Abstract
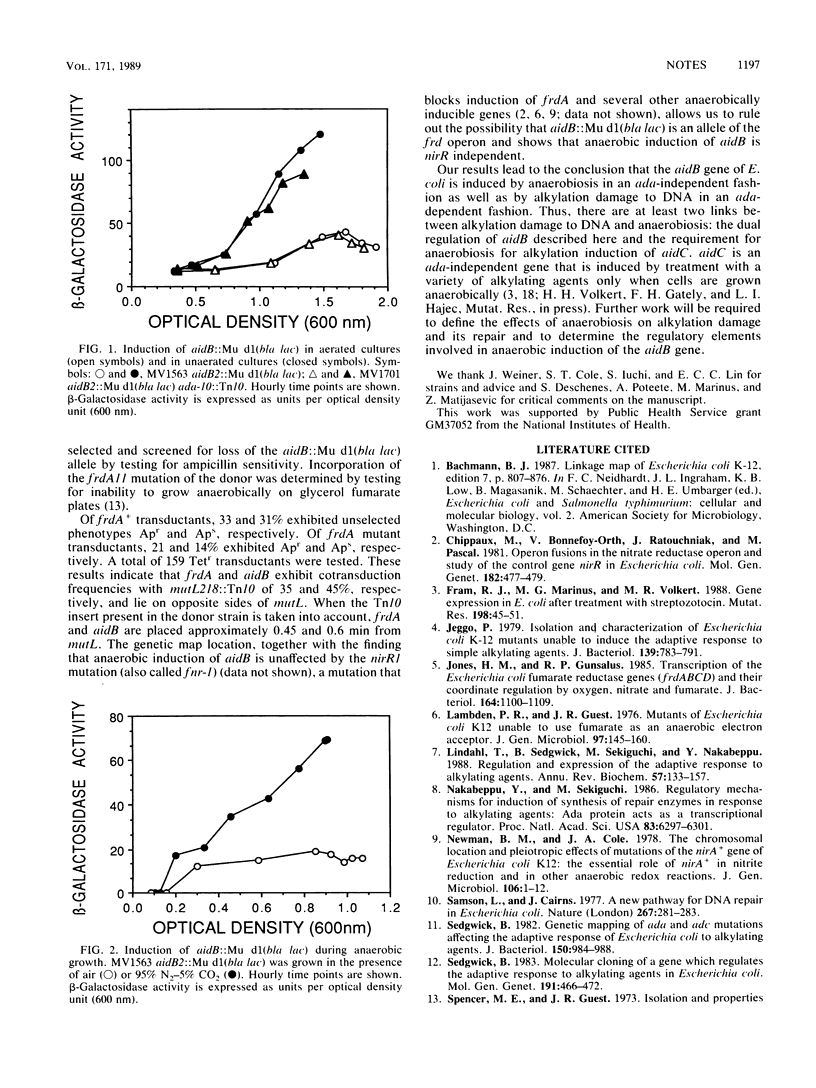
Induction of the adaptive response to alkylation damage results in the expression of four genes arranged in three transcriptional units: the ada-alkB operon and the alkA and aidB genes. Adaptive-response induction requires the ada gene product and occurs when cells are treated with methylating agents. In previous studies we noted that aidB, but not alkA or ada-alkB, was induced in the absence of alkylation damage as cells were grown to stationary phase. In this note we present evidence that aidB is induced by anaerobiosis. Thus, aidB is subject to dual regulation by ada-dependent alkylation induction and ada-independent anaerobic induction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chippaux M., Bonnefoy-Orth V., Ratouchniak J., Pascal M. C. Operon fusions in the nitrate reductase operon and study of the control gene nir R in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):477–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00293938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fram R. J., Marinus M. G., Volkert M. R. Gene expression in E. coli after treatment with streptozotocin. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;198(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli K-12 mutants unable to induce the adaptive response to simple alkylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):783–791. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.783-791.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. M., Gunsalus R. P. Transcription of the Escherichia coli fumarate reductase genes (frdABCD) and their coordinate regulation by oxygen, nitrate, and fumarate. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1100–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1100-1109.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Guest J. R. Mutants of Escherichia coli K12 unable to use fumarate as an anaerobic electron acceptor. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):145–160. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Sedgwick B., Sekiguchi M., Nakabeppu Y. Regulation and expression of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Regulatory mechanisms for induction of synthesis of repair enzymes in response to alkylating agents: ada protein acts as a transcriptional regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6297–6301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman B. M., Cole J. A. The chromosomal location and pleiotropic effects of mutations of the nirA+ gene of Escherichia coli K12: the essential role of nirA+ in nitrite reduction and in other anaerobic redox reactions. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 May;106(1):1–12. doi: 10.1099/00221287-106-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):281–283. doi: 10.1038/267281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B. Genetic mapping of ada and adc mutations affecting the adaptive response of Escherichia coli to alkylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):984–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.984-988.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B. Molecular cloning of a gene which regulates the adaptive response to alkylating agents in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):466–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00425764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Kilpatrick M. W., McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. The intracellular signal for induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R. Adaptive response of Escherichia coli to alkylation damage. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1988;11(2):241–255. doi: 10.1002/em.2850110210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R., Nguyen D. C., Beard K. C. Escherichia coli gene induction by alkylation treatment. Genetics. 1986 Jan;112(1):11–26. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


