Abstract
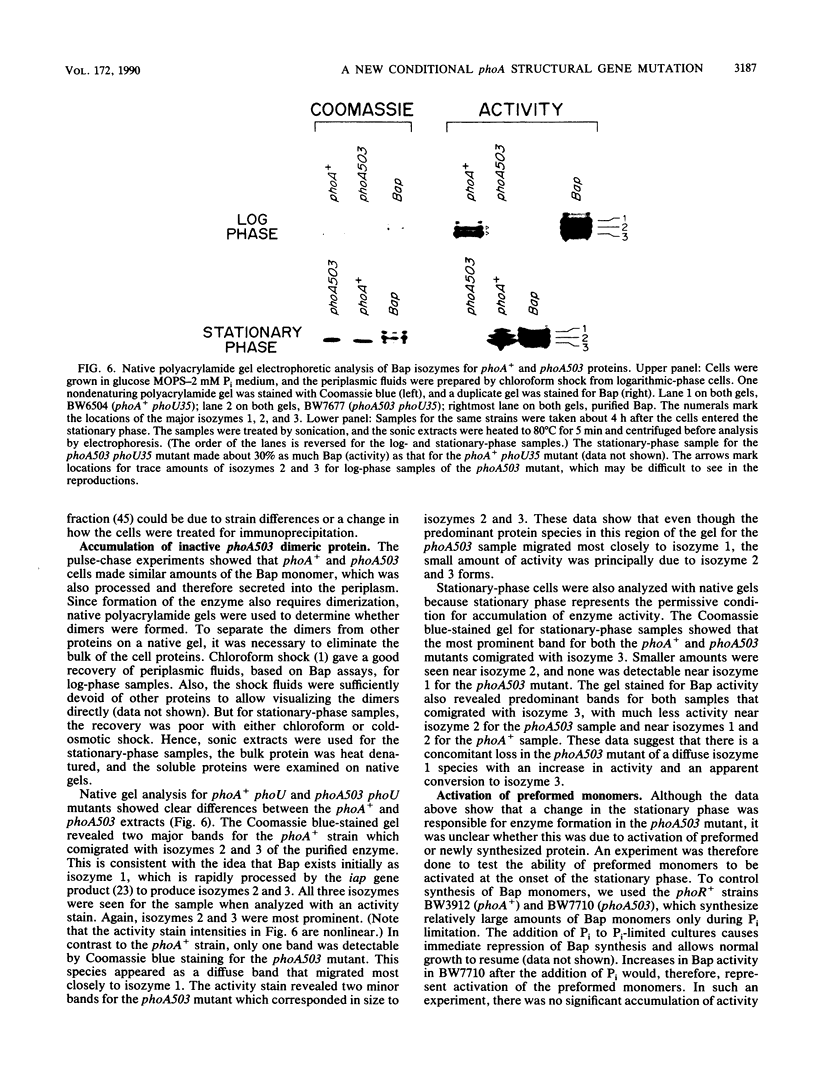
The phoA503 mutant was identified as a mutant that shows a novel phoA regulatory phenotype. The phoA503 allele dramatically reduces the synthesis of bacterial alkaline phosphatase activity during Pi starvation in an otherwise wild-type host and during the logarithmic growth phase in a phoR or phoU background. Near-normal amounts of enzyme activity are found in phoR phoA503 or phoU phoA503 mutants when starved for carbon, nitrogen, or sulfur or during the stationary phase, however. Marker rescue and DNA sequence analysis located the phoA503 mutation to the phoA coding region. It is a C-to-T transition that would cause a substitution of Val for Ala-22 in the mature protein. Transcriptional and translational lacZ fusions to both wild-type and mutant alleles demonstrated that phoA gene expression is unaltered. Also, the mutant protein was secreted and processed as efficiently as the wild type. Furthermore, the subunits appeared to dimerize and to be stable in the periplasm. But, greater than 98% of the dimers were inactive and found exclusively as isozyme 1. An activation of preformed phoA503 dimers occurred during the stationary phase with the concomitant conversion into isozymes 2 and 3. We propose that the phoA503 mutation affects a late stage in the formation of active enzyme. An unknown change when Pi is present during stationary-phase growth leads to formation of active dimers, which is responsible for this new conditional phenotype.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Prody C., Kustu S. Simple, rapid, and quantitative release of periplasmic proteins by chloroform. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1181–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1181-1183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. L., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Use of TnphoA to detect genes for exported proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of the plasmid-encoded gene for a periplasmic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1663–1669. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1663-1669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Determinants of membrane protein topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Kuang W. J., Chen E. Y. Nucleotide sequence of the alkaline phosphatase gene of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;44(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlebowski J. F., Armitage I. M., Coleman J. E. Allosteric interactions between metal ion and phosphate at the active sites of alkaline phosphatase as determined by 31P NMR and 113Cd NMR. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7053–7061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. E., Gettins P. Alkaline phosphatase, solution structure, and mechanism. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;55:381–452. doi: 10.1002/9780470123010.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove C. L., Gunsalus R. P. Regulation of the aroH operon of Escherichia coli by the tryptophan repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2158–2164. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2158-2164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Nelson H. C., Sauer R. T. Mutations in lambda repressor's amino-terminal domain: implications for protein stability and DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2676–2680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Wright A. Fusions of secreted proteins to alkaline phosphatase: an approach for studying protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5107–5111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Barnes W., Beckwith J. Signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):434–439. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.434-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino Y., Shinagawa H., Makino K., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the iap gene, responsible for alkaline phosphatase isozyme conversion in Escherichia coli, and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5429–5433. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5429-5433.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the phoB gene, the positive regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the phoR gene, a regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):549–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Hunt J. F., Beckwith J. Effects of signal sequence mutations on the kinetics of alkaline phosphatase export to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):160–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.160-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata A., Shinagawa H., Shima H. Alkaline phosphatase isozyme conversion by cell-free extract of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80765-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata A., Yamaguchi M., Izutani K., Amemura M. Escherichia coli mutants deficient in the production of alkaline phosphatase isozymes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):287–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.287-294.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafsdottir S., Wright C., Wright H. T., Chlebowski J. F. Crystals of a trypsin-modified alkaline phosphatase. Preliminary crystallographic characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):10002–10004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Sklar M. D., Gorini L. Ribosomal alterations controlling alkaline phosphatase isozymes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):291–299. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.291-299.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. H., Chlebowski J. F. Trypsin-modified alkaline phosphatase. Formation of apoenzyme monomer and hybrid dimer. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7557–7561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Andersen L. Multiple molecular forms of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 14;151(1):159–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb11886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Barrett K. The reversible dissociation of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Formation and reactivation of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4284–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Lin B. Genetic analysis of staphylococcal nuclease: identification of three intragenic "global" suppressors of nuclease-minus mutations. Genetics. 1985 Aug;110(4):539–555. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowadski J. M., Handschumacher M. D., Murthy H. M., Foster B. A., Wyckoff H. W. Refined structure of alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):417–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch K. L., Beckwith J. An Escherichia coli mutation preventing degradation of abnormal periplasmic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom M. S., Lory S. Mapping of export signals of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin with alkaline phosphatase fusions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3181–3188. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3181-3188.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Bacterial alkaline phosphatase clonal variation in some Escherichia coli K-12 phoR mutant strains. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1366–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1366-1371.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Boline J. A. Mapping and molecular cloning of the phn (psiD) locus for phosphonate utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1186–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1186-1196.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Chang B. D. The phoBR operon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5569–5574. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5569-5574.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Novel regulatory mutants of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):39–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Overlapping and separate controls on the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):283–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Sarthy A., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli pleiotropic mutant that reduces amounts of several periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):229–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.229-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Wilmes M. R., Young D. C. Control of bacterial alkaline phosphatase synthesis and variation in an Escherichia coli K-12 phoR mutant by adenyl cyclase, the cyclic AMP receptor protein, and the phoM operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1092–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1092-1102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff H. W., Handschumacher M., Murthy H. M., Sowadski J. M. The three dimensional structure of alkaline phosphatase from E. coli. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;55:453–480. doi: 10.1002/9780470123010.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




