Abstract
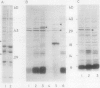
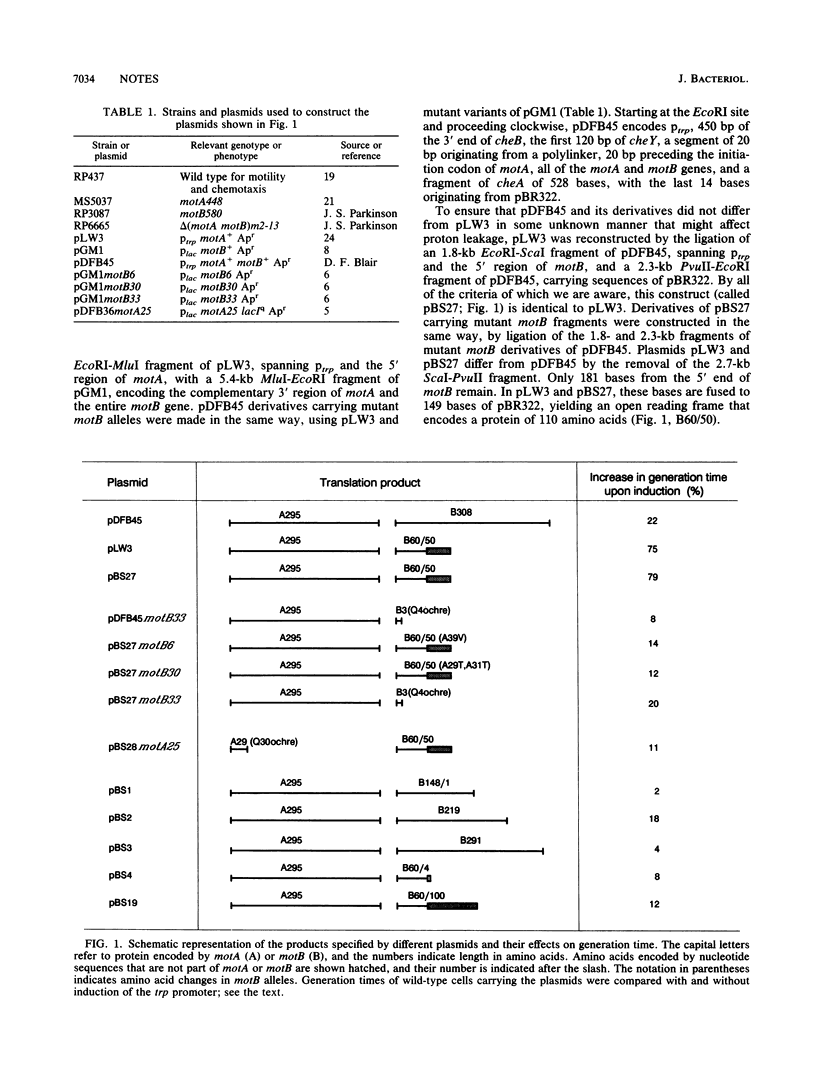
Cells that overexpress MotA (encoded on a plasmid derived from pBR322) grow slowly because of proton leakage. We have traced this defect to the coexpression of a fusion protein consisting of 60 amino acids from the N terminus of MotB and 50 amino acids specified by pBR322. Mutations within the N terminus, known to abolish function when present in full-length MotB, reversed the growth defect. Growth also was normal when MotA was coexpressed with wild-type MotB or with a series of MotB N-terminal fragments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J. Location of genes for motility and chemotaxis on the Escherichia coli genetic map. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):156–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.156-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. Restoration of torque in defective flagellar motors. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1678–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.2849208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. The MotA protein of E. coli is a proton-conducting component of the flagellar motor. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):439–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90595-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Kim D. Y., Berg H. C. Mutant MotB proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4049–4055. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4049-4055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F. The bacterial flagellar motor. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Berg H. C. Successive incorporation of force-generating units in the bacterial rotary motor. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):470–472. doi: 10.1038/309470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Mandel G., Simon M. I. Integral membrane proteins required for bacterial motility and chemotaxis. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:123–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun S. Y., Parkinson J. S. Bacterial motility: membrane topology of the Escherichia coli MotB protein. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):276–278. doi: 10.1126/science.2447650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean G. E., Macnab R. M., Stader J., Matsumura P., Burks C. Gene sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of the motA protein, a membrane-associated protein required for flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.991-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Aizawa S. The bacterial flagellum and flagellar motor: structure, assembly and function. Adv Microb Physiol. 1991;32:109–172. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Dapice M., Reese T. S. Effects of mot gene expression on the structure of the flagellar motor. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., DeRosier D. J. Bacterial flagellar structure and function. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):442–451. doi: 10.1139/m88-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Parkinson J. S. Genetic analysis of the bacterial flagellum. Trends Genet. 1991 Jun;7(6):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90436-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Caplan S. R., Berg H. C. Dynamics of a tightly coupled mechanism for flagellar rotation. Bacterial motility, chemiosmotic coupling, protonmotive force. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82889-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Matsumura P., Simon M. The identification of the mot gene product with Escherichia coli-lambda hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3126–3130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Operon controlling motility and chemotoxis in E. coli. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):577–580. doi: 10.1038/264577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Matsumura P., Vacante D., Dean G. E., Macnab R. M. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli motB gene and site-limited incorporation of its product into the cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):244–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.244-252.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. L., Macnab R. M. Co-overproduction and localization of the Escherichia coli motility proteins motA and motB. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3932–3939. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3932-3939.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. L., Macnab R. M. Overproduction of the MotA protein of Escherichia coli and estimation of its wild-type level. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):588–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.588-597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S., Kihara M., Isomura M., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1172-1179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Fujita H., Ishihara A., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):187–193. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.187-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]