Abstract
Atypical visceral leishmaniasis is increasingly reported in immunocompromised patients, including patients with AIDS. A case of visceral leishmaniasis in an HIV-infected Brazilian patient with pulmonary and peritoneal involvement is reported. Histological evaluation of pleural fluid and ascites aspirate revealed macrophages with intracellular Leishmania. Polymerase chain reaction analysis was positive for Leishmania in the pleural and ascitic fluid with use of primers specific for Leishmania chagasi. In addition to classical methods for diagnosing leishmaniasis, such as microscopy and culture, polymerase chain reaction detection and identification of Leishmania species in pleural effusions and ascites are important diagnostic tools that should be considered by clinicians evaluating HIV-infected patients from endemic areas of visceral leishmaniasis. The authors review the clinical manifestations, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of visceral leishmaniasis in immunocompetent and HIV-infected patients.
Key Words: Diagnosis, HIV, Leishmania, PCR, Polymerase chain reaction, Treatment
Leishmania and HIV coinfection is considered to be an emerging disease and threat in several countries in accordance with the World Health Organization data. The global experience, mainly in European countries, is marked by an increasing number of coinfection cases in this decade, leading to changes in the epidemiology, presentation and clinical outcome of visceral leishmaniasis. The disease spectrum of leishmaniasis ranges from self-healing cutaneous lesions to fatal systemic disease, depending on the species of the parasite and the host immune response. Visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar), which is caused by Leishmania donovani, Leishmania chagasi and Leishmania infantum is the most serious form of leishmaniasis (1,2). Cell-mediated immune mechanisms are responsible for controlling leishmanial infections. The clinical manifestations of leishmaniasis depend on complex interactions resulting from the parasite's invasiveness, tropism and pathogenicity, and the host's genetically determined immune responses. Lower respiratory tract and peritoneal involvement in immunocompetent individuals are rare (3,4), but it has been described in HIV-infected patients (5-9). The present study reports an atypical case of visceral leishmaniasis with pulmonary and peritoneal involvement in a Brazilian patient with AIDS diagnosed by microscopy and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of Leishmania chagasi in the pleural and ascitic fluid. The recent diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of visceral leishmaniasis are also reviewed.
CASE PRESENTATION
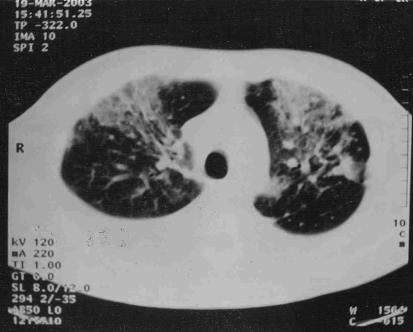
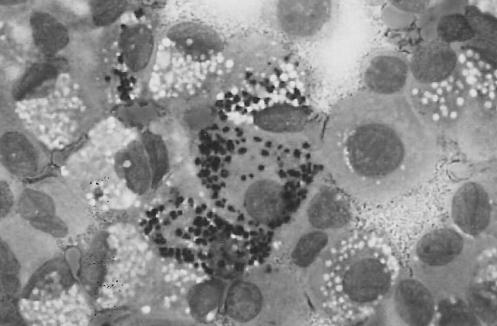
A 35-year-old HIV-positive Brazilian man was admitted with a three-month history of fever, night sweats and weight loss. The patient lived in southern Brazil, and had no travel history, other than a trip to a large city in the northeastern area of Brazil 15 years ago. He was presumptively treated for tuberculosis with rifampin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide without resolution of his symptoms. On admission, physical examination revealed hepatosplenomegaly and ascites. His CD4 count was 1.08x109/L , and he was not currently receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy because of recent episodes of nausea and vomiting. Laboratory studies included: hemoglobin, 5.03 mmol/L; leukocytes, 3.6x109/L; platelets, 13x109/L; and creatinine, 79.5µmol/L. A chest x-ray and thoracic computed tomography showed a right pleural effusion with diffuse bilateral lung infiltration (Figure 1). Microscopy of pleural effusion and ascites aspirate revealed the presence of numerous macrophages containing many intracellular amastigotes consistent with Leishmania species (Figure 2). PCR analysis was positive for Leishmania in the pleural fluid and ascites with use of primers specific for L chagasi (10-11).
Figure 1.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography images showing bilateral infiltrates with pleural effusion
Figure 2.
Pleural fluid macrophage containing many intracellular amastigotes consistent with Leishmania species (Wright-Giemsa stain, original magnification x 100)
Intravenous amphotericin B (0.8 mg/kg) was initiated. By 20 days of therapy, the fevers and night sweats had disappeared, and the liver and spleen decreased in size. After completing 30 days of amphotericin B treatment, suppressive therapy with itraconazole (100 mg/day) along with highly active antiretroviral therapy was started. He showed no evidence of relapse during a one-year follow-up period.
DISCUSSION
Visceral leishmaniasis is endemic in southern Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia and areas of China and Africa as well as Latin America (1). In Latin America, L chagasi produces sporadic cases in scattered rural areas, but relatively large outbreaks in major cities in northeastern Brazil (12). Reactivation of latent disease seems to be the mode of acquisition of visceral leishmaniasis in patients with AIDS who have lived in endemic areas (13,14).
The clinical manifestations of visceral leishmaniasis are similar throughout the world (1). The incubation period varies, ranging anywhere between three to eight months. Large numbers of amastigote-infected mononuclear phagocytes in the liver and spleen result in progressive hypertrophy. The onset of symptoms may be gradual or sudden. In subacute or chronic cases, there is an insidious onset of abdominal enlargement due to hepatosplenomegaly, fever, weakness, loss of appetite, pallor and weight loss (1,2). The symptoms can persist for weeks to several months before patients come to medical attention; in acute cases, there is an abrupt onset of high fever and chills, sometimes with a periodicity that mimics malaria.
Visceral leishmaniasis may be the first opportunistic infection in persons with HIV, or it may complicate the terminal stages of AIDS (3,12,13). The clinical features of HIV-related visceral leishmaniasis are similar to those seen in individuals without HIV. Because of the lack of cellular immunity in patients with AIDS, especially with advanced disease, patients may experience severe and atypical forms of visceral leishmaniasis (12). The majority of HIV-infected persons with visceral leishmaniasis present with fever, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly, but atypical presentations are common. The disease may disseminate to the skin and other organs, and presentation outside the reticuloendothelial system may mislead the clinician. Skin manifestations in visceral leishmaniasis are frequent. Kala-azar means 'black sickness' and refers to the earthgray skin colour that is common in infected individuals, especially in India. Diffuse nodular skin lesions may also occur. Mucosal lesions, oral and nasal ulcers may accompany systemic illness, particularly in patients in Sudan. Splenomegaly may be absent, while gastrointestinal symptoms are among the most frequent complaints in individuals infected with HIV. Involvement of the oral mucosa, esophagus, stomach, peritoneum and small intestine are reported as well (3,13,14). Another symptom previously reported among HIV-infected patients is the lower respiratory tract involvement in immunocompromised patients (3-8).
A definitive diagnosis depends on the demonstration of Leishmania amastigotes in tissue or the isolation of promastigotes in culture. Splenic puncture is the most sensitive diagnostic method, especially in HIV-infected patients, although hemorrhaging is a risk (1). Bone marrow aspiration is less sensitive, but safer. Liver biopsy is less likely to be diagnostic than splenic puncture or bone marrow biopsy, and carries the risk of hemorrhaging. Lymph node aspiration may be diagnostic when enlarged nodes are present. Amastigotes have been identified in macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, pleural effusions, or biopsy specimens of the oropharynx, stomach or intestine. Detection of Leishmania amastigotes is rare in these sites, but has been reported previously in other immunocompromised patients (5,6). However, most HIV patients with visceral leishmaniasis and lung involvement had amastigotes in macrophages from bronchoalveolar lavage specimens and lung and peritoneal tissue biopsy. An unusual feature of our patient was the presence of pulmonary infiltrates with pleural effusion and ascites, which contained a large number of intracellular amastigotes. Cultures of aspirates from tissues such as spleen, bone marrow, liver, lymph node and blood, especially in patients with concurrent HIV, may be positive for promastigote forms. These can be identified in cultures within a few days, but several weeks may be required for the concentration to reach the level of detection. Specimens can be inoculated in Noxy, McNeal and Nicolle media (15).
Antileishmanial antibodies are usually present in high titre among immunocompetent patients with visceral leishmaniasis. These antibodies are frequently absent or of low titre in patients with concurrent HIV infection (16). Cross-reacting antibodies may be present in patients with leprosy, Chagas's disease, malaria, schistosomiasis, toxoplasmosis or cutaneous leishmaniasis (17). The leishmanin (Montenegro) skin test result is useful for epidemiology studies but has no value for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis (18). The skin test is positive in most persons in whom infection spontaneously resolves or who have undergone successful chemotherapy.
Initial PCR techniques required tissue samples, had limited sensitivity and were time consuming. More recently introduced methods detect the highly variable regions of the kinetoplast DNA mini-circles and have improved sensitivity, specificity and speed of diagnosis (10). The nested PCR assay is probably the best noninvasive test for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis, with a sensitivity of 95% in peripheral blood and 100% in bone marrow. Nested PCR has also been useful for monitoring the efficacy of treatment. Post-treatment relapse was identified five months earlier using nested PCR than previous diagnostic methods (11).
Organic salts of pentavalent antimony have been the cornerstone of treatment for all forms of leishmaniasis for more than 60 years. Two major pentavalent antimonials include sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam, GlaxoWellcome, United Kingdom) and meglumine (Glucantime, Rhodia, Brazil) (19). The drugs are given intravenously or intramuscularly and are of equal efficacy when used in equivalent doses. The recommended regimen consists of once-daily injections of the fulldose drug (20 mg/kg) for 30 days. Disadvantages of antimonials include the parenteral mode of administration, the long duration of therapy and adverse reactions including fatigue, myalagias, electrocardiography abnormalities, elevated liver enzymes and chemical pancreatitis. Adjunctive interferon gamma therapy may accelerate or improve the response to antimonial therapy in some difficult cases (20). However, the high cost of interferon gamma precludes its widespread use in the developing world.
Many oral agents have been tested as single or combination therapy of visceral leishmaniasis (21). Ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, terbinafine and metronidazole were found to be ineffective. Miltefosine blocks the proliferation of Leishmania and alters phospholipid and sterol composition. At 100 mg/day (2.5 mg/kg/day), for 21 to 28 days, it was effective for both untreated and antimony-resistant patients with visceral leishmaniasis (22). Although conventional amphotericin B is an alternative first-line treatment, amphotericin B lipid formulation has a better tolerability and can be used for short-course treatment (23,24). However, there are no reports of large case series of experience with lipid amphotericin B in these patients.
At present, there is no role for primary prophylaxis against Leishmania infection in HIV-infected patients. The best accepted approach for secondary prophylaxis is the monthly administration of 20 mg/kg sodium stibogluconate intravenously or intramuscularly. Aternatives include intravenously pentamidine every three or four weeks, liposomal amphotericin B every two weeks, or oral allopurinol and itraconazole (9,25). Leishmania secondary prophylaxis is withdrawn with CD4 of counts 2x109/L, because relapses are not encountered with higher CD4 counts (26). Despite reports of high rates of failure or relapse in HIV patients with visceral leishmaniasis, our patient had an excellent clinical response to amphotericin B and suppressive doses of itraconazole.
CONCLUSION
Because the incidence of HIV increases in areas in which Leishmania species are endemic, visceral leishmaniasis is being recognized more frequently as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS. Therefore, the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis should be considered in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients living or returning from endemic areas with systemic illness and multiorgan involvement. In addition to classical methods for diagnosing leishmaniasis, such as microscopy and culture, PCR detection and identification of Leishmania species in body fluids are important diagnostic tools that should be considered by clinicians evaluating patients from endemic areas of visceral leishmaniasis.
References
- 1.Berman JD. Human leishmaniasis: Clinical, diagnostic and chemotherapeutic developments in the last 10 years.Clin Infect Dis 1997;24:684-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pearson RD, Souza AQ. Clinical spectrum of leishmaniasis.Clin Infect Dis 1996;22:1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alvar J, Canavate C, Gutierrez-Solar B, et al. Leishmania and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection: The first 10 years.Clin Microbiol Rev 1997;10:298-319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Duarte MI, da Matta VL, Corbett CE, Laurenti MD, Chebabo R, Goto H. Interstitial pneumonitis in human visceral leishmaniasis.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1989;83:73-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chenoweth CE, Singal S, Pearson RD, Betts RF, Markovitz DM. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related visceral leishmaniasis presenting in a pleural effusion.Chest 1993;103:648-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Munoz-Rodriguez FJ, Padro S, Pastor P, et al. Pleural and peritoneal leishmaniasis in an AIDS patient.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1997;16:246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Casado JL, Cuesta C, Sanchez JA, Guerrero A. Solitary pulmonary nodule due to Leishmania in a patient with AIDS.Clin Infect Dis 1998;26:532-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Romeu J, Srera G, Carreres A, Condom MJ, Clotet B. Visceral leishmaniasis involving the lung and a cutaneous Kaposi's sarcoma lesion.AIDS 1991;5:172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Matheron S, Cabie A, Parquin F, et al. Visceral leishmaniasis and HIV infection: Unusual presentation with pleuropulmonary involvement, and effects of secondary prophylaxis.AIDS 1992;6:238-40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barker DC, Gibson LJ, Kennedy WP, Nasser AA, Williams RH. The potential of using recombinant DNA species-specific probes for the identification of tropical Leishmania. Parasitology 1986;92(Suppl):S139-74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cruz I, Canavate C, Rubio JM, et al. A nested polymerase chain reaction (Ln-PCR) for diagnosing and monitoring Leishmania infantum infection in patients co-infected with immunodeficiency virus.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2002;96(Suppl 1):S185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Badaró R, Jones TC, Lorenço R, et al. A prospective study of visceral leishmaniasis in an endemic area of Brazil.J Infect Dis 1986;154:639-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pintado V, López-Vélez R. HIV-associated visceral leishmaniasis.Clin Microbiol Infect 2001;7:291-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pintado V, Martín-Rabadán P, Rivera ML, Moreno S, Bouza E. Visceral leishmaniasis in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- infected and non-HIV-infected patients: A comparative study.Medicine 2001;80:54-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.López-Vélez R, Laguna F, Alvar J, et al. Parasitic culture of buffy coat for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients.J Clin Microbiol 1995;33:937-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mary C, Lamouroux D, Dunan S, Quiilici M. Western blot analysis of antibodies to Leishmania infantum antigens: Potential of the 14-kD and 16-kD antigens for diagnosis and epidemiological purposes.Am J Trop Med Hyg 1992;47:764-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kar K. Serological diagnosis of leishmaniasis.Crit Rev Microbiol 1995;21:123-52.7639932 [Google Scholar]
- 18.da Costa CA, de Toledo VP, enaro O, Williams P, Mayrink W. Montenegro skin test: Evaluation of the composition and stability of the antigen preparation.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1996;91:193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Herwaldt BL, Berman JD. Recommendations for treating leishmaniaisis with sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam) and review of pertinent clinical studies.Am J Trop Med Hyg 1992;46:296-306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sundar S, Singh VP, Sharma S, Makharia MK, Murray HW. Response to interferon-gamma plus pentavalent antimony in Indian visceral leishmaniasis.J Infect Dis 1997;176:1117-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Murray HW. Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar): A decade of progress and future approaches.Int J Infect Dis 2000;4:158-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sundar S, Jha TK, Thakur CP, at al. Oral miltefosine for Indian visceral leishmaniasis.N Engl J Med 2002;347:1739-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mishra M, Biswas UK, Jha Am, Khan AB. Amphotericin versus sodium stibogluconate in first-line treatment of Indian kala-azar.Lancet 1994;344:1599-600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sundar S, Agrawall G, Rai M, Makharia MK, Murray HW. Treatment of Indian visceral leishmaniasis with single or daily infusions of low dose liposomal amphotericin B: Randomized trial.BMJ 2001;323:419-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lafeuillade A, Chaffanjon P, Delbeke E, Quilichini R. Maintenance itraconazole for visceral leishmaniasis in HIV infection.Am J Med 1992;92:449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Berenguer J, Cosin J, Miralles P, Lopez JC, Padilla B. Discontinuation of secondary anti-Leishmania prophylaxis in HIV-infected patients which have responded to highly active antiretroviral therapy.AIDS 2000;14:2946-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]