Abstract
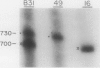
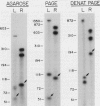
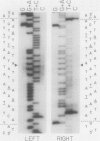
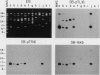
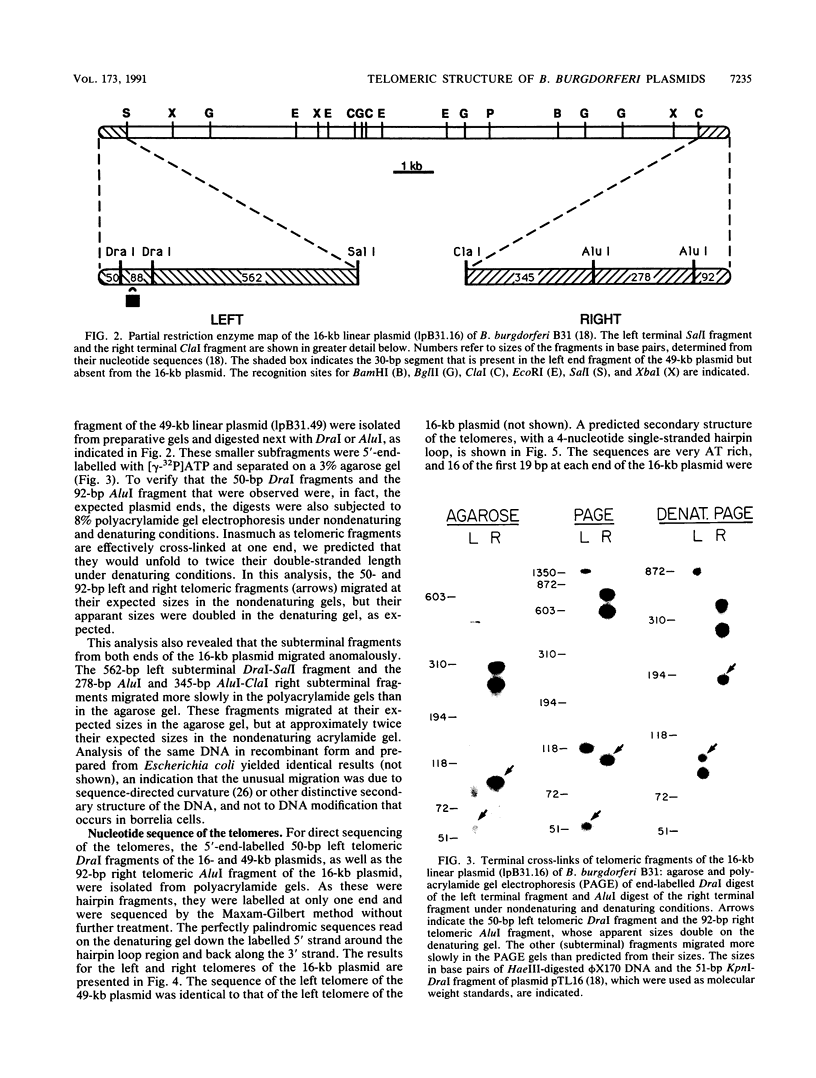
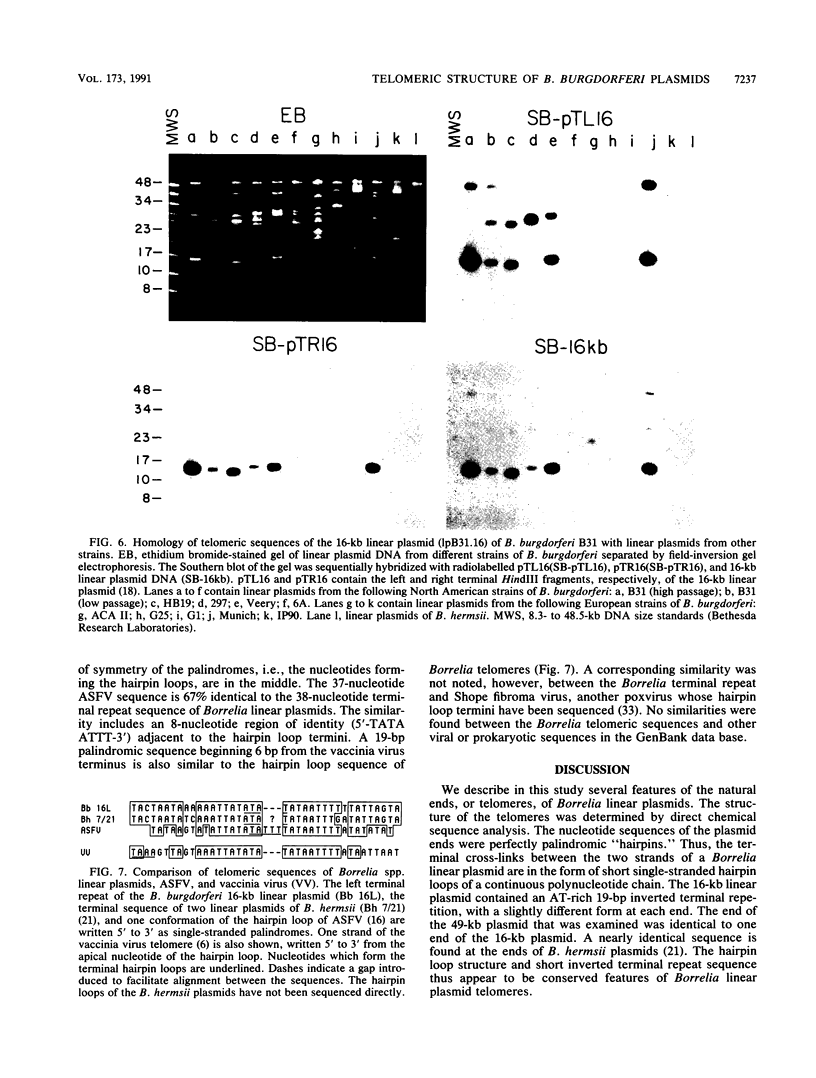
Spirochetes of the genus Borrelia have double-stranded linear plasmids with covalently closed ends. The physical nature of the terminal connections was determined for the 16-kb linear plasmid of the B31 strain of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi. Native telomeric fragments representing the left and right ends of this plasmid were isolated and subjected to Maxam-Gilbert sequence analysis. At the plasmid ends the two DNA strands formed an uninterrupted, perfectly palindromic, AT-rich sequence. This Borrelia linear plasmid consisted of a continuous polynucleotide chain that is fully base paired except for short single-stranded hairpin loops at each end. The left and right telomeres of the 16-kb plasmid were identical for 16 of the first 19 nucleotide positions and constituted an inverted terminal repeat with respect to each other. The left telomere of the 49-kb plasmid of strain B31 was identical to the corresponding telomere of the 16-kb plasmid. Different-sized plasmids of other strains of B. burgdorferi also contained sequences homologous to the left end of the 16-kb plasmid. When the borrelia telomeres were compared with telomeric sequences of other linear double-stranded DNA replicons, sequence similarities were noted with poxviruses and particularly with the iridovirus agent of African swine fever. The latter virus and a Borrelia sp. share the same tick vector. These findings suggest that the novel linear plasmids of Borrelia originated through a horizontal genetic transfer across kingdoms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F. Biology of Borrelia species. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):381–400. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.381-400.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Schrumpf M. E. Polymorphisms of major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Incompletely base-paired flip-flop terminal loops link the two DNA strands of the vaccinia virus genome into one uninterrupted polynucleotide chain. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Zaballos A., Salas M., Blanco L. Structural and functional relationships between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4219–4225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis T. H., Day A. A hairpin plastid genome in barley. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2769–2774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Isolation and properties of the DNA of African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):479–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escarmís C., Salas M. Nucleotide sequence at the termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1446–1450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F., Barbosa E., Moss B. Visualization of an inverted terminal repetition in vaccinia virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4863–4867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard J. M., Cummings D. J. Structure and replication of mitochondrial DNA from Paramecium aurelia. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):593–609. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Talavera A., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Hairpin loop structure of African swine fever virus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6835–6844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Bergström S., Barbour A. G. Cloning and sequence analysis of linear plasmid telomeres of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):811–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Nakamura K., Sakaguchi K. A linear DNA plasmid from Streptomyces rochei with an inverted terminal repetition of 614 base pairs. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):761–766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Hirai K., Gunge N., Hishinuma F. Hairpin plasmid--a novel linear DNA of perfect hairpin structure. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1881–1886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitten T., Barbour A. G. Juxtaposition of expressed variable antigen genes with a conserved telomere in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6077–6081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusby E., Fife K. H., Berns K. I. Nucleotide sequence of the inverted terminal repetition in adeno-associated virus DNA. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):402–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.402-409.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Freije J. M., Parra F., Méndez E., Viñuela E. Mapping and sequence of the gene coding for protein p72, the major capsid protein of African swine fever virus. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90432-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Efstratiadis A. Fractionation of low molecular weight DNA or RNA in polyacrylamide gels containing 98% formamide or 7 M urea. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):299–305. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Graves R. L., Rothe C. T. The white pock (mu) mutants of rabbit poxvirus. III. Terminal DNA sequence duplication and transposition in rabbit poxvirus. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowright W., Parker J., Peirce M. A. African swine fever virus in ticks (Ornithodoros moubata, murray) collected from animal burrows in Tanzania. Nature. 1969 Mar 15;221(5185):1071–1073. doi: 10.1038/2211071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic D., Edlinger C., Richaud C., Grimont F., Dufresne Y., Perolat P., Baranton G., Grimont P. A. Two genomic species in Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1990 May;141(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton C., DeLange A. M., McFadden G. Tumorigenic poxviruses: genomic organization and DNA sequence of the telomeric region of the Shope fibroma virus genome. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):20–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D. Origin of concatemeric T7 DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):197–201. doi: 10.1038/newbio239197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Vega I., Viñuela E., Blasco R. Genetic variation and multigene families in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90293-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]