Abstract
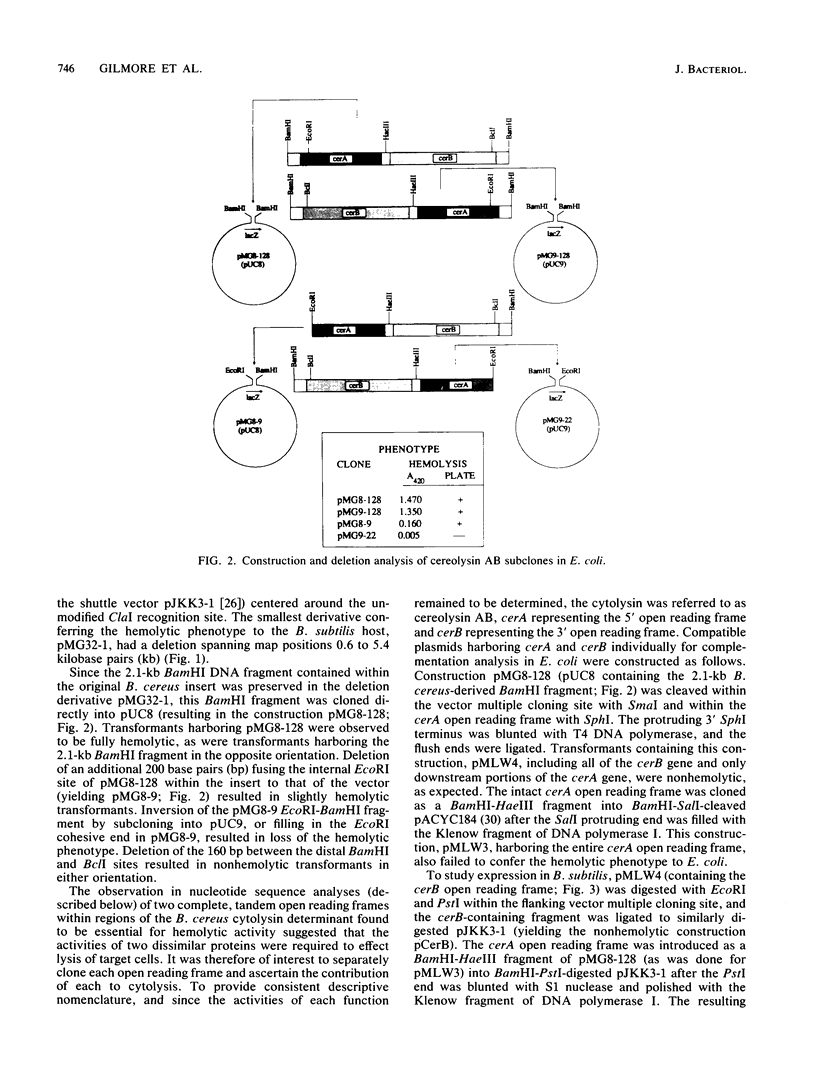
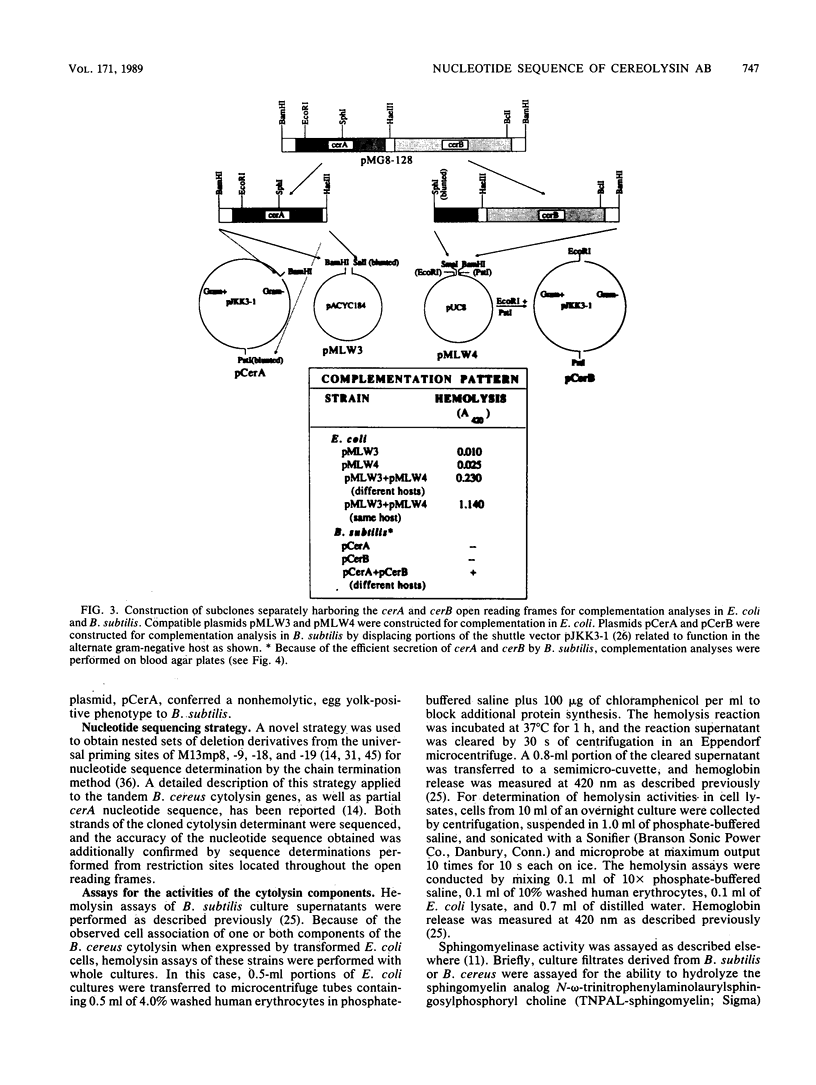
A cloned cytolytic determinant from the genome of Bacillus cereus GP-4 has been characterized at the molecular level. Nucleotide sequence determination revealed the presence of two open reading frames. Both open reading frames were found by deletion and complementation analysis to be necessary for expression of the hemolytic phenotype by Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli hosts. The 5' open reading frame was found to be nearly identical to a recently reported phospholipase C gene derived from a mutant B. cereus strain which overexpresses the respective protein, and it conferred a lecithinase-positive phenotype to the B. subtilis host. The 3' open reading frame encoded a sphingomyelinase. The two tandemly encoded activities, phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase, constitute a biologically functional cytolytic determinant of B. cereus termed cereolysin AB.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansell S. E., Lawton E. B., McRae S., Mortimer G., Cursons R. T. Endophthalmitis due to Bacillus cereus: case report. N Z Med J. 1980 Jul 9;92(663):12–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Linder R., Avigad L. S. Nature and mechanism of action of the CAMP protein of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):838–844. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.838-844.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørklid E., Little C. The isoelectric point of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):161–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouza E., Grant S., Jordan C., Yook R. H., Sulit H. L. Bacillus cereus endogenous panophthalmitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979 Mar;97(3):498–499. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1979.01020010248012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Shorr R. G., Bomalaski J. S. Antibodies prepared to Bacillus cereus phospholipase C crossreact with a phosphatidylcholine preferring phospholipase C in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley C. M., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., van Deenen L. L. Lytic and non-lytic degradation of phospholipids in mammalian erythrocytes by pure phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 25;307(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coolbaugh J. C., Williams R. P. Production and characterization of two hemolysins of Bacillus cereus. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Nov;24(11):1289–1295. doi: 10.1139/m78-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L., Grushoff-Kosyk P. S., Bernheimer A. W. Purification of cereolysin and the electrophoretic separation of the active (reduced) and inactive (oxidized) forms of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):144–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.144-154.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSSUM K. SEPARATION OF HEMOLYSIN AND EGG YOLK TURBIDITY FACTOR IN CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF BACILLUS CEREUS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:400–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilmore K. S., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the gene specifying the bifunctional 6'-aminoglycoside acetyltransferase 2"-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase enzyme in Streptococcus faecalis and identification and cloning of gene regions specifying the two activities. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):631–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.631-638.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Dinur T., Barenholz Y. A spectrophotometric method for determination of sphingomyelinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 28;530(3):503–507. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazitt Y., Ohad I., Loyter A. Changes in phosoholipid susceptibility toward phospholipases induced by ATP depletion in avian and amphibian erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 28;382(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90373-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Grandi G., Hahn J., Grandi R., Dubnau D. Conformational alteration of mRNA structure and the posttranscriptional regulation of erythromycin-induced drug resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6081–6097. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. C., O'Day D. M., Head W. S. Fulminating panophthalmitis due to exogenous infection with Bacillus cereus: report of 4 cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 1982 Mar;66(3):205–208. doi: 10.1136/bjo.66.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation: mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7079–7083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes W. L., Weeks C. R., Iandolo J. J., Ferretti J. J. Immunologic cross-reactivity of type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) and staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):837–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.837-838.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Matsushita M., Tomita M., Taguchi R. Effects of metal ions on sphingomyelinase activity of Bacillus cereus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Sep;249(2):588–595. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Mori M., Ohyabu T., Taguchi R. Studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. I. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):247–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Yamanegi M., Taguchi R., Miyashita T., Ohyabu T. Studies on phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C type) of Bacillus cereus. I. purification, properties and phosphatase-releasing activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 19;450(2):154–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Holm T., Guddal P. H., Sletten K., Haugli F. B., Little C. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreft J., Berger H., Härtlein M., Müller B., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis of the hemolysin (cereolysin) determinant from Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):681–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.681-689.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreft J., Hughes C. Cloning vectors derived from plasmids and phage of Bacillus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:1–17. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. Conformational studies on phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. The effect of urea on the enzyme. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):977–986. doi: 10.1042/bj1750977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C., Johansen S. Unfolding and refolding of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus in solutions of guanidinium chloride. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1790509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C., Rumsby M. G. Lysis of erythrocytes from stored human blood by phospholipase C (Bacillus cereus). Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):39–46. doi: 10.1042/bj1880039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Little C., Sletten K., Wallin R., Johnsen S., Flengsrud R., Prydz H. Some characteristics of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEIN M. W., LOGAN G. F., Jr Partial purification and properties of two phospholipases of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:369–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.369-381.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Sugahara T., Ohsaka A. Phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):710–725. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Molecular properties and kinetic studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;704(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C. Bacillus cereus toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;13(3):453–505. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle K. J., Otnaess A. B., Prydz H. Inhibition of the synthesis of phospholipase C in Bacillus cereus by a component of the growth medium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Jun;85(3):219–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., Kastelijn D., van Deenen L. L. The asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the human red cell membrane. A combined study using phospholipases and freeze-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):178–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa Y., Ohsaka A. Purification and some properties of phospholipase C (alpha-toxin) of Clostridium perfringens. J Biochem. 1977 Jan;81(1):115–126. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]