Abstract
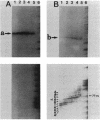
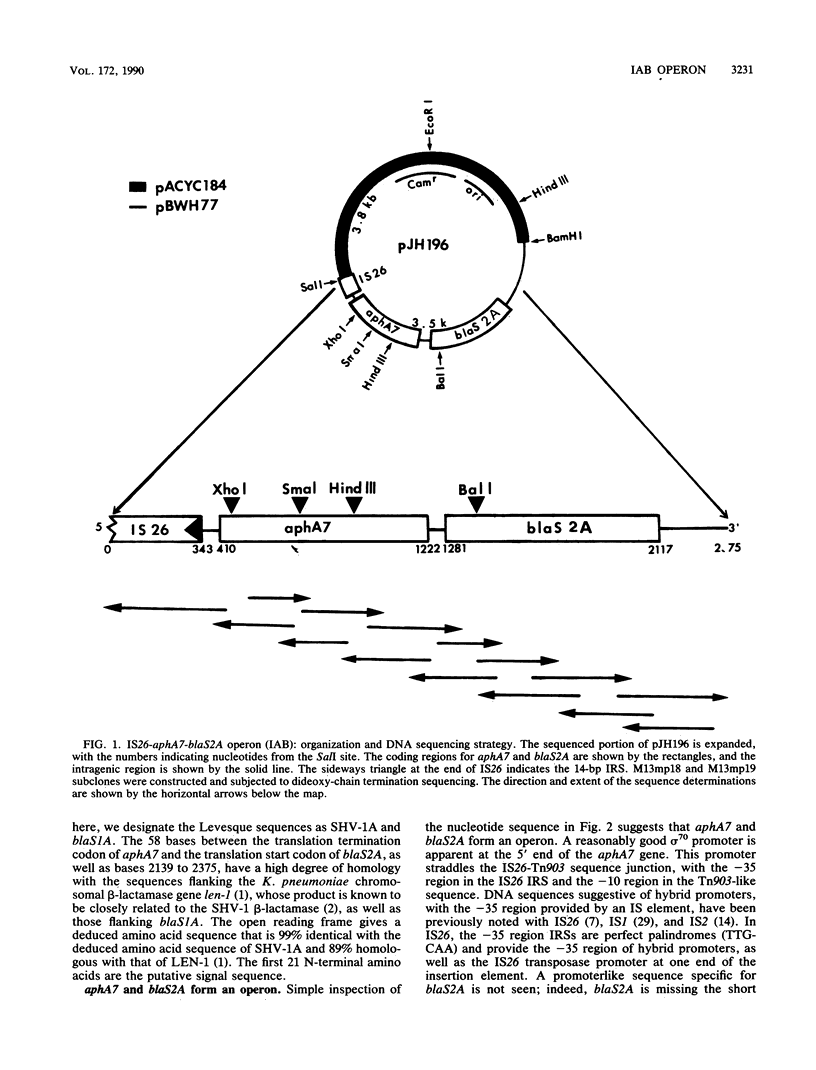
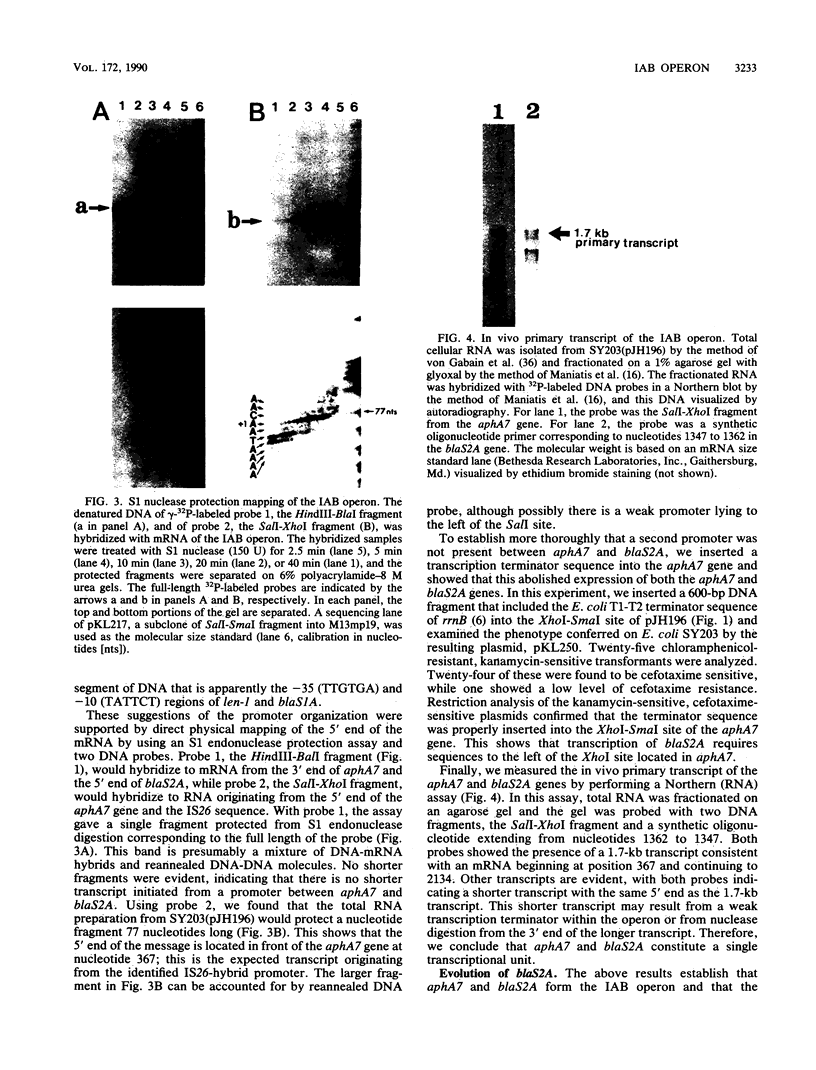
The plasmid pBWH77, originally found in an isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae, harbors a new antibiotic resistance operon containing two resistance genes transcribed from an IS26-hybrid promoter, as shown by nucleotide sequencing, mRNA mapping, and the effect of inserting a transcription terminator within the promoter-proximal gene. The nucleotide sequence of this region revealed that the operon (IAB) is made up of three sections that are closely related to previously described genetic elements. The -35 region of the promoter, together with the adjacent sequence, is identical to sequences of the IS26 element. One of the resistance genes, aphA7, which is located next to the hybrid promoter, confers assistance to neomycin and structurally related aminoglycosides. This aphA7 gene is highly homologous to aphA1 of Tn903, with five nucleotide differences. The second gene, blaS2A, encodes an evolved SHV-type beta-lactamase with a pI of 7.6 that confers resistance to the broad-spectrum cephalosporins cefotaxime and ceftizoxime. The deduced amino acid sequence of SHV-2A shows that amino acid 238 is a serine, a residue reported to confer resistance to cefotaxime. We discuss how the operon may have evolved by a combination of insertion sequence-mediated genetic rearrangements and acquisitive evolution. Using phylogenetic parsimony, we show that aphA7 in the IAB operon evolved from an ancestral form similar to aphA1 in Tn903 and that blaS2A evolved from an ancestral form similar to blaS1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa Y., Ohta M., Kido N., Fujii Y., Komatsu T., Kato N. Close evolutionary relationship between the chromosomally encoded beta-lactamase gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the TEM beta-lactamase gene mediated by R plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy M., Peduzzi J., Labia R. Complete amino acid sequence of p453-plasmid-mediated PIT-2 beta-lactamase (SHV-1). Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):73–79. doi: 10.1042/bj2510073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy M., Péduzzi J., Ben Yaghlane H., Labia R. Single amino acid substitution between SHV-1 beta-lactamase and cefotaxime-hydrolyzing SHV-2 enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bräu B., Pilz U., Piepersberg W. Genes for gentamicin-(3)-N-acetyltransferases III and IV: I. Nucleotide sequence of the AAC(3)-IV gene and possible involvement of an IS140 element in its expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00327434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. Transposable genetic elements and plasmid evolution. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):731–738. doi: 10.1038/263731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Sapienza C. Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):601–603. doi: 10.1038/284601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Ferré B., Goldstein F. W., Rizk N., Pinto-Schuster E., Acar J. F., Collatz E. SHV-5, a novel SHV-type beta-lactamase that hydrolyzes broad-spectrum cephalosporins and monobactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):951–956. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J. D., O'Brien T. F., Syvanen M. Functional and structural map of pLST1000: a multiresistance plasmid widely distributed in Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid. 1988 Sep;20(2):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F., Pinto M. E., Jiang H. Broad-spectrum, transmissible beta-lactamases. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 15;319(11):723–724. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809153191114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Normark S. Insertion of IS2 creates a novel ampC promoter in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):809–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Gomez-Lus R., Ortiz J. M., Garcia-Lobo J. M. Structure and mobilization of an ampicillin and gentamicin resistance determinant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1266–1270. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollet B., Clerget M., Meyer J., Iida S. Organization of the Tn6-related kanamycin resistance transposon Tn2680 carrying two copies of IS26 and an IS903 variant, IS903. B. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.55-60.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollet B., Iida S., Shepherd J., Arber W. Nucleotide sequence of IS26, a new prokaryotic mobile genetic element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6319–6330. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevers P., Saedler H. Transposable genetic elements as agents of gene instability and chromosomal rearrangements. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):109–115. doi: 10.1038/268109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobuta K., Tolmasky M. E., Crosa L. M., Crosa J. H. Sequencing and expression of the 6'-N-acetyltransferase gene of transposon Tn1331 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3769–3773. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3769-3773.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Paul G., Vedel G., Nevot P. Résistance plasmidique aux céphalosporines de 3e génération. Presse Med. 1988 Oct 26;17(37):1883–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Teter B., Chandler M., Galas D. J. Functional promoters created by the insertion of transposable element IS1. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reanney D. Extrachromosomal elements as possible agents of adaptation and development. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):552–590. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.552-590.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roupas A., Pitton J. S. R factor-mediated and chromosomal resistance to ampicillin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):186–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. B., Schilling J. W., Wilson A. C. Adaptive evolution in the stomach lysozymes of foregut fermenters. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):401–404. doi: 10.1038/330401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton C. J., Strike P. A pathway for the evolution of the plasmid NTP16 involving the novel kanamycin resistance transposon Tn4352. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Isenberg K. E., Wright A. F. Adaptive evolution of G-protein coupled receptor genes. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Jul;6(4):342–353. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]