Abstract
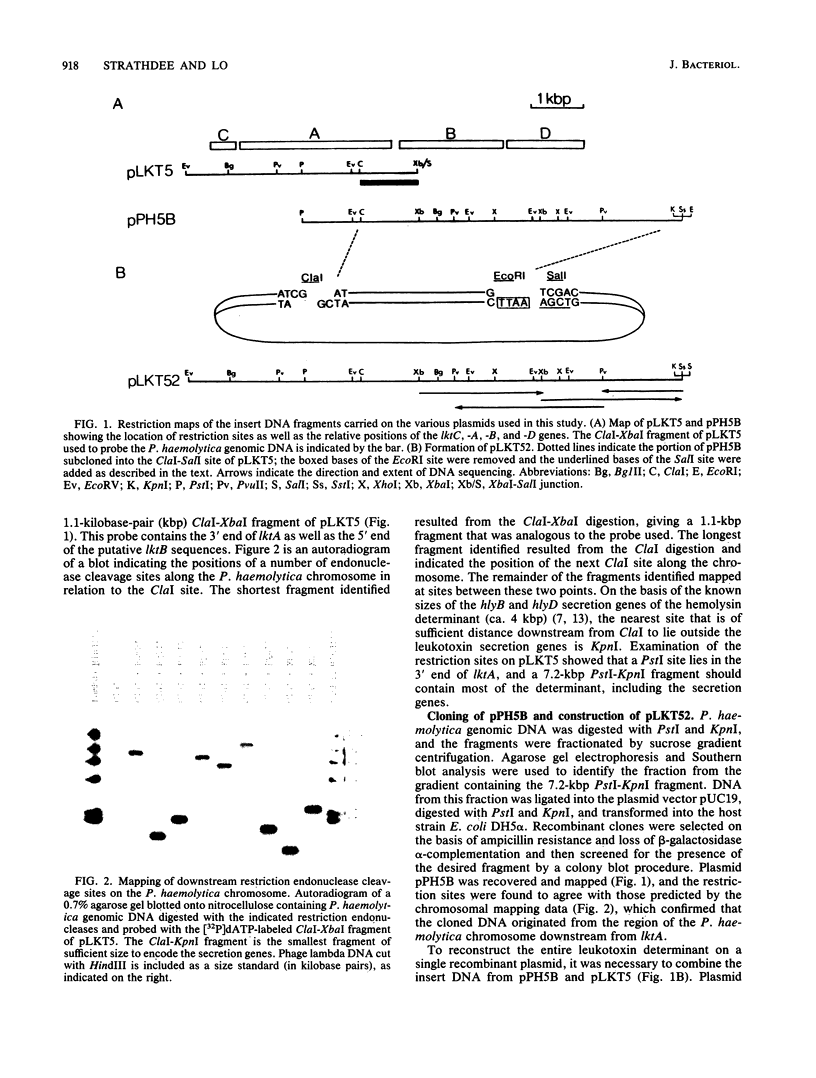
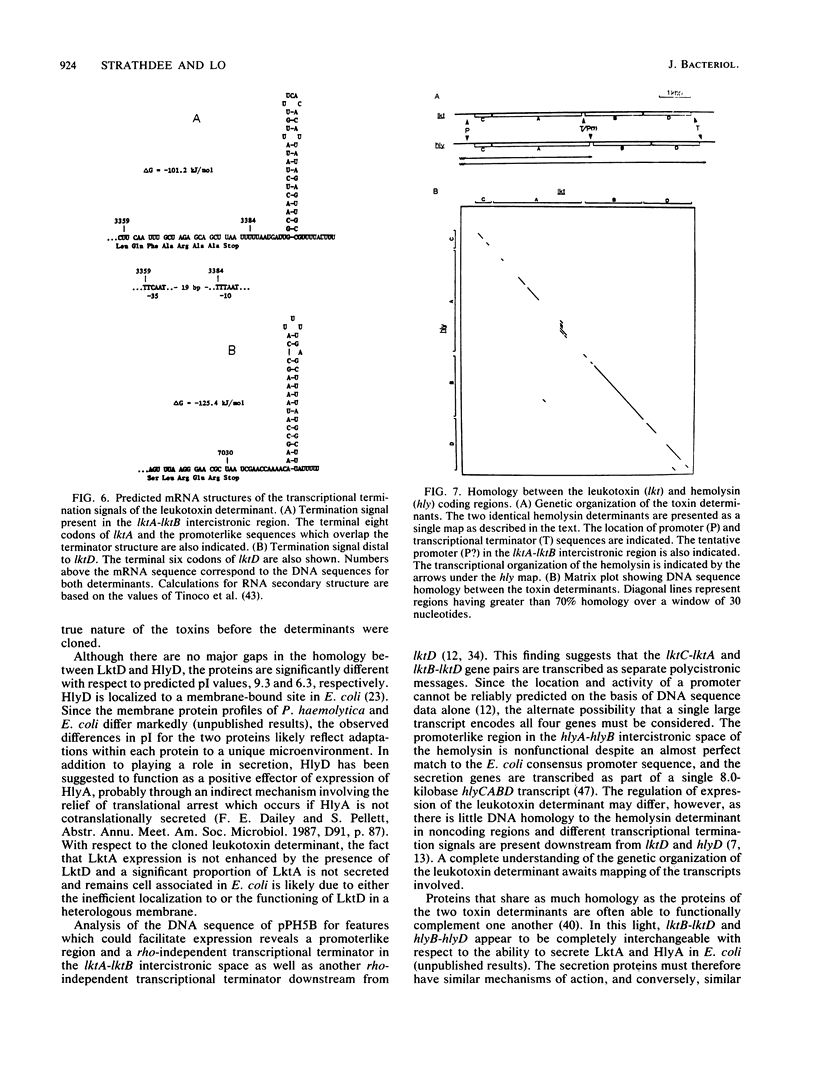
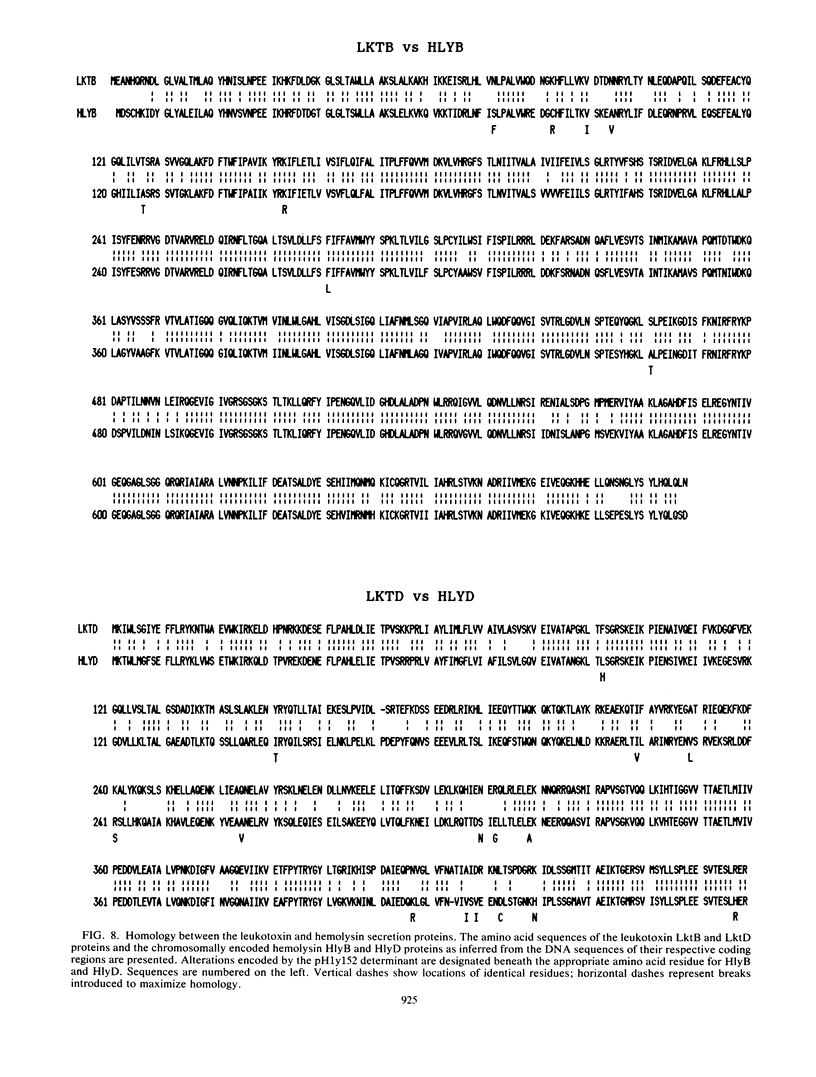
The structural gene of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant is highly homologous to that of the Escherichia coli hemolysin determinant, which also encodes a specialized set of genes involved in the secretion of the hemolysin. In this report, we describe the cloning and nucleotide sequence of the analogous secretion genes from P. haemolytica which make up the remainder of the leukotoxin determinant. The secretion genes were cloned directly from the P. haemolytica chromosome to form the recombinant plasmid pPH5B. By subcloning the secretion genes together with the leukotoxin structural gene, the cloned leukotoxin determinant was reconstructed on a single plasmid, pLKT52, which directs the synthesis of active leukotoxin to the culture supernatant when expressed in E. coli. DNA sequence analysis showed the presence of two secretion genes, designated lktB and lktD in order of their genetic organization, which code for proteins of 79.7 and 54.7 kilodaltons, both of which were detected when pLKT52 was expressed in E. coli minicells. The lktB and lktD genes were found to be highly homologous to the hlyB and hlyD secretion genes of the hemolysin determinant, and the predicted LktB-HlyB and LktD-HlyD proteins were 90.5 and 75.6% homologous. Nucleotide sequence homology between the leukotoxin and hemolysin determinants was limited to the C, A, B, and D coding regions, although the presence of similar transcriptional terminators in the A-B intercistronic region is suggestive of a similar transcriptional organization. On the basis of these data, we hypothesize that the two determinants share a common evolutionary history and are prototypes for a widely disseminated family of virulence factors, the RTX cytotoxins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Post D., Struck D. K. Identification and characterization of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2348–2354. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2348-2354.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Lee E. Y., Welch R. A. Escherichia coli hemolysin is released extracellularly without cleavage of a signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):88–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.88-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach J. H., Endicott J. A., Juranka P. F., Henderson G., Sarangi F., Deuchars K. L., Ling V. Homology between P-glycoprotein and a bacterial haemolysin transport protein suggests a model for multidrug resistance. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):485–489. doi: 10.1038/324485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Ladant D., Sezer O., Pichot F., Ullmann A., Danchin A. The calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. The carboxy-terminal region of haemolysin 2001 is required for secretion of the toxin from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02428042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmel M. E., Yates M. D., Lauerman L. H., Squire P. G. Purification and partial characterization of a macrophage cytotoxin from Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):764–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaehler K. L., Markam R. J., Muscoplat C. C., Johnson D. W. Evidence of cytocidal effects of Pasteurella haemolytica on bovine peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1690–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
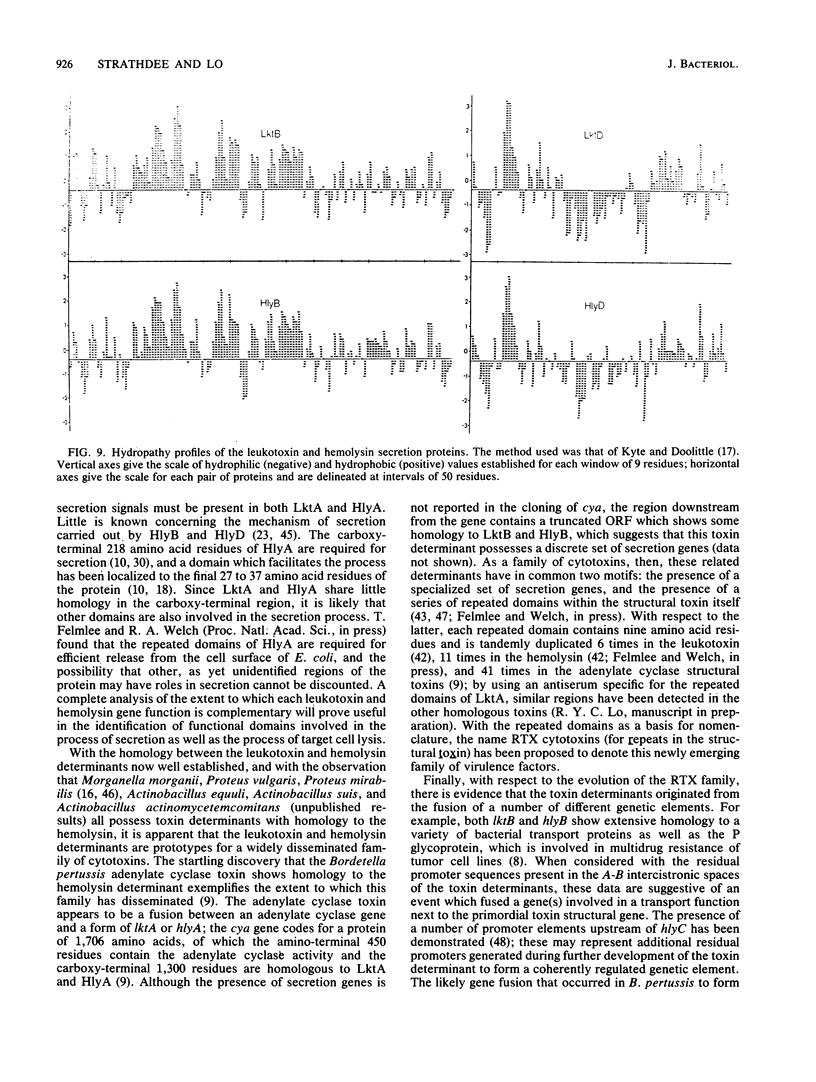
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Cameron L. A. A simple immunological detection method for the direct screening of genes from clone banks. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;64(1):73–76. doi: 10.1139/o86-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Shewen P. E., Strathdee C. A., Greer C. N. Cloning and expression of the leukotoxin gene of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):667–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.667-671.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Vogel M., Goebel W. Mutations affecting activity and transport of haemolysin in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):238–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00333579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Identification of polypeptides required for the export of haemolysin 2001 from E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):529–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00331351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicaud J. M., Mackman N., Gray L., Holland I. B. Characterisation of HlyC and mechanism of activation and secretion of haemolysin from E. coli 2001. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 5;187(2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicaud J. M., Mackman N., Gray L., Holland I. B. The C-terminal, 23 kDa peptide of E. coli haemolysin 2001 contains all the information necessary for its secretion by the haemolysin (Hly) export machinery. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80838-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Rdest U., Goebel W. Determination of the functions of hemolytic plasmid pHly152 of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):233–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.233-247.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable microcomputer environment for DNA and protein sequence manipulation and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):479–488. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R. DNA sequence analysis on the IBM-PC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):601–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Zieg J., Silverman M., Mandel G., Doolittle R. Phase variation: evolution of a controlling element. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1370–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.6251543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3233–3236. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3233-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W., Vogel M., Goebel W. Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):200–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.200-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Identification of two different hemolysin determinants in uropathogenic Proteus isolates. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2183–2190. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2183-2190.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Pellett S. Transcriptional organization of the Escherichia coli hemolysin genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1622–1630. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1622-1630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]