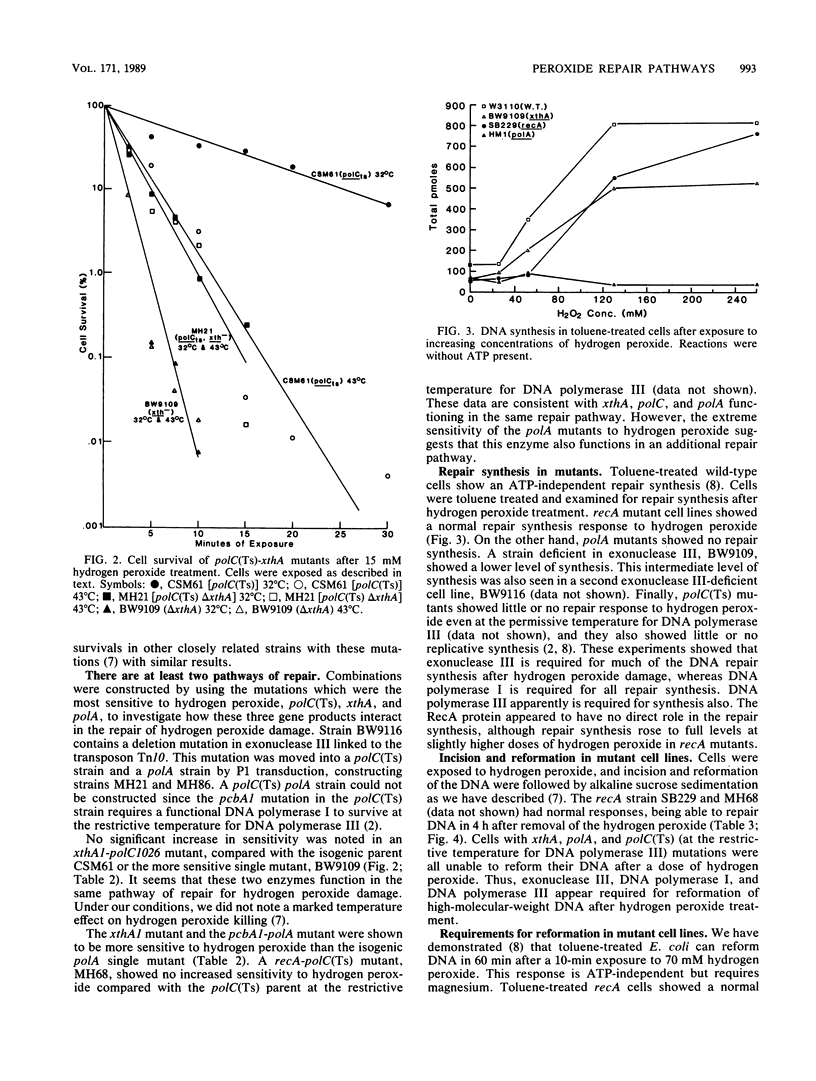
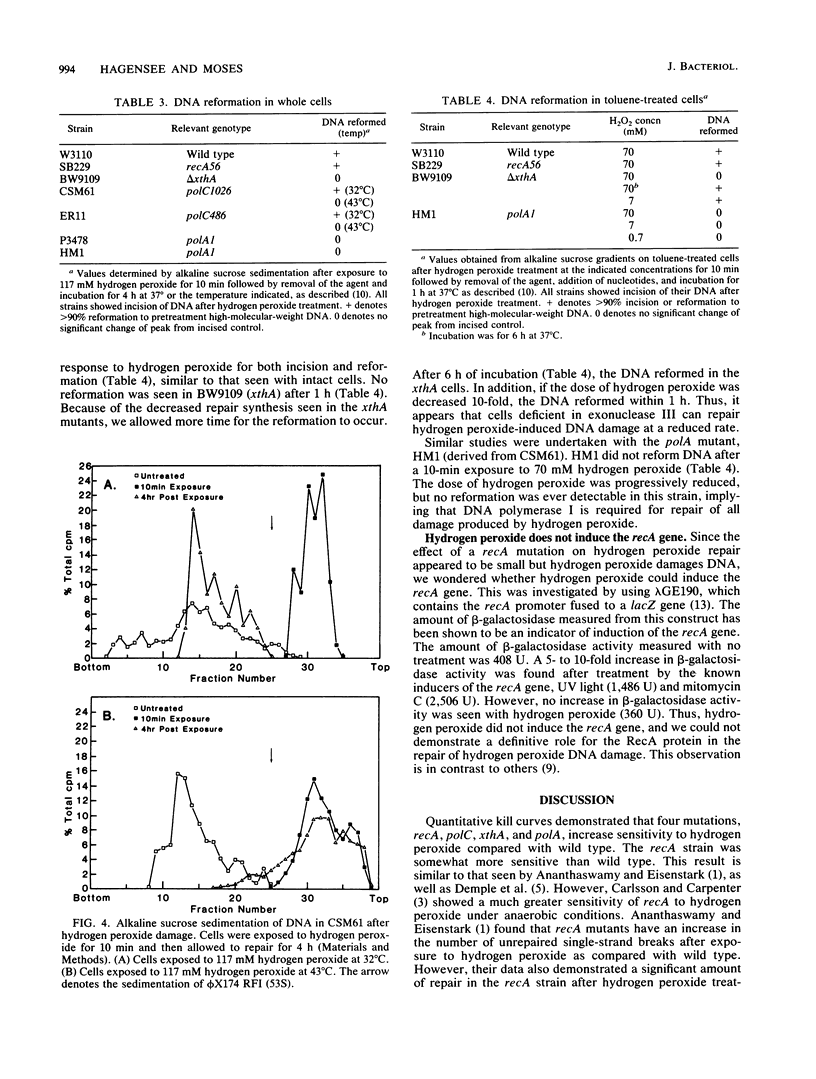
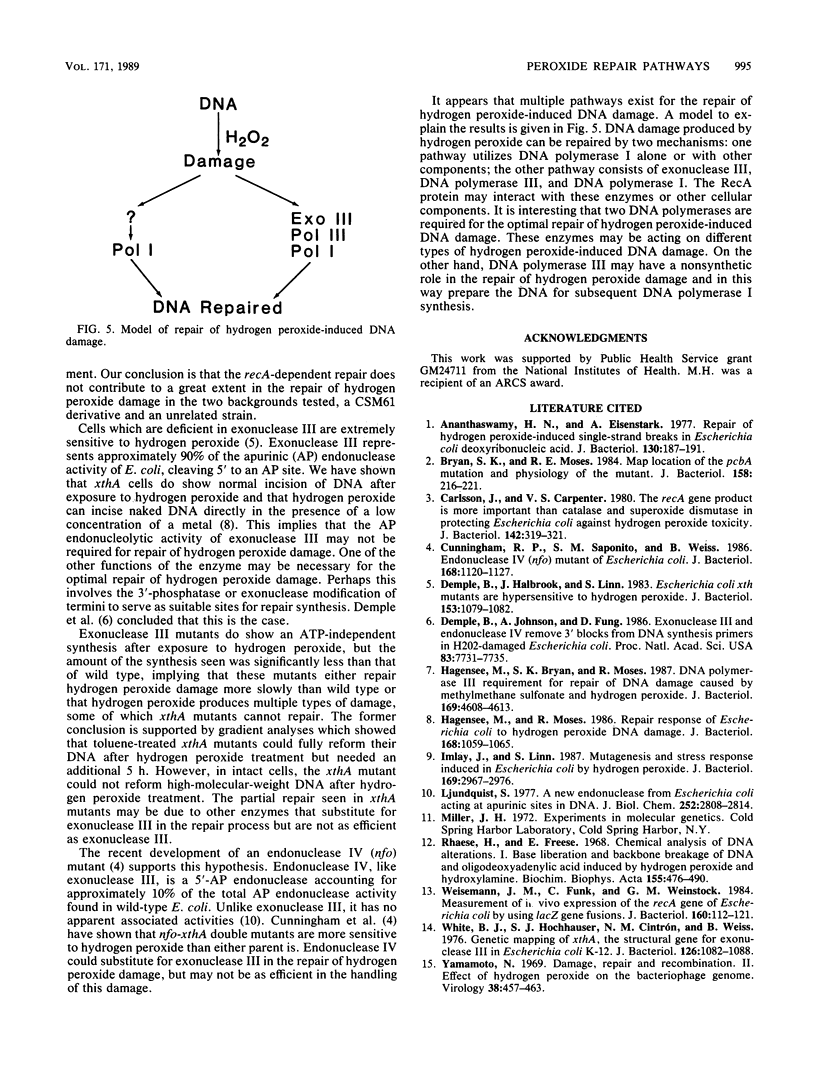
Abstract
The repair response of Escherichia coli to hydrogen peroxide has been examined in mutants which show increased sensitivity to this agent. Four mutants were found to show increased in vivo sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide compared with wild type. These mutants, in order of increasing sensitivity, were recA, polC, xthA, and polA. The polA mutants were the most sensitive, implying that DNA polymerase I is required for any repair of hydrogen peroxide damage. Measurement of repair synthesis after hydrogen peroxide treatment demonstrated normal levels for recA mutants, a small amount for xthA mutants, and none for polA mutants. This is consistent with exonuclease III being required for part of the repair synthesis seen, while DNA polymerase I is strictly required for all repair synthesis. Sedimentation analysis of cellular DNA after hydrogen peroxide treatment showed that reformation was absent in xthA, polA, and polC(Ts) strains but normal in a recA cell line. By use of a lambda phage carrying a recA-lacZ fusion, we found hydrogen peroxide does not induce the recA promoter. Our findings indicate two pathways of repair for hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage. One of these pathways would utilize exonuclease III, DNA polymerase III, and DNA polymerase I, while the other would be DNA polymerase I dependent. The RecA protein seems to have little or no direct function in either repair pathway.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthaswamy H. N., Eisenstark A. Repair of hydrogen peroxide-induced single-strand breaks in Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.187-191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan S. K., Moses R. E. Map location of the pcbA mutation and physiology of the mutant. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.216-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Carpenter V. S. The recA+ gene product is more important than catalase and superoxide dismutase in protecting Escherichia coli against hydrogen peroxide toxicity. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):319–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.319-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Saporito S. M., Spitzer S. G., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV (nfo) mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1120-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J., Linn S. Escherichia coli xth mutants are hypersensitive to hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1079–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1079-1082.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Johnson A., Fung D. Exonuclease III and endonuclease IV remove 3' blocks from DNA synthesis primers in H2O2-damaged Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7731–7735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagensee M. E., Bryan S. K., Moses R. E. DNA polymerase III requirement for repair of DNA damage caused by methyl methanesulfonate and hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4608–4613. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4608-4613.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagensee M. E., Moses R. E. Repair response of Escherichia coli to hydrogen peroxide DNA damage. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1059–1065. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1059-1065.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. Mutagenesis and stress responses induced in Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2967–2976. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2967-2976.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist S. A new endonuclease from Escherichia coli acting at apurinic sites in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2808–2814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaese H. J., Freese E. Chemical analysis of DNA alterations. I. Base liberation and backbone breakage of DNA and oligodeoxyadenylic acid induced by hydrogen peroxide and hydroxylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):476–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisemann J. M., Funk C., Weinstock G. M. Measurement of in vivo expression of the recA gene of Escherichia coli by using lacZ gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):112–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.112-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. J., Hochhauser S. J., Cintron N. M., Weiss B. Genetic mapping of xthA, the structural gene for exonuclease III in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1082–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1082-1088.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N. Damage, repair, and recombination. II. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on the bacteriophage genome. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


