Abstract
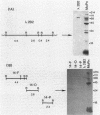
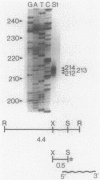
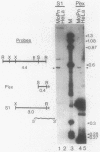
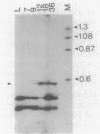
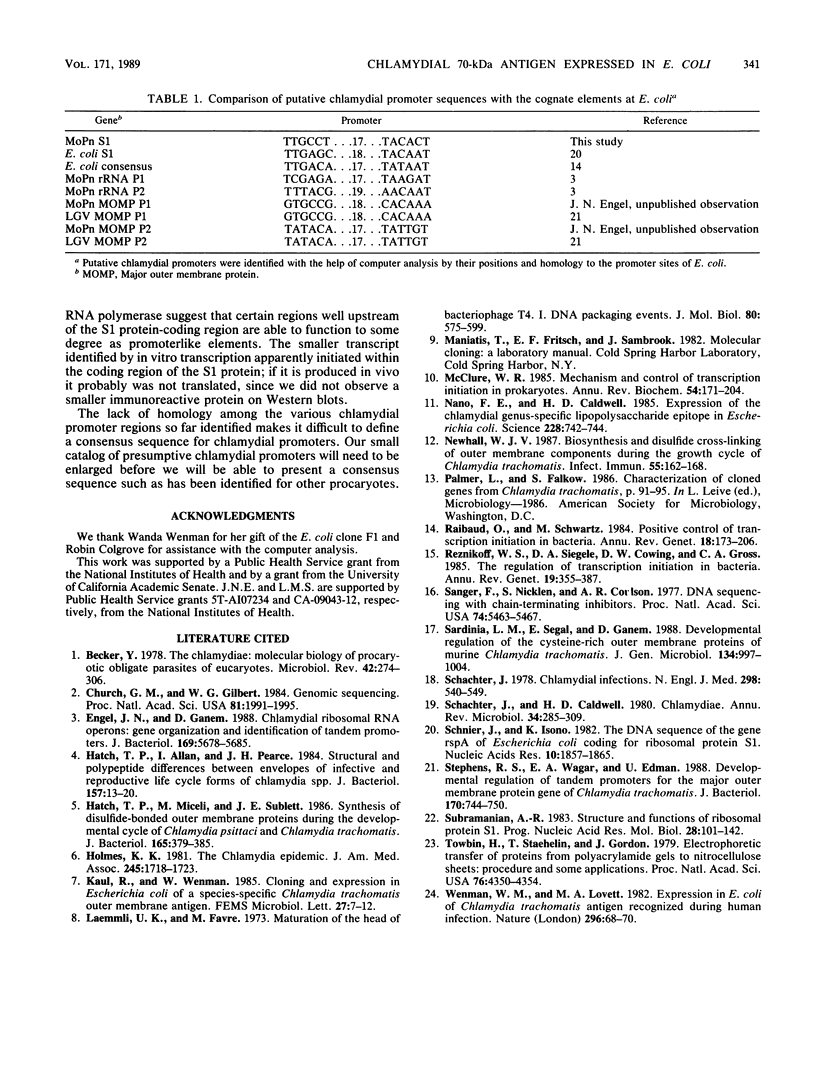
In an attempt to identify chlamydial genes whose native promoters allow them to be expressed in Escherichia coli, we isolated and characterized a chlamydial gene identified by screening a library of chlamydial DNA with antichlamydial antibodies. This gene encodes a 70-kilodalton immunoreactive polypeptide in E. coli hosts. Sequence analysis of the 5' portion of the gene identified its product as the chlamydial homolog of the E. coli ribosomal protein S1. The site of transcription initiation of the mRNA in chlamydiae was determined, and its putative promoter regions were identified. These regions apparently do not function efficiently in E. coli; in vitro transcripts generated by using E. coli RNA polymerase did not start at the authentic chlamydial initiation site. Several in vitro transcripts both larger and smaller than the authentic transcript were seen; presumably, these transcripts result from adventitious promoterlike elements in adjacent chlamydial DNA and may be responsible for the expression of the gene in E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker Y. The chlamydia: molecular biology of procaryotic obligate parasites of eucaryocytes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):274–306. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.274-306.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial rRNA operons: gene organization and identification of putative tandem promoters. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5678–5685. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5678-5685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Sublett J. E. Synthesis of disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.379-385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. K. The Chlamydia epidemic. JAMA. 1981 May 1;245(17):1718–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nano F. E., Caldwell H. D. Expression of the chlamydial genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope in Escherichia coli. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):742–744. doi: 10.1126/science.2581315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., 5th Biosynthesis and disulfide cross-linking of outer membrane components during the growth cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.162-168.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Segal E., Ganem D. Developmental regulation of the cysteine-rich outer-membrane proteins of murine Chlamydia trachomatis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. Chlamydial infections (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):540–549. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnier J., Isono K. The DNA sequence of the gene rpsA of Escherichia coli coding for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1857–1865. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Edman U. Developmental regulation of tandem promoters for the major outer membrane protein gene of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.744-750.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Structure and functions of ribosomal protein S1. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:101–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Lovett M. A. Expression in E. coli of Chlamydia trachomatis antigen recognized during human infection. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):68–70. doi: 10.1038/296068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]