Abstract
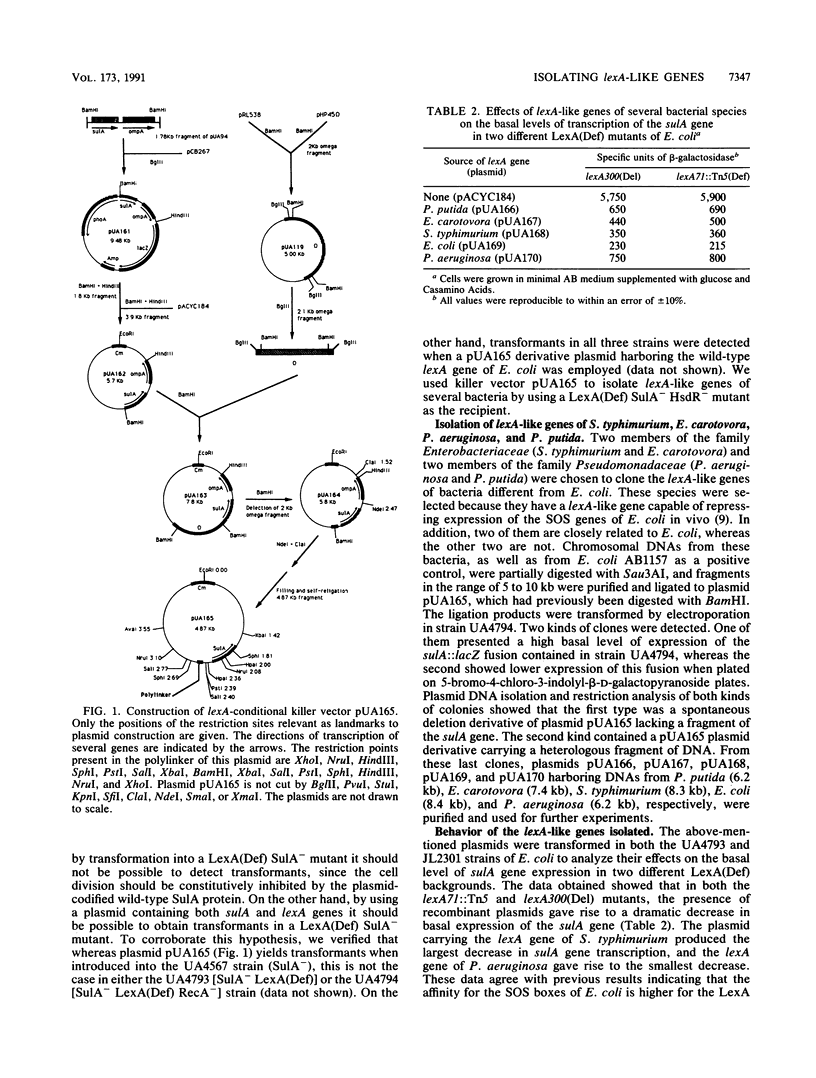
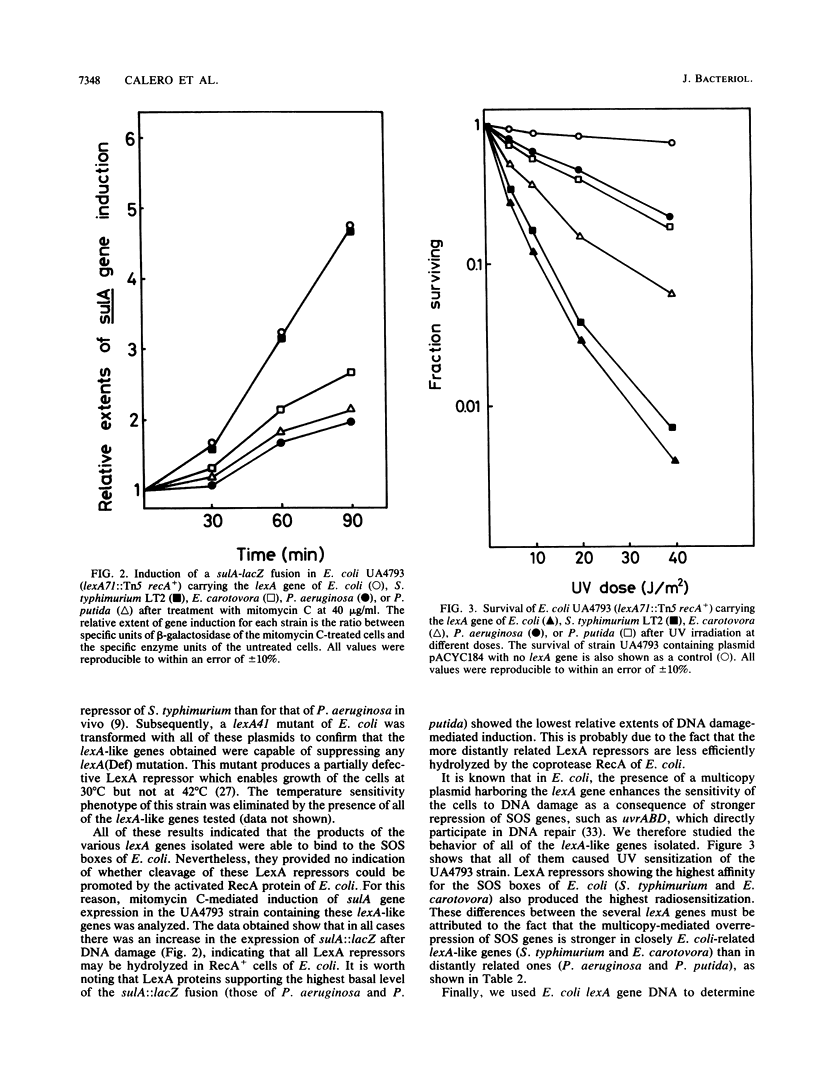
A system to isolate lexA-like genes of bacteria directly was developed. It is based upon the fact that the presence of a lexA(Def) mutation is lethal to SulA+ cells of Escherichia coli. This system is composed of a SulA- LexA(Def) HsdR- strain and a lexA-conditional killer vector (plasmid pUA165) carrying the wild-type sulA gene of E. coli and a polylinker in which foreign DNA may be inserted. By using this method, the lexA-like genes of Salmonella typhimurium, Erwinia carotovora, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and P. putida were cloned. We also found that the LexA repressor of S. typhimurium presented the highest affinity for the SOS boxes of E. coli in vivo, whereas the LexA protein of P. aeruginosa had the lowest. Likewise, all of these LexA repressors were cleaved by the activated RecA protein of E. coli after DNA damage. Furthermore, under high-stringency conditions, the lexA gene of E. coli hybridized with the lexA genes of S. typhimurium and E. carotovora but not with those of P. aeruginosa and P. putida.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbé J., Gibert I., Llagostera M., Guerrero R. DNA repair systems in the phototrophic bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):961–966. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Miller R. V. Effects of norfloxacin on DNA metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Helinski D. R. Isolation and characterization of the recA gene of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.311-316.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaregola S., D'Ari R., Huisman O. Quantitative evaluation of recA gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):430–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00334135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Roberts J. W. E. coli recA protein-directed cleavage of phage lambda repressor requires polynucleotide. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):26–30. doi: 10.1038/283026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai J., Wolk C. P. A versatile class of positive-selection vectors based on the nonviability of palindrome-containing plasmids that allows cloning into long polylinkers. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):119–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez de Henestrosa A. R., Calero S., Barbé J. Expression of the recA gene of Escherichia coli in several species of gram-negative bacteria. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;226(3):503–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00260664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibert I., Barbé J. Cyclic AMP stimulates transcription of the structural gene of the outer-membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 15;56(3):307–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb03197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibert I., Calero S., Barbé J. Measurement of in vivo expression of nrdA and nrdB genes of Escherichia coli by using lacZ gene fusions. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Feb;220(3):400–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00391745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. A., Little J. W. Allele replacement in Escherichia coli by use of a selectable marker for resistance to spectinomycin: replacement of the lexA gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5913–5915. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5913-5915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R., Gottesman S. Cell-division control in Escherichia coli: specific induction of the SOS function SfiA protein is sufficient to block septation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener S. L., McNamee K. P., McEntee K. Cloning and characterization of recA genes froM Proteus vulgaris, Erwinia carotovora, Shigella flexneri, and Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.153-160.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Molecular cloning and characterization of the recA gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):568–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.568-572.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman H. B., Witkin E. M. DNA degradation, UV sensitivity and SOS-mediated mutagenesis in strains of Escherichia coli deficient in single-strand DNA binding protein: effects of mutations and treatments that alter levels of Exonuclease V or recA protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(1):92–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00330329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. Autodigestion of lexA and phage lambda repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1375–1379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Edmiston S. H., Pacelli L. Z., Mount D. W. Cleavage of the Escherichia coli lexA protein by the recA protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall J. O., Witkin E. M., Kogoma T., Roegner-Maniscalco V. Constitutive expression of the SOS response in recA718 mutants of Escherichia coli requires amplification of RecA718 protein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):728–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.728-734.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Kokjohn T. A. General microbiology of recA: environmental and evolutionary significance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D., Charbit A. High efficiency transformation of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella typhi by electroporation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):156–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00315809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. R., Mount D. W. Differential repression of SOS genes by unstable lexA41 (tsl-1) protein causes a "split-phenotype" in Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):27–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90623-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley N. B., Reeves P. R. Chloramphenicol resistance cloning vector based on pUC9. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):54–57. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles B., Defais M. Signal of induction of recA protein in E. coli. Mutat Res. 1984 Feb;131(2):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Beck C. F. New expression vectors for identifying and testing signal structures for initiation and termination of transcription. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:452–461. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Goodwin P. A. Interspecies regulation of the SOS response by the E. coli lexA+ gene. Mutat Res. 1985 May;145(3):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman E. S., Peterson P. Plaque color method for rapid isolation of novel recA mutants of Escherichia coli K-12: new classes of protease-constitutive recA mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):677–687. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.677-687.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K. RecA protein-dependent proteolysis of bacteriophage lambda repressor Characterization of the reaction and stimulation by DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10883–10888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ysern P., Clerch B., Castańo M., Gibert I., Barbé J., Llagostera M. Induction of SOS genes in Escherichia coli and mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium by fluoroquinolones. Mutagenesis. 1990 Jan;5(1):63–66. doi: 10.1093/mutage/5.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink R. T., Engwall J. K., McEvoy J. L., Chatterjee A. K. recA is required in the induction of pectin lyase and carotovoricin in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):390–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.390-396.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



