Abstract
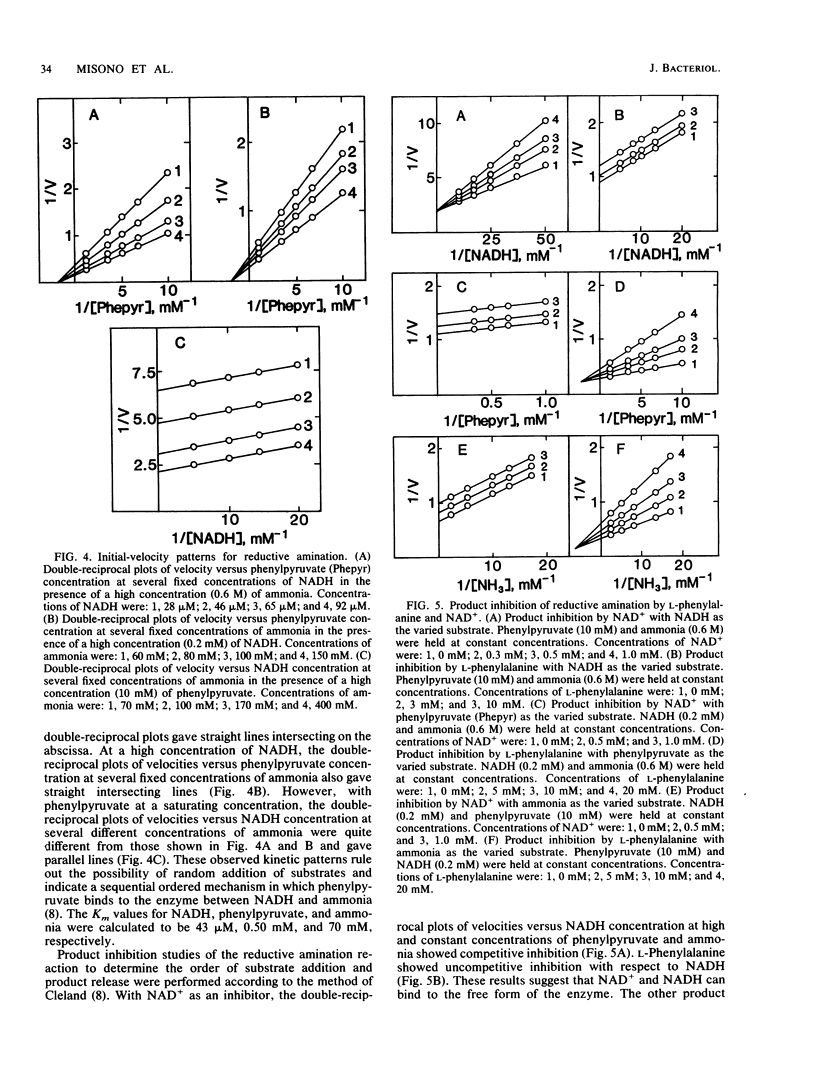
NAD+-dependent phenylalanine dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.) was purified to homogeneity from a crude extract of Rhodococcus maris K-18 isolated from soil. The enzyme had a molecular mass of about 70,000 daltons and consisted of two identical subunits. The enzyme catalyzed the oxidative deamination of L-phenylalanine and several other L-amino acids and the reductive amination of phenylpyruvate and p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate. The enzyme required NAD+ as a natural coenzyme. The NAD+ analog 3-acetylpyridine-NAD+ showed much greater coenzyme activity than did NAD+. D-Phenylalanine, D-tyrosine, and phenylethylamine inhibited the oxidative deamination of L-phenylalanine. The enzyme reaction was inhibited by p-chloromercuribenzoate and HgCl2. Initial-velocity and product inhibition studies showed that the reductive amination proceeded through a sequential ordered ternary-binary mechanism. NADH bound first to the enzyme, followed by phenylpyruvate and then ammonia, and the products were released in the order L-phenylalanine and NAD+. The Michaelis constants were as follows: L-phenylalanine, 3.8 mM; NAD+, 0.25 mM; NADH, 43 microM; phenylpyruvate, 0.50 mM; and ammonia, 70 mM.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano Y., Nakazawa A., Endo K., Hibino Y., Ohmori M., Numao N., Kondo K. Phenylalanine dehydrogenase of Bacillus badius. Purification, characterization and gene cloning. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 1;168(1):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano Y., Nakazawa A., Endo K. Novel phenylalanine dehydrogenases from Sporosarcina ureae and Bacillus sphaericus. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10346–10354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. J., van der Drift C. Purification and properties of L-erythro-3,5-diaminohexanoate dehydrogenase from Clostridium sticklandii. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):292–299. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton J. S., Fisher J. R. Nonlinear kinetics of glutamate dehydrogenase. Studies with substrates--glutamate and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 16;10(4):577–585. doi: 10.1021/bi00780a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIOTTI M. M., KAPLAN N. O., STOLZENBACH F. E. Reaction of pyridine nucleotide analogues with dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):833–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. The reductive amination of 2-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):409–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1180409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LéJohn H. B., Jackson S. G., Klassen G. R., Sawula R. V. Regulation of mitochondrial glutamic dehydrogenase by divalent metals, nucleotides, and alpha-ketoglutarate. Correlations between the molecular and kinetic mechanisms, and the physiological implications. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5346–5356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misono H., Soda K. Properties of meso-alpha,epsilon-diaminopimelate D-dehydrogenase from Bacillus sphaericus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10599–10605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashima T., Soda K. Purification and properties of alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus sphaericus. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):29–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima T., Misono H., Soda K. Properties of crystalline leucine dehydrogenase from Bacillus sphaericus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5719–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olomucki A., Thomé-Beau F. Study of coenzyme binding site of octopine dehydrogenase using analogues of NAD+. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):109–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL J. M., MONTGOMERY G. A., BOCK R. M. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of DPN and analogs of DPN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Jun;82(2):288–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somack R., Costilow R. N. 2,4-diaminopentanoic acid C 4 dehydrogenase. Purification and properties of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson R. M., LéJohn H. B. Glutamic dehydrogenases of Oomycetes. Kinetic mechanism and possible vvolutionary history. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2127–2135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





