Abstract
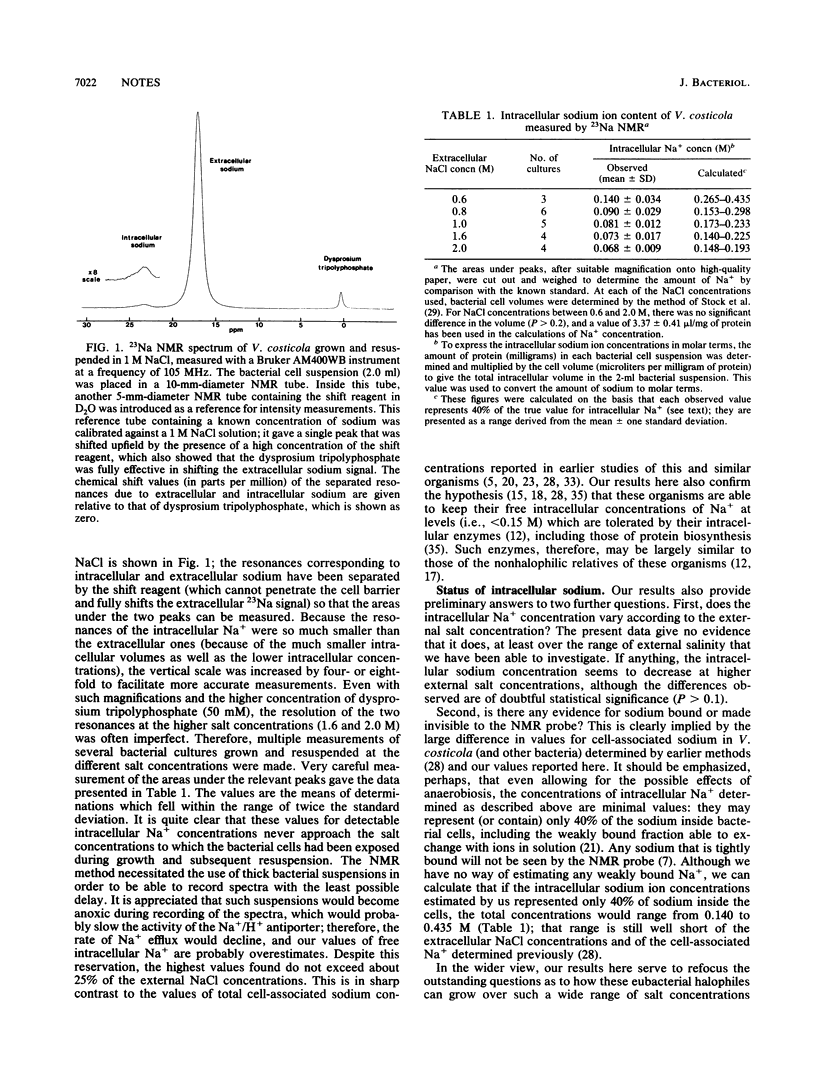
We present new data obtained by 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, which can distinguish free intracellular sodium from cell-bound sodium, showing that the intracellular concentration of Na+ the halophilic eubacterium Vibrio costicola is only 5 to 20% of that in the extracellular medium. Previous methods could not distinguish free intracellular Na+ from that bound to cell structures, and it was believed that in halophilic eubacteria the total monovalent cation concentration inside matched that of the NaCl outside. Information obtained by the newer technology raises fundamental questions about the ways in which these organisms and others which live in hypersaline environments function and cope with osmotic stress.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balschi J. A., Cirillo V. P., Springer C. S., Jr Direct high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cation transport in vivo, Na+ transport in yeast cells. Biophys J. 1982 Jun;38(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84566-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):803–846. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.803-846.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle A. M., Macnab R. M., Shulman R. G. Measurement of intracellular sodium concentration and sodium transport in Escherichia coli by 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3288–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth M. P., Kushner D. J. Nutrition and distribution of salt response in populations of moderately halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):253–261. doi: 10.1139/m70-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M., Gilboa H. Sodium exchange between two sites. The binding of sodium to halotolerant bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 18;538(2):268–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaide F., Kushner D. J., Sprott G. D. Proton circulation in Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.681-686.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaide F., Kushner D. J., Sprott G. D. Proton motive force and Na+/H+ antiport in a moderate halophile. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):537–544. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.537-544.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M., Russell N. J. Life at the limits. Considerations on how bacteria can grow at extremes of temperature and pressure, or with high concentrations of ions and solutes. Sci Prog. 1987;71(283 Pt 3):381–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui M., Wada S. Intracellular concentrations of Na+, K+, and cl minus of a moderately halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Oct;19(10):1181–1186. doi: 10.1139/m73-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regev R., Peri I., Gilboa H., Avi-Dor Y. 13C NMR study of the interrelation between synthesis and uptake of compatible solutes in two moderately halophilic eubacteria. Bacterium Ba1 and Vibro costicola. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Apr;278(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell N. J., Kogut M. Haloadaptation: salt sensing and cell-envelope changes. Microbiol Sci. 1985 Nov;2(11):345–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindler D. B., Wydro R. M., Kushner D. J. Cell-bound cations of the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):698–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.698-703.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. Growth of a marine Vibrio alginolyticus and moderately halophilic V. costicola becomes uncoupler resistant when the respiration-dependent Na+ pump functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):636–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.636-643.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udagawa T., Unemoto T., Tokuda H. Generation of Na+ electrochemical potential by the Na+-motive NADH oxidase and Na+/H+ antiport system of a moderately halophilic Vibrio costicola. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2616–2622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wydro R. M., Madira W., Hiramatsu T., Kogut M., Kushner D. J. Salt-sensitive in vitro protein synthesis by a moderately halophilic bacterium. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):824–825. doi: 10.1038/269824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



