Abstract
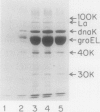
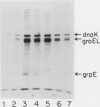
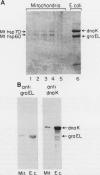
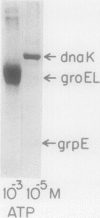
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) of the Hsp70 and GroEL families associate with a variety of cell proteins in vivo. However, the formation of such complexes has not been systematically studied. A 31-kDa fusion protein (CRAG), which contains 12 residues of cro repressor, truncated protein A, and 14 residues of beta-galactosidase, when expressed in Escherichia coli, was found in complexes with DnaK, GrpE, protease La, and GroEL. When an E. coli extract not containing CRAG was applied to an affinity column containing CRAG, DnaK, GroEL, and GrpE were selectively bound. These HSPs did not bind to a normal protein A column. DnaK, GrpE, and the fraction of GroEL could be eluted from the CRAG column with ATP but not with a nonhydrolyzable ATP analog. The ATP-dependent release of DnaK and GroEL also required Mg2+, but GrpE dissociated with ATP alone. The binding and release of DnaK and GroEL were independent events, but the binding of GrpE required DnaK. Inactivation of DnaJ, GrpE, and GroES did not affect the association or dissociation of DnaK or GroEL from CRAG. The DnaK and GrpE proteins could be eluted with 10(-6) M ATP, but 10(-4) M was required for GroEL release. This approach allows a one-step purification of these proteins from E. coli and also the isolation of the DnaK and GroEL homologs from yeast mitochondria. Competition experiments with oligopeptide fragments of CRAG showed that DnaK and GroEL interact with different sites on CRAG and that the cro-derived domain of CRAG contains the DnaK-binding site.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkareva E. S., Lissin N. M., Girshovich A. S. Transient association of newly synthesized unfolded proteins with the heat-shock GroEL protein. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):254–257. doi: 10.1038/336254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar G. N., Tilly K., Woolford C., Hendrix R., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the groES morphogenetic protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12414–12419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Kramer J., Shilling J., Werner-Washburne M., Holmes S., Kosic-Smithers J., Nicolet C. M. SSC1, an essential member of the yeast HSP70 multigene family, encodes a mitochondrial protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3000–3008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Böhni P. C., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase are located in the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13028–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Hemmingsen S. M. Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Chappell T. G., Rothman J. E. Peptide binding and release by proteins implicated as catalysts of protein assembly. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):385–390. doi: 10.1126/science.2756425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaitanaris G. A., Papavassiliou A. G., Rubock P., Silverstein S. J., Gottesman M. E. Renaturation of denatured lambda repressor requires heat shock proteins. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1013–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90066-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Casson L. P., Goldberg A. L. Heat shock regulatory gene htpR influences rates of protein degradation and expression of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6647–6651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goloubinoff P., Gatenby A. A., Lorimer G. H. GroE heat-shock proteins promote assembly of foreign prokaryotic ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oligomers in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):44–47. doi: 10.1038/337044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Purification and properties of groE, a host protein involved in bacteriophage assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C., Chandrasekhar G. N., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli DnaK and GrpE heat shock proteins interact both in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1590–1596. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1590-1596.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S., Lill R., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C., Bassford P. J., Jr, Kumamoto C. A., Wickner W. Three pure chaperone proteins of Escherichia coli--SecB, trigger factor and GroEL--form soluble complexes with precursor proteins in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2703–2709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. Role of the Escherichia coli DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins in the initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6632–6636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Osipiuk J., Zylicz M., Ang D., Skorko J., Georgopoulos C. Physical interactions between bacteriophage and Escherichia coli proteins required for initiation of lambda DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3022–3029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullin T. W., Hallberg R. L. A highly evolutionarily conserved mitochondrial protein is structurally related to the protein encoded by the Escherichia coli groEL gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):371–380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann J., Horwich A. L., Neupert W., Hartl F. U. Protein folding in mitochondria requires complex formation with hsp60 and ATP hydrolysis. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):125–130. doi: 10.1038/341125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek K. H., Walker G. C. Escherichia coli dnaK null mutants are inviable at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.283-290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. Heat-shock proteins. Coming in from the cold. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):776–777. doi: 10.1038/332776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Ang D., Liberek K., Georgopoulos C. Initiation of lambda DNA replication with purified host- and bacteriophage-encoded proteins: the role of the dnaK, dnaJ and grpE heat shock proteins. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1601–1608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein of Escherichia coli possesses an ATPase and autophosphorylating activity and is essential in an in vitro DNA replication system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6431–6435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]