPase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19480–19487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. H+-ATPase from plasma membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Avena sativa roots: purification and reconstitution. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:533–544. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kielland-Brandt M. C., Fink G. R. Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na+ + K+), K+- and Ca2+-ATPases. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):689–693. doi: 10.1038/319689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membranes of plants and fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Poulter R. T., Sullivan P. A. Candida albicans: biology, genetics, and pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:579–614. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. A., Allaudeen H. S., Whitman M. H., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Isolation and characterization of a beta-tubulin gene from Candida albicans. Gene. 1988;63(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart E., Gow N. A., Bowen D. V. Cytoplasmic alkalinization during germ tube formation in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulaszewski S., Grenson M., Goffeau A. Modified plasma-membrane ATPase in mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo C. G., Serrano R. Physiology of mutants with reduced expression of plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Yeast. 1989 Jul-Aug;5(4):307–319. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]