Abstract
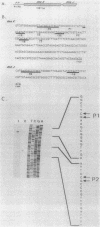
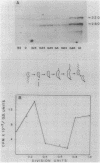
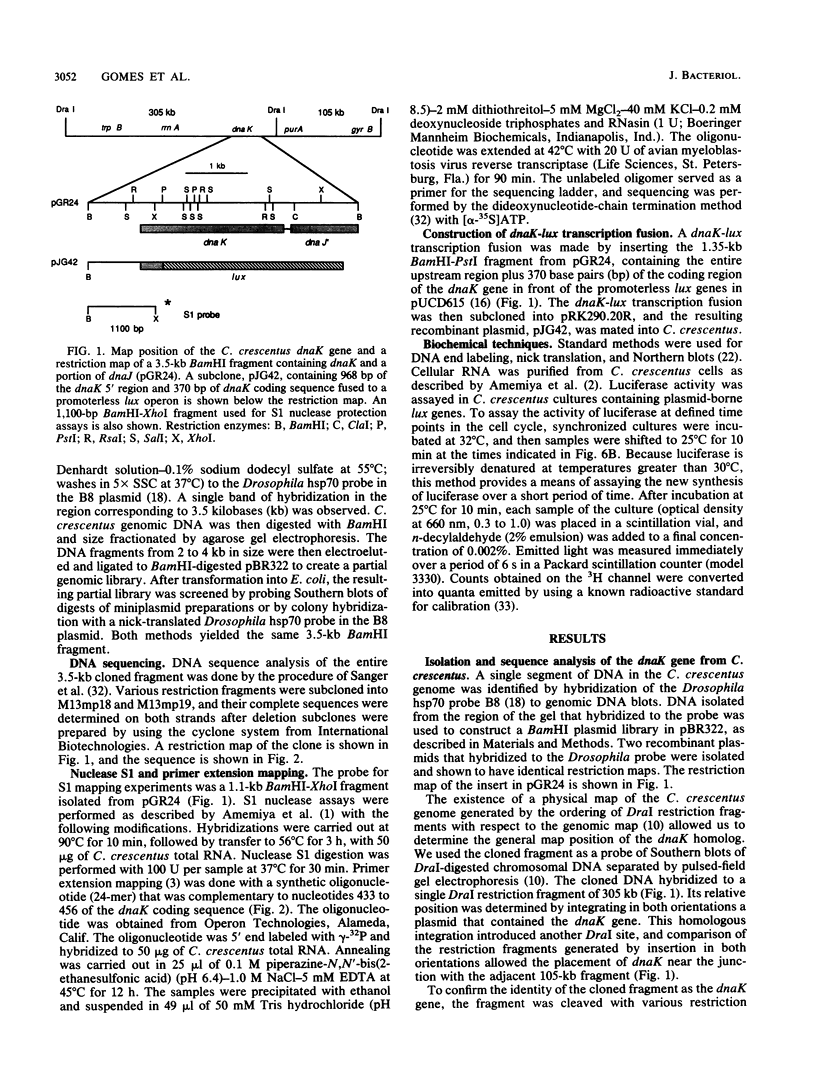
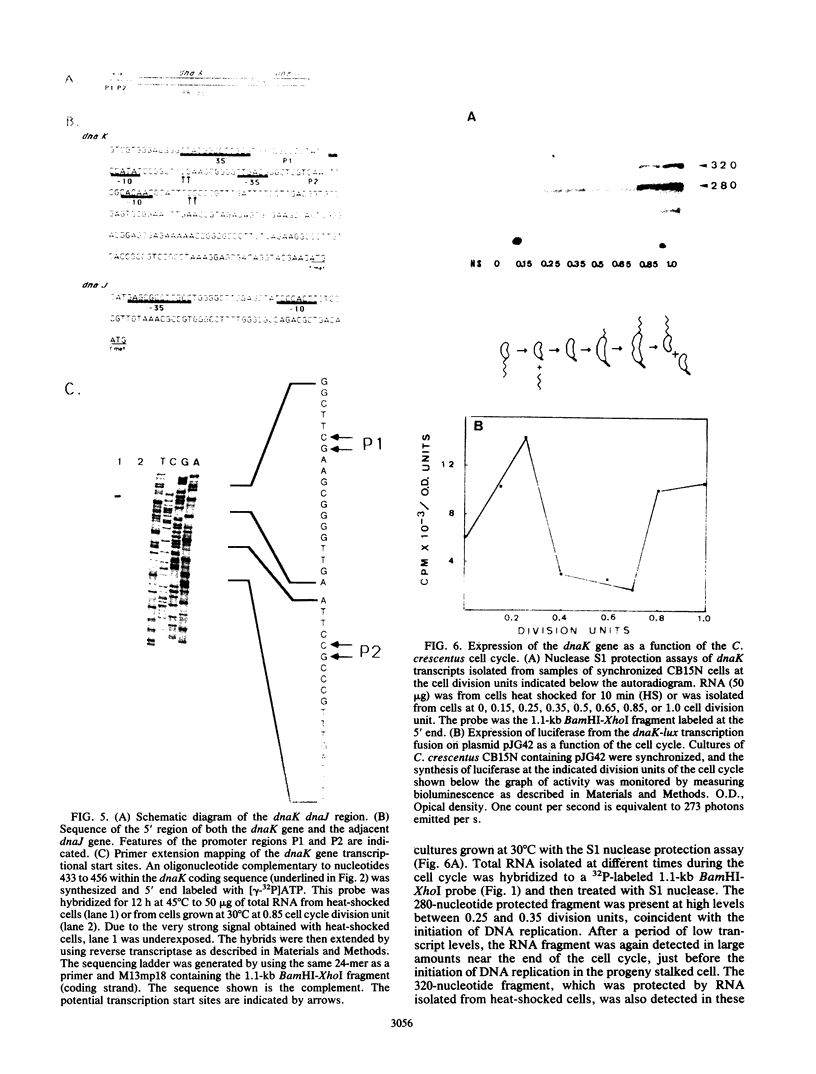
Caulobacter crescentus has a single dnaK gene that is highly homologous to the hsp70 family of heat shock genes. Analysis of the cloned and sequenced dnaK gene has shown that the deduced amino acid sequence could encode a protein of 67.6 kilodaltons that is 68% identical to the DnaK protein of Escherichia coli and 49% identical to the Drosophila and human hsp70 protein family. A partial open reading frame 165 base pairs 3' to the end of dnaK encodes a peptide of 190 amino acids that is 59% identical to DnaJ of E. coli. Northern blot analysis revealed a single 4.0-kilobase mRNA homologous to the cloned fragment. Since the dnaK coding region is 1.89 kilobases, dnaK and dnaJ may be transcribed as a polycistronic message. S1 mapping and primer extension experiments showed that transcription initiated at two sites 5' to the dnaK coding sequence. A single start site of transcription was identified during heat shock at 42 degrees C, and the predicted promoter sequence conformed to the consensus heat shock promoters of E. coli. At normal growth temperature (30 degrees C), a different start site was identified 3' to the heat shock start site that conformed to the E. coli sigma 70 promoter consensus sequence. S1 protection assays and analysis of expression of the dnaK gene fused to the lux transcription reporter gene showed that expression of dnaK is temporally controlled under normal physiological conditions and that transcription occurs just before the initiation of DNA replication. Thus, in both human cells (I. K. L. Milarski and R. I. Morimoto, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:9517-9521, 1986) and in a simple bacterium, the transcription of a hsp70 gene is temporally controlled as a function of the cell cycle under normal growth conditions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amemiya K., Bellofatto V., Shapiro L., Feingold J. Transcription initiation in vitro and in vivo at a highly conserved promoter within a 16 S ribosomal RNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Tilly K., Craig E., King J., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli K12 dnaJ+ gene. A gene that encodes a heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1782–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras I., Shapiro L., Henry S. Membrane phospholipid composition of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1130–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1130-1136.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
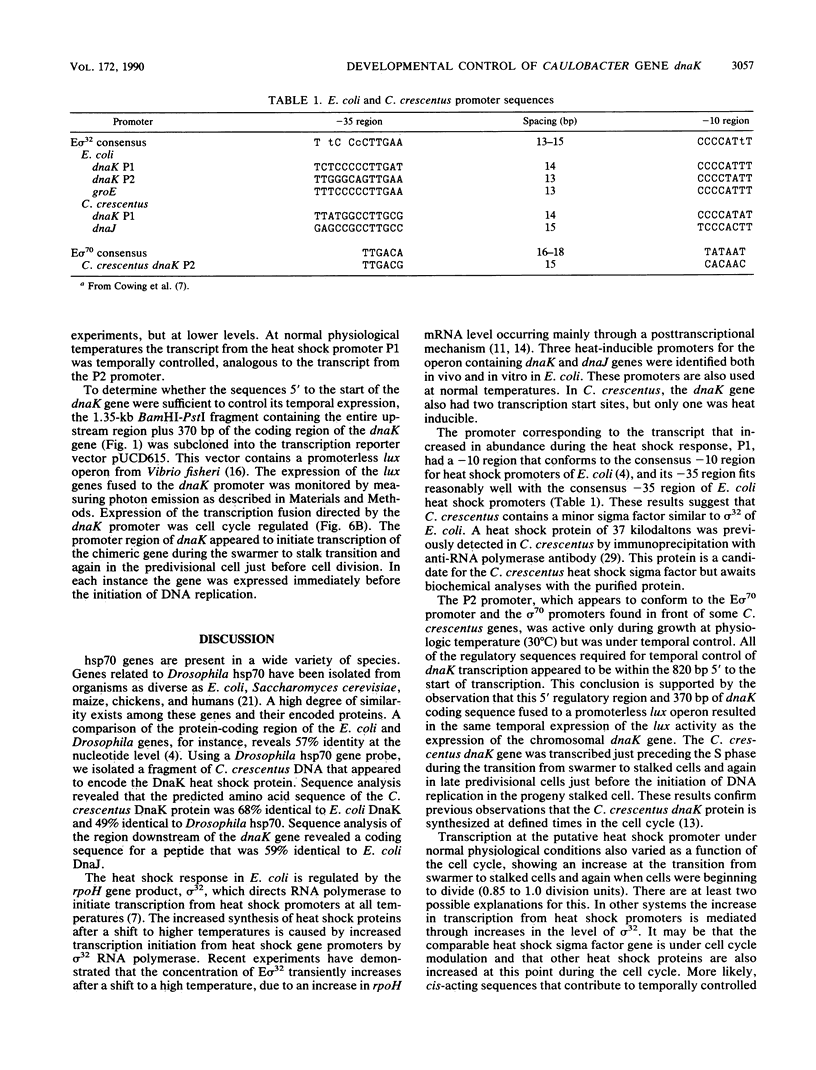
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnen S. T., Newton A. Chromosome replication during development in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Gerardot C. J. Use of pulsed-field-gradient gel electrophoresis to construct a physical map of the Caulobacter crescentus genome. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Vaughn V., Walter W. A., Neidhardt F. C., Gross C. A. Regulation of the promoters and transcripts of rpoH, the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M., Agabian N. Envelope-associated nucleoid from Caulobacter crescentus stalked and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.294-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes S. L., Juliani M. H., Maia J. C., Silva A. M. Heat shock protein synthesis during development in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):923–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.923-930.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen S. L., VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Levels of major proteins of Escherichia coli during growth at different temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):185–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.185-194.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka T., Rogowsky P. M., Kado C. I. Characterization of the virE locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1529–1536. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1529-1536.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Drosophila gene related to the major heat shock-induced gene is transcribed at normal temperatures and not induced by heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):525–529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Sequence of three copies of the gene for the major Drosophila heat shock induced protein and their flanking regions. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90430-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C., McMacken R. Initiation of DNA replication on single-stranded DNA templates catalyzed by purified replication proteins of bacteriophage lambda and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Morimoto R. I. Expression of human HSP70 during the synthetic phase of the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9517–9521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mues G. I., Munn T. Z., Raese J. D. A human gene family with sequence homology to Drosophila melanogaster Hsp70 heat shock genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):874–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki M., Tamura F., Nishimura S., Uchida H. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli dnaJ gene and purification of the gene product. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1778–1781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek K. H., Walker G. C. Escherichia coli dnaK null mutants are inviable at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.283-290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter S. H., Shapiro L. Asymmetric segregation of heat-shock proteins upon cell division in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Uchida H. Organization and expression of the dnaJ and dnaK genes of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 4;164(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00267592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmetterer G., Wolk C. P., Elhai J. Expression of luciferases from Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio fischeri in filamentous cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):411–414. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.411-414.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Uchida H., Sunshine M., Saito H., Georgopoulos C. P., Feiss M. Genetic analysis of two genes, dnaJ and dnaK, necessary for Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 4;164(1):9–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00267593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]