Abstract
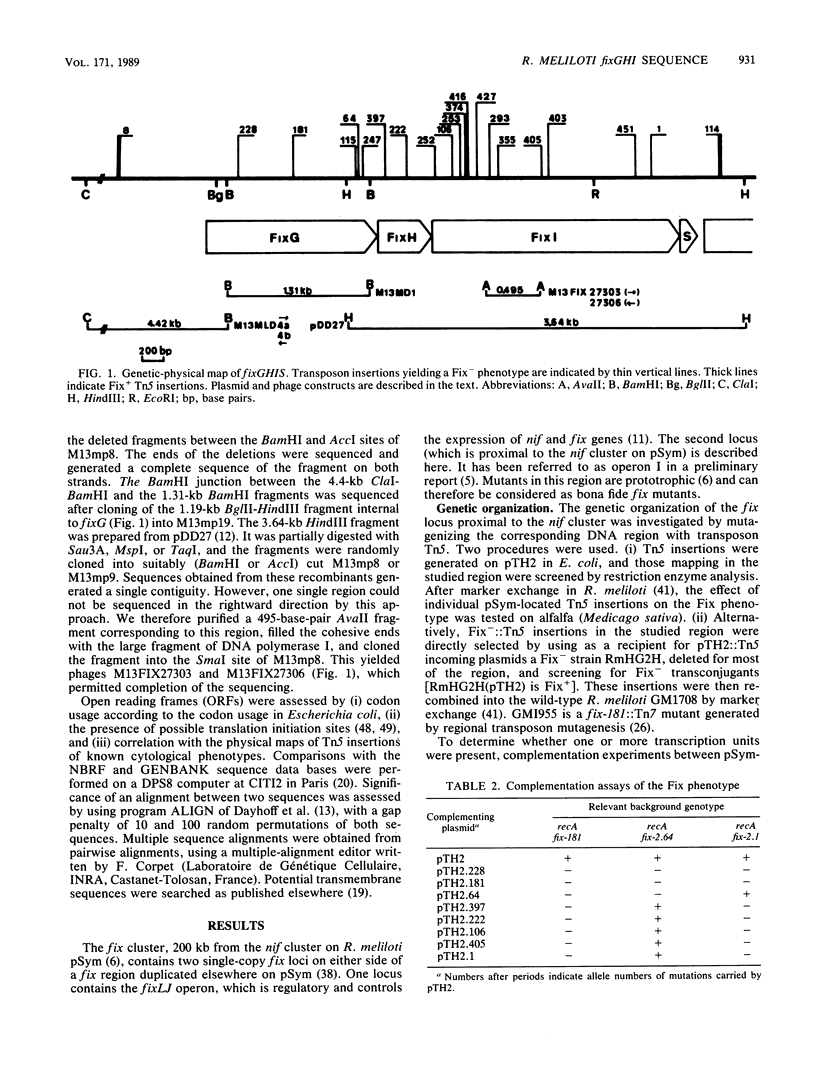
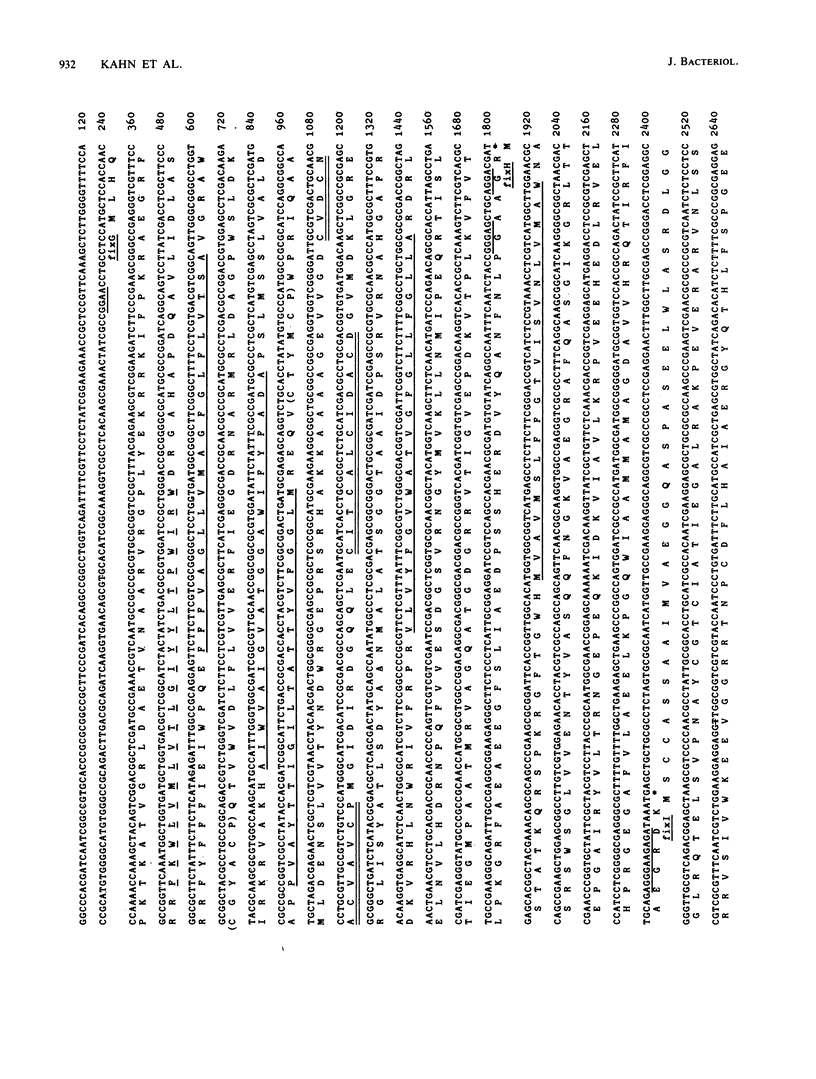
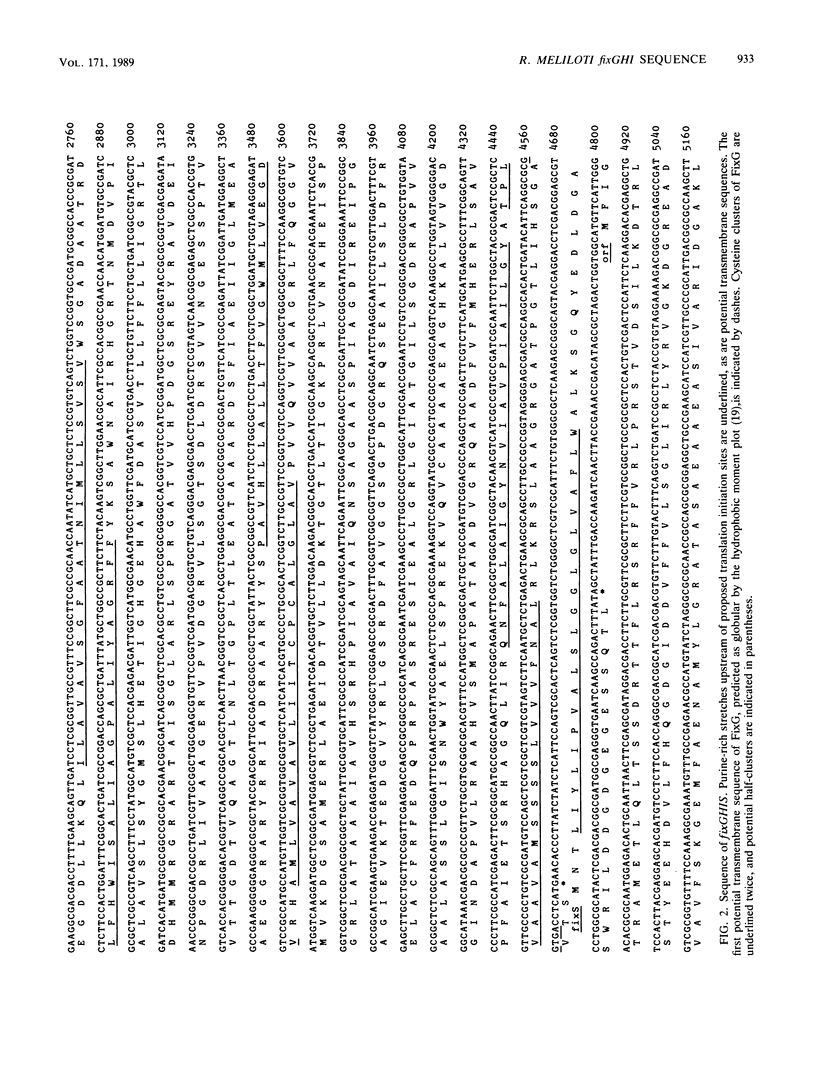
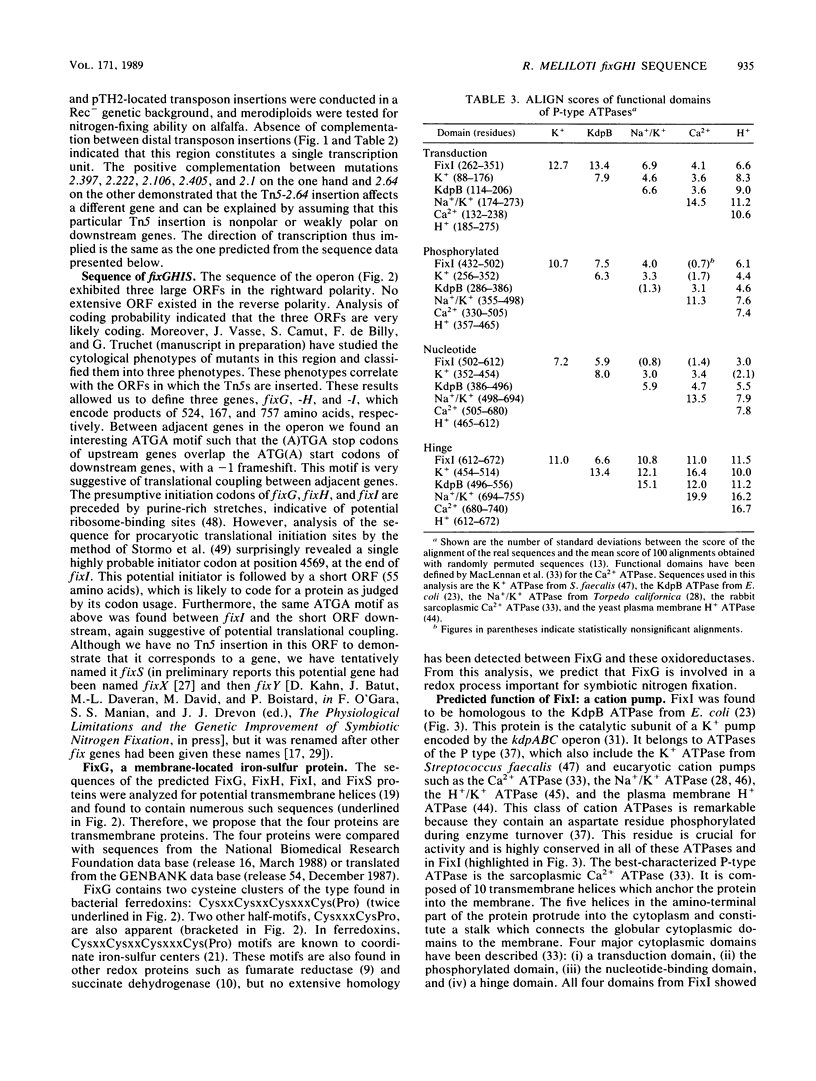
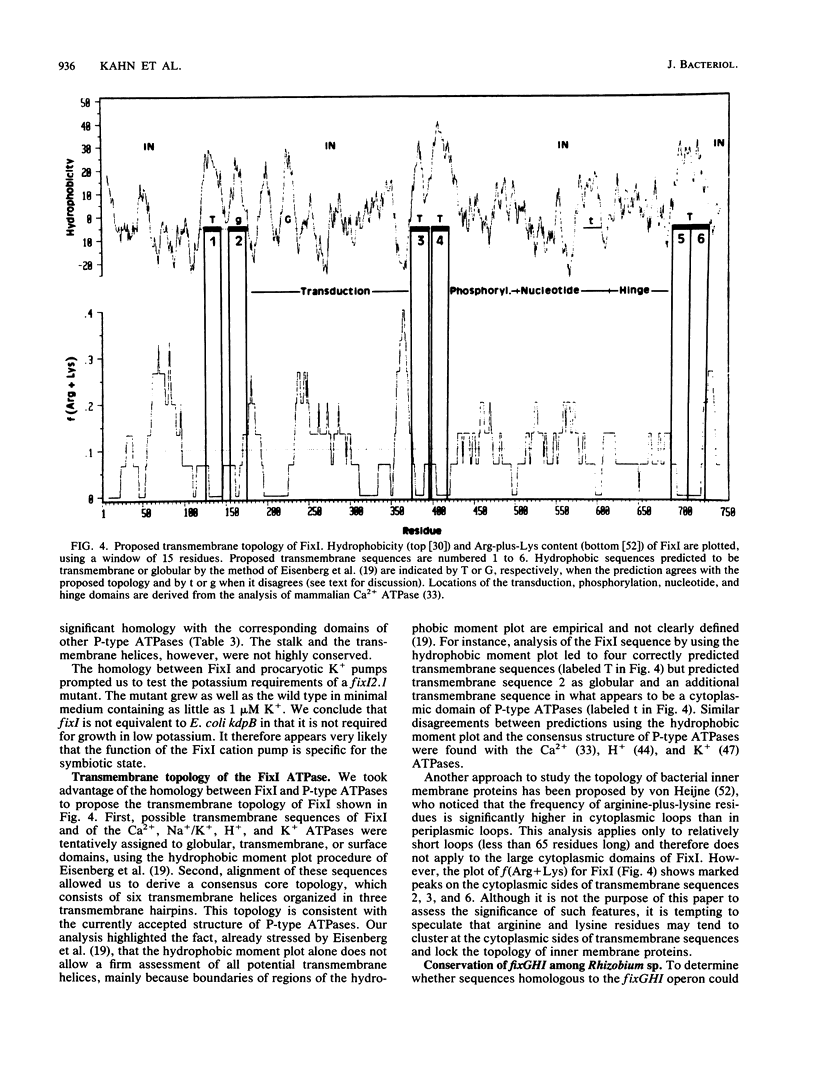
We present genetic and structural analyses of a fix operon conserved among rhizobia, fixGHI from Rhizobium meliloti. The nucleotide sequence of the operon suggests it may contain a fourth gene, fixS. Adjacent open reading frames of this operon showed an overlap between TGA stop codons and ATG start codons in the form of an ATGA motif suggestive of translational coupling. All four predicted gene products contained probable transmembrane sequences. FixG contained two cysteine clusters typical of iron-sulfur centers and is predicted to be involved in a redox process. FixI was found to be homologous with P-type ATPases, particularly with K+ pumps from Escherichia coli and Streptococcus faecalis but also with eucaryotic Ca2+, Na+/K+, H+/K+, and H+ pumps, which implies that FixI is a pump of a specific cation involved in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Since prototrophic growth of fixI mutants appeared to be unimpaired, the predicted FixI cation pump probably has a specifically symbiotic function. We suggest that the four proteins FixG, FixH, FixI, and FixS may participate in a membrane-bound complex coupling the FixI cation pump with a redox process catalyzed by FixG.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar O. M., Reiländer H., Arnold W., Pühler A. Rhizobium meliloti nifN (fixF) gene is part of an operon regulated by a nifA-dependent promoter and codes for a polypeptide homologous to the nifK gene product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5393–5400. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5393-5400.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W., Rump A., Klipp W., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Nucleotide sequence of a 24,206-base-pair DNA fragment carrying the entire nitrogen fixation gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):715–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M., Son P. H. Kilo-sequencing: creation of an ordered nest of asymmetric deletions across a large target sequence carried on phage M13. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:98–122. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Klingensmith J. A., Gibbons S. L., Ausubel F. M. Conservation of structure and location of Rhizobium meliloti and Klebsiella pneumoniae nifB genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1120–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1120-1126.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Grundström T., Jaurin B., Robinson J. J., Weiner J. H. Location and nucleotide sequence of frdB, the gene coding for the iron-sulphur protein subunit of the fumarate reductase of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):211–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence encoding the iron-sulphur protein subunit of the succinate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):507–517. doi: 10.1042/bj2230507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Domergue O., Pognonec P., Kahn D. Transcription patterns of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic plasmid pSym: identification of nifA-independent fix genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2239–2244. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2239-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G. F., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Genetic manipulations in Rhizobium meliloti utilizing two new transposon Tn5 derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00331029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A. The genetic complexity of nitrogen fixation. The ninth Fleming lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2745–2755. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Nees D. W., Raymond C. K., Loroch A. I., Ludwig R. A. Characterization of three genomic loci encoding Rhizobium sp. strain ORS571 N2 fixation genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):72–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.72-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl C. D., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Genetic and structural analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti fixA, fixB, fixC, and fixX genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1127–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1127-1136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondrat C., Dessen P., Le Beux P. Principle of codification for quick comparisons with the entire biomolecule databanks and associated programs in FORTRAN 77. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):197–204. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama K., Nagahara Y., Tsukihara T., Katsube Y., Hase T., Matsubara H. Tertiary structure of Bacillus thermoproteolyticus [4Fe-4S] ferredoxin. Evolutionary implications for bacterial ferredoxins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Wieczorek L., Altendorf K., Reicin A. S., Dorus E., Epstein W. Sequence homology between two membrane transport ATPases, the Kdp-ATPase of Escherichia coli and the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4746–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Noguchi S., Noda M., Takahashi H., Ohta T., Kawamura M., Nojima H., Nagano K., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of Torpedo californica (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):733–736. doi: 10.1038/316733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B., Altendorf K., Epstein W. Identification of the structural proteins of an ATP-driven potassium transport system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3216–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrè M. T., Moroni A., Albergoni F. G., Marrè E. Plasmalemma redox activity and h extrusion: I. Activation of the h-pump by ferricyanide-induced potential depolarization and cytoplasm acidification. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):25–29. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. O., Long S. R. Generalized transduction in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):125–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.125-129.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Prakash R. K., Atherly A. G. Conservation of symbiotic nitrogen fixation gene sequences in Rhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.21-26.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renalier M. H., Batut J., Ghai J., Terzaghi B., Gherardi M., David M., Garnerone A. M., Vasse J., Truchet G., Huguet T. A new symbiotic cluster on the pSym megaplasmid of Rhizobium meliloti 2011 carries a functional fix gene repeat and a nod locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2231–2238. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2231-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Casse-Delbart F., Dusha I., David M., Boucher C. Megaplasmids in the plant-associated bacteria Rhizobium meliloti and Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.402-406.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein B., Stern A. I. Relationship of Transplasmalemma Redox Activity to Proton and Solute Transport by Roots of Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1986 Apr;80(4):805–811. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. Directed transposon Tn5 mutagenesis and complementation analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kielland-Brandt M. C., Fink G. R. Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na+ + K+), K+- and Ca2+-ATPases. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):689–693. doi: 10.1038/319689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of the rat stomach (H+ + K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16788–16791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Schwartz A., Lingrel J. B. Amino-acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):691–695. doi: 10.1038/316691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solioz M., Mathews S., Fürst P. Cloning of the K+-ATPase of Streptococcus faecalis. Structural and evolutionary implications of its homology to the KdpB-protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7358–7362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Zimmerman J. L., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. A Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic regulatory gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Reiländer H., Pühler A. Mapping and expression of a regulatory nitrogen fixation gene (fixD) of Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2751–2756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03999.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




