Abstract
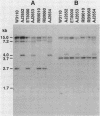
During nitrogen-limited growth, Escherichia coli expresses a specific ammonium or methylammonium ion transport system (Amt). Strains carrying defects in Amt have been isolated following Tn10 transposon mutagenesis. These mutants have less than 10% of the transport activity of the parental strain. Glutamate, glutamine, arginine, or high levels (20 mM) of ammonium will serve as the sole nitrogen source for growth of these strains, and glutamine synthetase is normally expressed and repressed by the nitrogen regulatory (Ntr) system. When transformed with plasmid pGln84, containing lacZ fused to an Ntr promoter (glnLp), the Amt mutants expressed a normal level of beta-galactosidase. Furthermore, P1 bacteriophage transduction of the amt mutation into an Ntr mutant, normally constitutive for Amt, gave Amt- transductants. Therefore, the mutations are unlikely to lie within genes affecting Ntr elements. Following transformation with plasmid libraries of E. coli genomic DNA constructed in pUC9, two plasmids conferring the Amt+ phenotype on the amt mutants were isolated. These plasmids were unable to complement the Amt- phenotype of Ntr- mutants. Restriction digestion of these plasmids revealed common fragments, and Southern blot analyses indicated that the Amt-complementing sequence and the site of Tn10 insertion in the genome occur in the same 3.4-kilobase HindIII-SalI fragment. Insertion of TnphoA into this fragment produced amt::phoA fusions which gave high levels of alkaline phosphatase under nitrogen-limiting conditions but low levels during ammonia excess. This suggests that the amt product contains domains which are exported to the periplasm.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boquet P. L., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Use of TnphoA to detect genes for exported proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of the plasmid-encoded gene for a periplasmic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1663–1669. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1663-1669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno R., Pahel G., Magasanik B. Role of glnB and glnD gene products in regulation of the glnALG operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.816-822.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castorph H., Kleiner D. Some properties of a Klebsiella pneumoniae ammonium transport negative mutant (Amt-). Arch Microbiol. 1984 Oct;139(2-3):245–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00402008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damper P. D., Epstein W., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Thallous ion is accumulated by potassium transport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4165–4169. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Grenson M. Methylamine/ammonia uptake systems in saocharomyces cerevisiae: multiplicity and regulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00267857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackette S. L., Skye G. E., Burton C., Segel I. H. Characterization of an ammonium transport system in filamentous fungi with methylammonium-14C as the substrate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4241–4250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar A., Epstein W., Barnes E. M., Jr Characterization of ammonium (methylammonium)/potassium antiport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7528–7532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar A., Schulman I., MacNeil D., Barnes E. M., Jr Role of the Escherichia coli glnALG operon in regulation of ammonium transport. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):281–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.281-284.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Borman P. A rapid biochemical method for purifying high molecular weight bacterial chromosomal DNA for restriction enzyme analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3631–3631. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Even H. L., Dunlop P., Larimore F. L. Methylamine and ammonia transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):502–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.502-509.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servín-González L., Ortiz M., González A., Bastarrachea F. glnA mutations conferring resistance to methylammonium in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1631–1639. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno-Nishio S., Backman K. C., Magasanik B. Regulation at the glnL-operator-promoter of the complex glnALG operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1247–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1247-1251.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]