Abstract
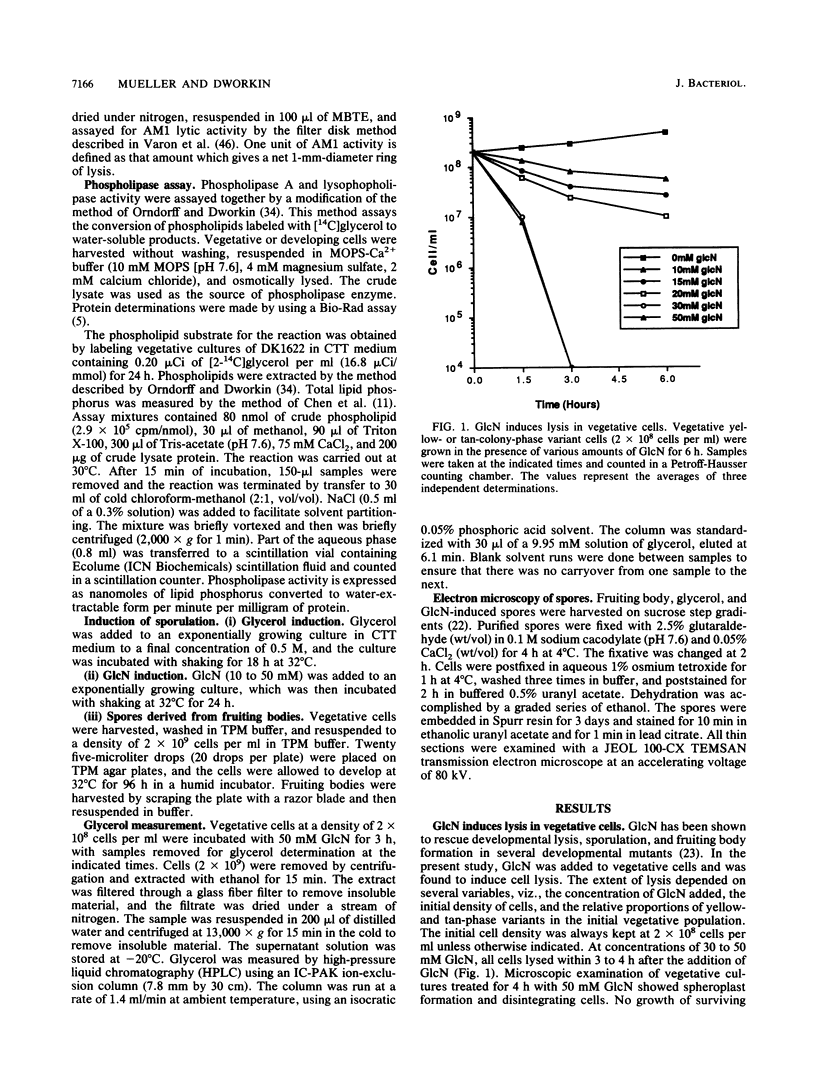
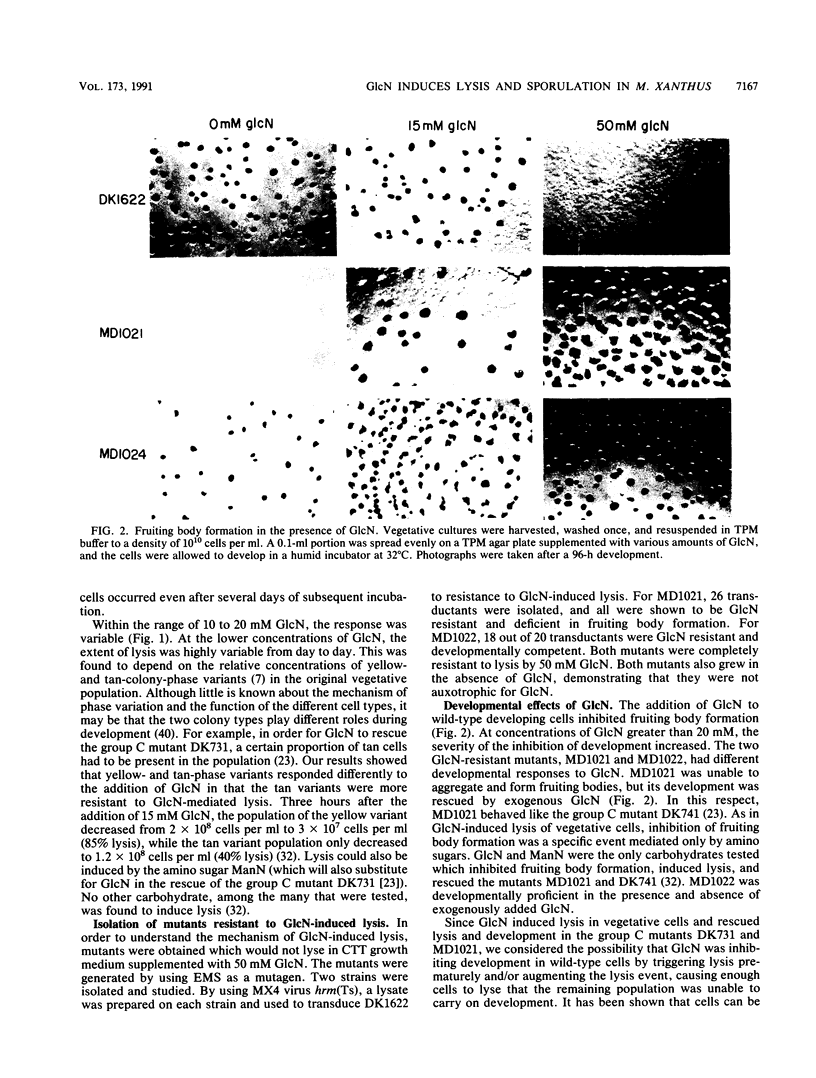
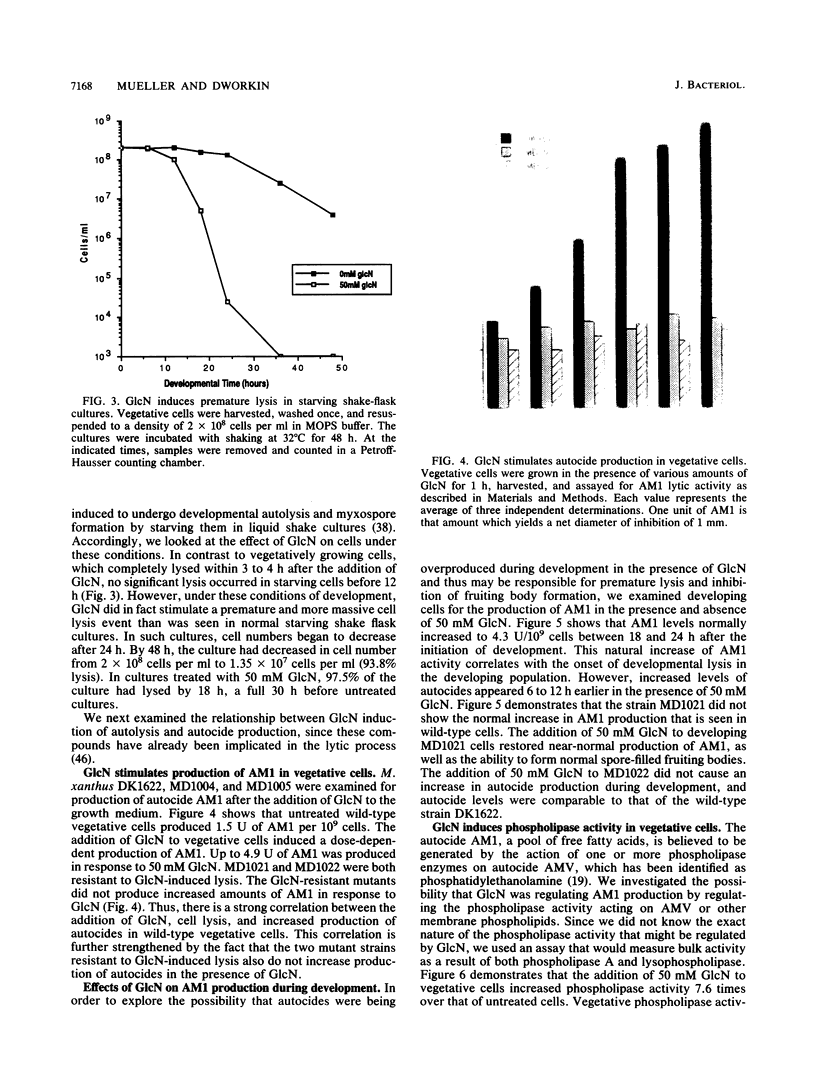
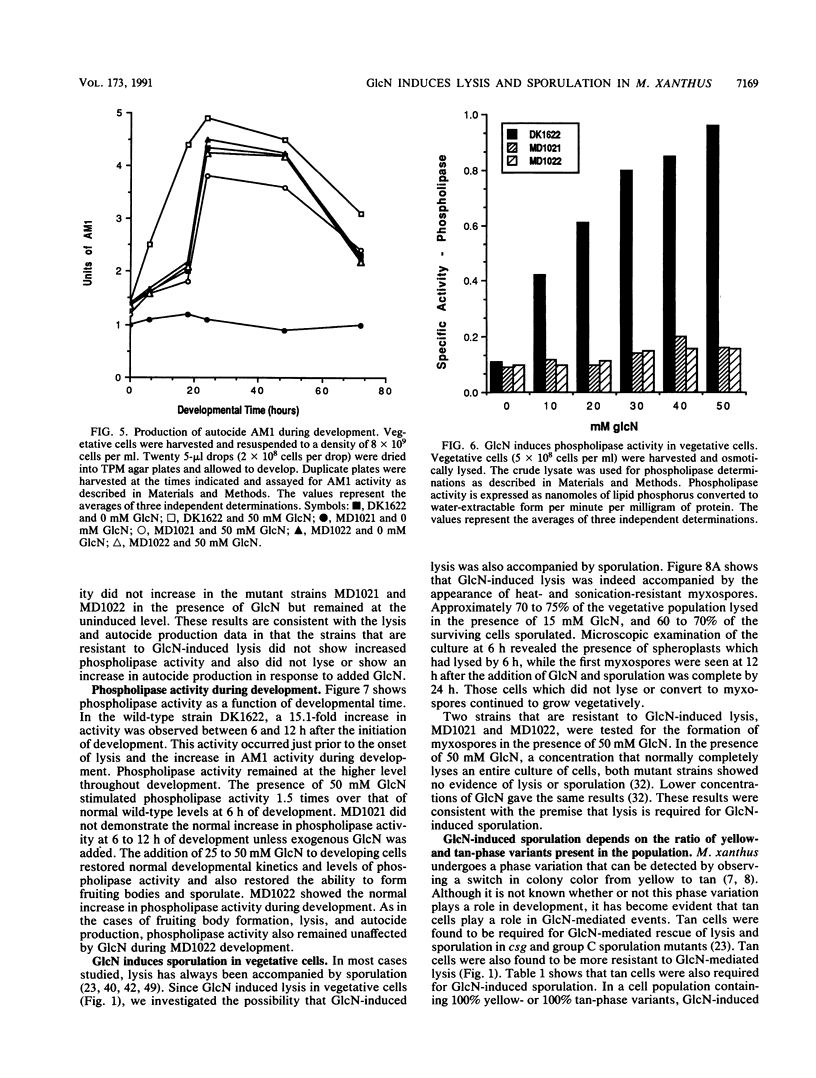
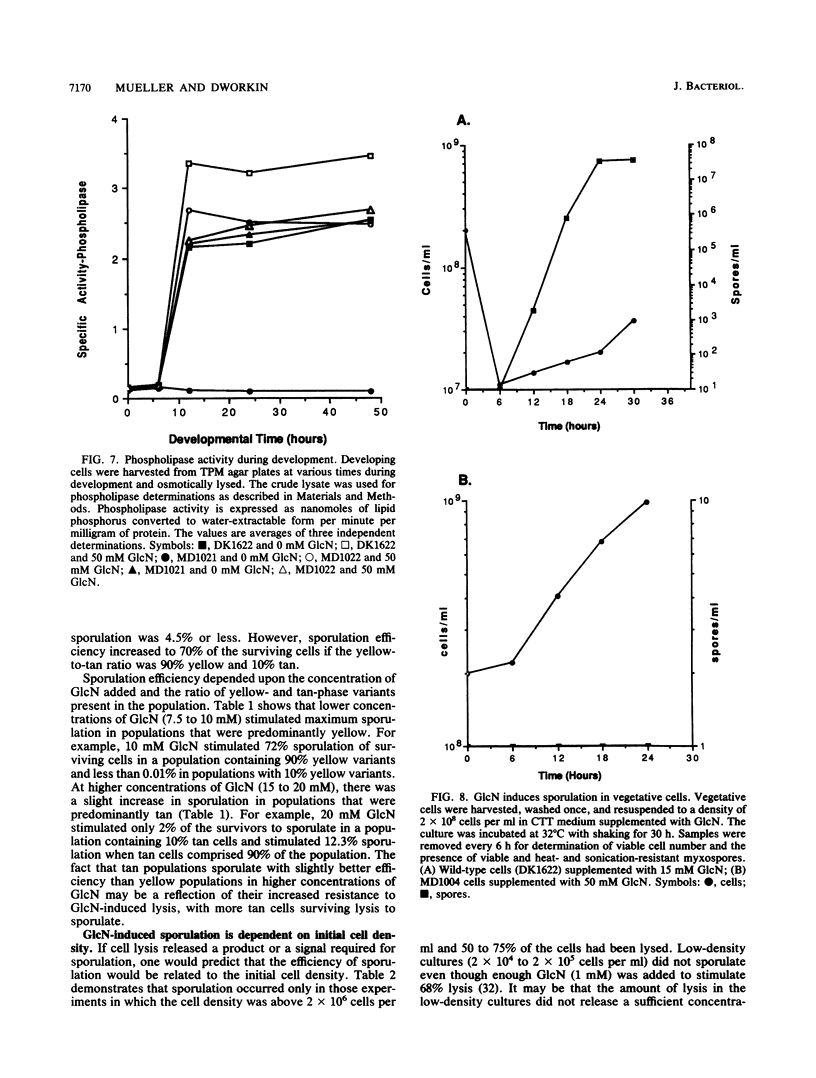
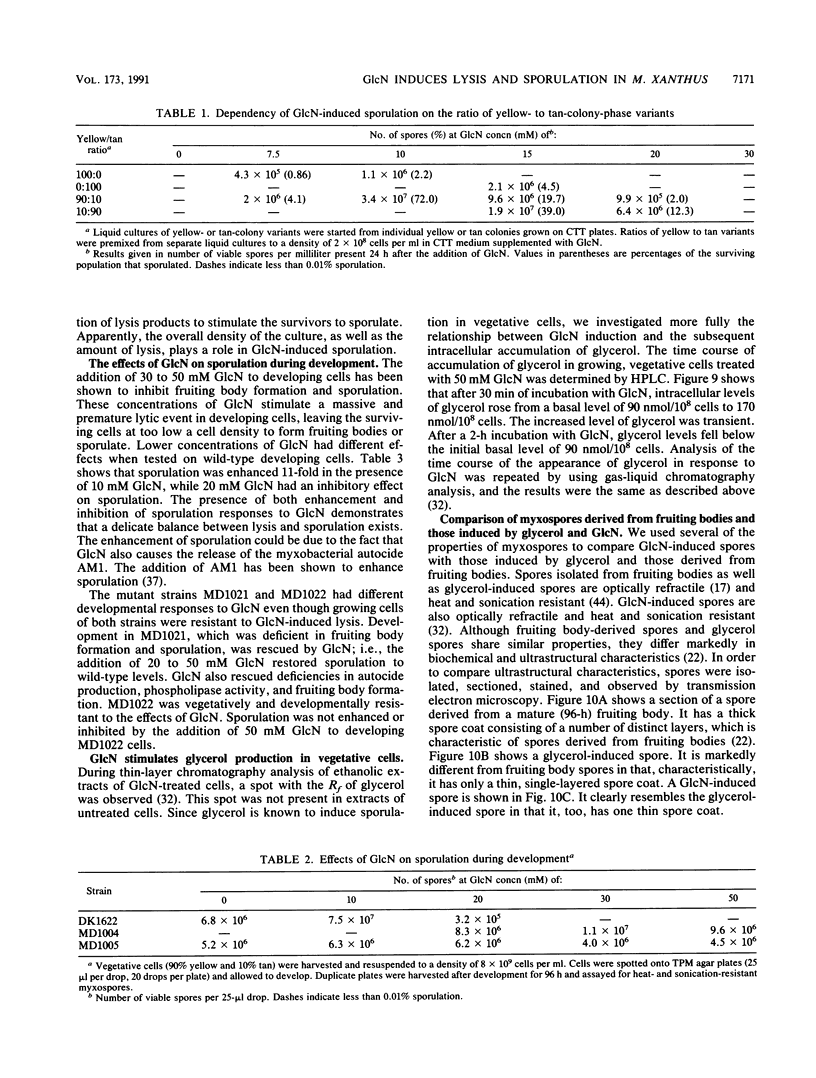
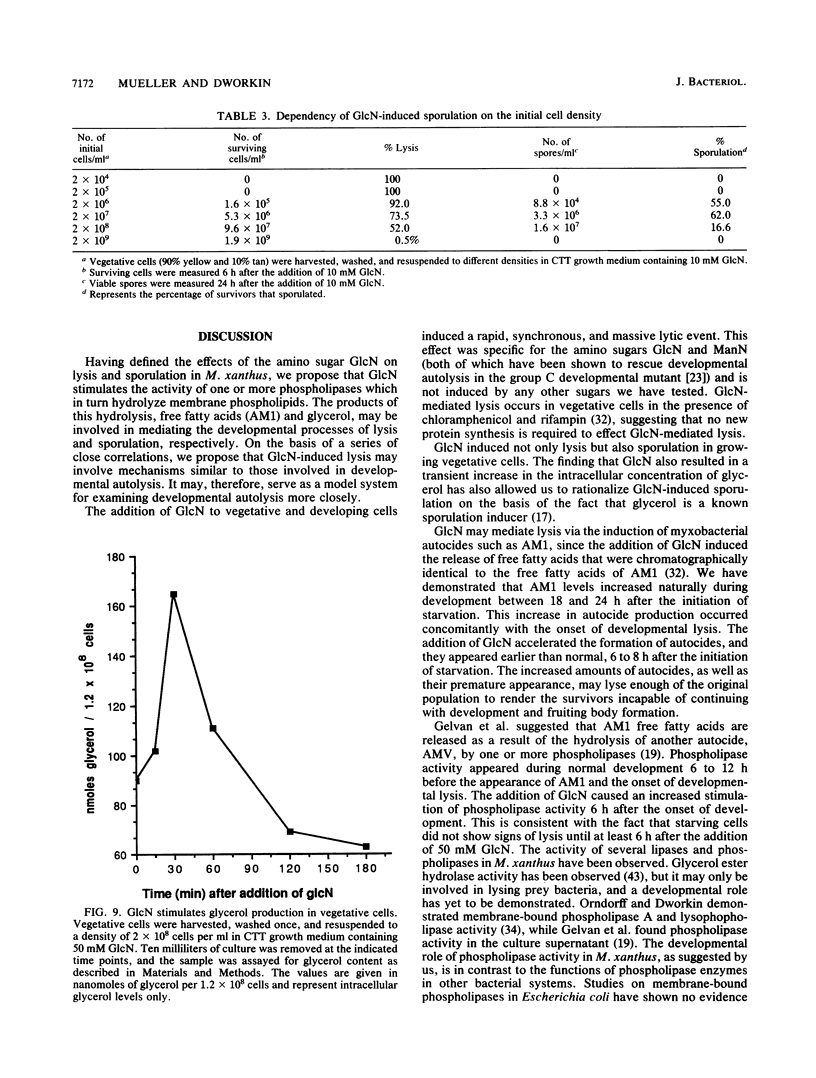
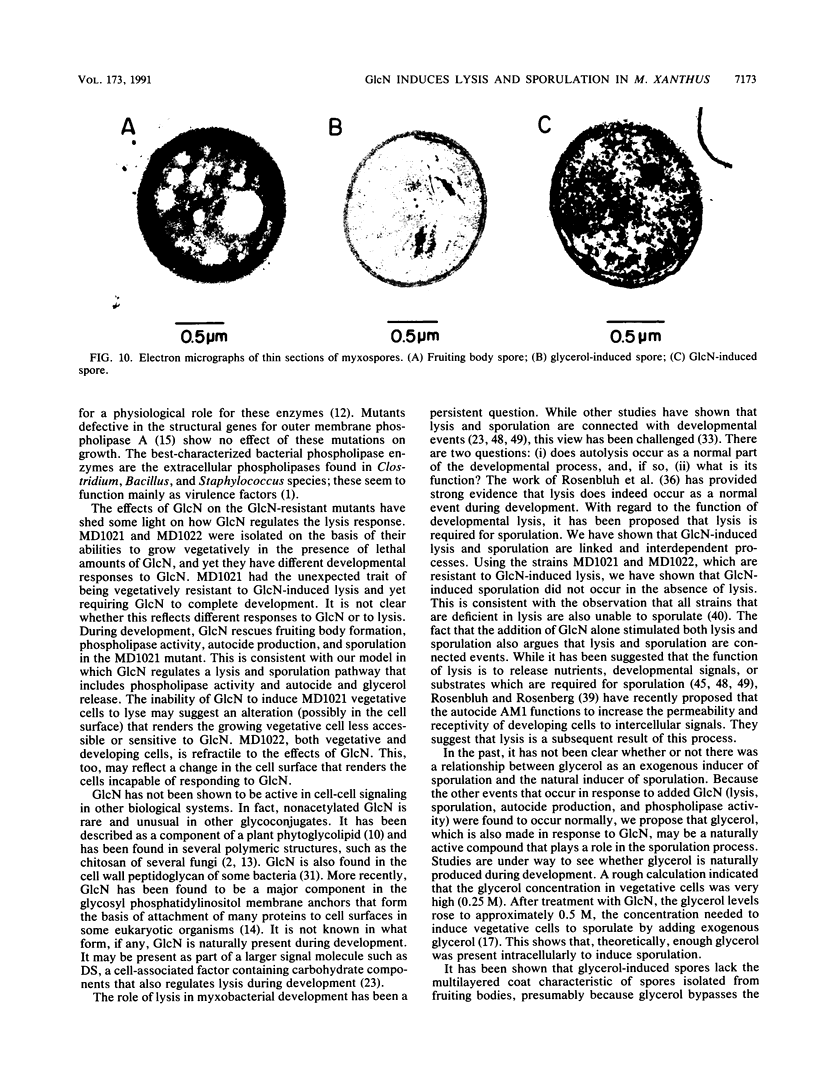
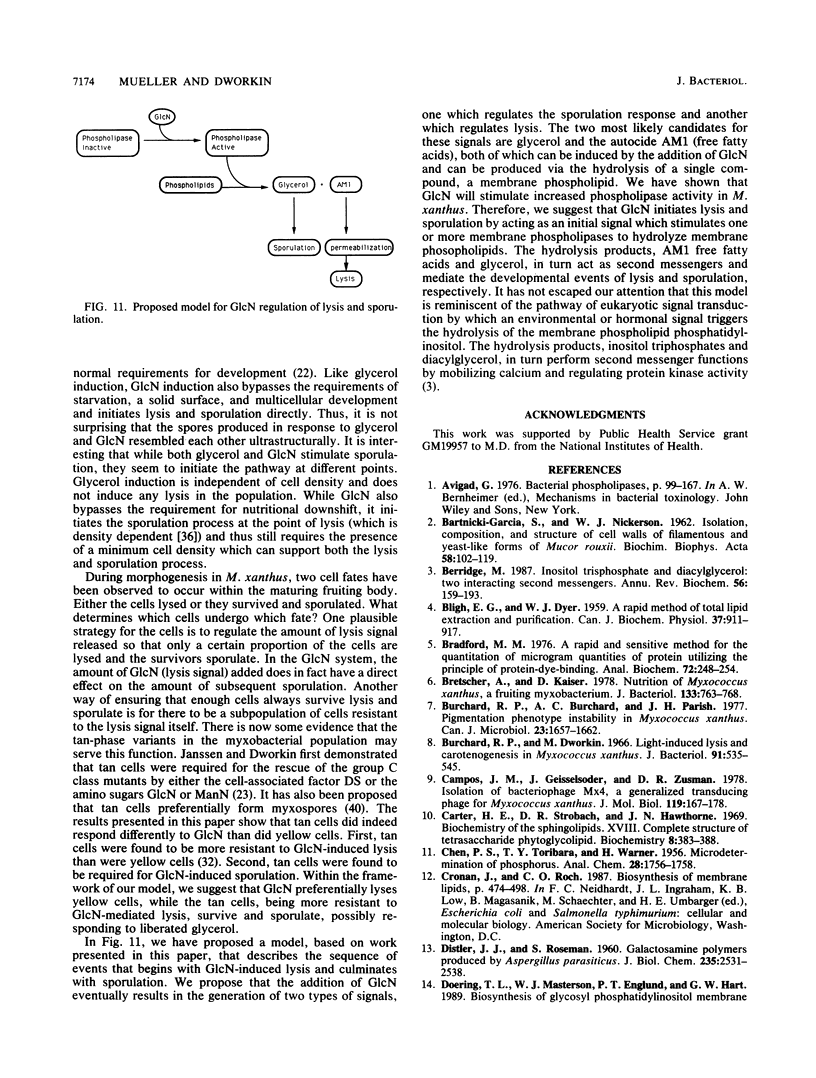
Glucosamine (GlcN), which has previously been shown to rescue fruiting body formation, lysis, and sporulation in a developmental mutant (G. Janssen and M. Dworkin, Dev. Biol. 112:194-202, 1985), induced lysis in vegetative and developing wild-type cells and inhibited fruiting body formation. It also resulted in a transient, intracellular increase in the concentration of glycerol, a known sporulation inducer, and sporulation of the surviving cells. Phospholipase activity, which was shown to be normally developmentally regulated, increased 7.6-fold after treatment of vegetative cells with 50 mM GlcN. Likewise, autocidal activity, which normally increased 18 to 24 h after the initiation of development, increased 20% when vegetative or developing cells were exposed to GlcN. Two mutants resistant to GlcN-induced lysis (MD1021 and MD1022) were isolated and showed neither an increase in autocide production nor an increase in phospholipase activity in response to added GlcN. MD1021 was developmentally deficient, and GlcN rescued fruiting body formation as well as phospholipase activity and autocide production. We propose that GlcN exerts its lytic effect by regulating the activity of phospholipase enzymes that release autocides, compounds that are believed to be responsible for developmental autolysis. GlcN-induced sporulation was found to depend on several factors: the initial cell density, the amount of lysis induced by GlcN, and the presence of tan-phase variants. An initial cell density of greater than 2 x 10(5) cells per ml was required to support GlcN-induced sporulation, and sporulation did not occur unless 50 to 75% of these cells had lysed. Mutants that were resistant to GlcN-induced lysis also did not sporulate in the presence of GlcN. The effects of GlcN on developing cells depended on the concentration of GlcN added; the addition of low concentrations of GlcN resulted in enhancement of sporulation, while higher concentrations resulted in the inhibition of sporulation. The ultrastructure of GlcN-induced spores resembled that of spores induced by the exogenous addition of glycerol, in contrast to spores isolated from mature fruiting bodies. A model by which GlcN may regulate both lysis and sporulation is presented.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTNICKI-GARCIA S., NICKERSON W. J. Isolation, composition, and structure of cell walls of filamentous and yeast-like forms of Mucor rouxii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 26;58:102–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90822-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Burchard A. C., Parish J. H. Pigmentation phenotype instability in Myxococcus xanthus. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1657–1662. doi: 10.1139/m77-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Dworkin M. Light-induced lysis and carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):535–545. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.535-545.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. E., Strobach D. R., Hawthorne J. N. Biochemistry of the sphingolipids. 18. Complete structure of tetrasaccharide phytoglycolipid. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):383–388. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISTLER J. J., ROSEMAN S. Galactosamine polymers produced by Aspergillus parasiticus. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2538–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., NIEDERPRUEM D. J. ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN VEGETATIVE CELLS AND MICROCYSTS OF MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:316–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.316-322.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. NUTRITIONAL REGU.ATION OF MORPHOGENESIS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:67–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.67-72.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Nojima S. Nature of Escherichia coli mutants deficient in detergent-resistant and/or detergent-sensitive phospholipase A. J Biochem. 1976 Dec;80(6):1247–1258. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Kaiser D. Cell interactions in myxobacterial growth and development. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):18–24. doi: 10.1126/science.3929384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelvan I., Varon M., Rosenberg E. Cell-density-dependent killing of Myxococcus xanthus by autocide AMV. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):844–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.844-848.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. G., Comai K. Rapid separation of neutral lipids, free fatty acids and polar lipids using prepacked silica Sep-Pak columns. Lipids. 1988 Dec;23(12):1146–1149. doi: 10.1007/BF02535281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Dworkin M. Cell-cell interactions in developmental lysis of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Social gliding is correlated with the presence of pili in Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D. C-factor: a cell-cell signaling protein required for fruiting body morphogenesis of M. xanthus. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90211-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Inouye S., Inouye M. Patterns of protein production in Myxococcus xanthus during spore formation induced by glycerol, dimethyl sulfoxide, and phenethyl alcohol. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1076–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1076-1082.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R., Kuner J., Hagen D., Manoil C., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions of Myxococcus xanthus: analysis of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1394–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1394-1404.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Reexamination of the role of autolysis in the development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4103–4112. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4103-4112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Nir R., Sahar E., Rosenberg E. Cell-density-dependent lysis and sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus in agarose microbeads. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4923–4929. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4923-4929.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Autocide AMI rescues development in dsg mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1513–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1513-1518.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus in liquid shake flask cultures. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4521–4524. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4521-4524.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Gill R. E., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus and the spoC locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Kaiser D. Murein components rescue developmental sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):462–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.462-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S. Z., Dworkin M. Resistance of vegetative cells and microcysts of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):883–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.883-887.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Cohen S., Rosenberg E. Autocides produced by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1146–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1146-1150.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Tietz A., Rosenberg E. Myxococcus xanthus autocide AMI. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):356–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.356-361.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Developmentally induced autolysis during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.798-802.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Morphogenesis and developmental interactions in myxobacteria. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):516–523. doi: 10.1126/science.806967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]