Abstract
The toluene degradative transposon Tn4651 is included within another transposon, Tn4653, and both of these elements are members of the Tn3 family. The tnpA gene product of each element mediates formation of cointegrates as intermediate products of transposition, and the tnpS and tnpT gene products encoded by Tn4651 take part in resolution of both Tn4651- and Tn4653-mediated cointegrates. Sequence analysis demonstrated that Tn4651 and Tn4653 have 46- and 38-base-pair terminal inverted repeats, respectively, and that both elements generate 5-base-pair duplication of the target sequence upon transposition. Complementation tests of the Tn4651- and Tn4653-encoded transposition functions with those of Tn3, Tn21, and Tn1721 showed that (i) the trans-acting transposition functions encoded by Tn4651 were not interchangeable with those encoded by the four other transposons, (ii) the Tn4653 tnpA function was interchangeable with the Tn1721 function, and (iii) Tn4653 coded for a resolvase (tnpR gene product) that complemented the tnpR mutations of Tn21 and Tn1721. The Tn4653 tnpR gene was located just 5' upstream of the tnpA gene and shared extensive sequence homology with the Tn1721 tnpR gene. The res region was located adjacent to the tnpR gene, and sequence analysis indicated that failure of the Tn4653 tnpR product to resolve the Tn4653-mediated cointegrates is ascribed to an incomplete structure of the res region.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbuchner J., Schmitt R. Transposon Tn1721: site-specific recombination generates deletions and inversions. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):300–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00330655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Winnie J. N., Fritzinger D., Pridmore R. D. The nucleotide sequence of the tnpA gene completes the sequence of the Pseudomonas transposon Tn501. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5657–5669. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver W. P., Grinsted J., Fritzinger D. C., Brown N. L., Altenbuchner J., Rogowsky P., Schmitt R. DNA sequences of and complementation by the tnpR genes of Tn21, Tn501 and Tn1721. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00334812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., de la Cruz F., Altenbuchner J., Schmitt R. Complementation of transposition of tnpA mutants of Tn3, Tn21, Tn501, and Tn1721. Plasmid. 1982 Nov;8(3):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M. S. Uses of the transposon gamma delta in the analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:362–369. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., McCarthy B. J., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. DNA sequence analysis of the transposon Tn3: three genes and three sites involved in transposition of Tn3. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil H., Keil S., Williams P. A. Molecular analysis of regulatory and structural xyl genes of the TOL plasmid pWW53-4. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 May;133(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-5-1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulien P., Downing R. G., Broda P. Excision of the 40kb segment of the TOL plasmid from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 involves direct repeats. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):97–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00271202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mötsch S., Schmitt R., Avila P., de la Cruz F., Ward E., Grinsted J. Junction sequences generated by 'one-ended transposition'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3335–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W. Revised sequence of the tetracycline-resistance gene of pBR322. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P., Halford S. E., Schmitt R. Definition of three resolvase binding sites at the res loci of Tn21 and Tn1721. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2135–2141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P., Schmitt R. Tn1721-encoded resolvase: structure of the tnpR gene and its in vitro functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):176–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00383332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R., Altenbuchner J., Wiebauer K., Arnold W., Pühler A., Schöffl F. Basis of transposition and gene amplification by Tn1721 and related tetracycline-resistance transposons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):59–65. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffl F., Arnold W., Pühler A., Altenbuchner J., Schmitt R. The tetracycline resistance transposons Tn1721 and Tn1771 have three 38-base-pair repeats and generate five-base-pair direct repeats. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):87–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00339010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. E., Williams P. A. Physical and functional mapping of two cointegrate plasmids derived from RP4 and TOL plasmid pDK1. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Sep;134(9):2463–2474. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-9-2463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Gill R., Falkow S. The generation of a ColE1-Apr cloning vehicle which allows detection of inserted DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;142(3):239–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00425649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
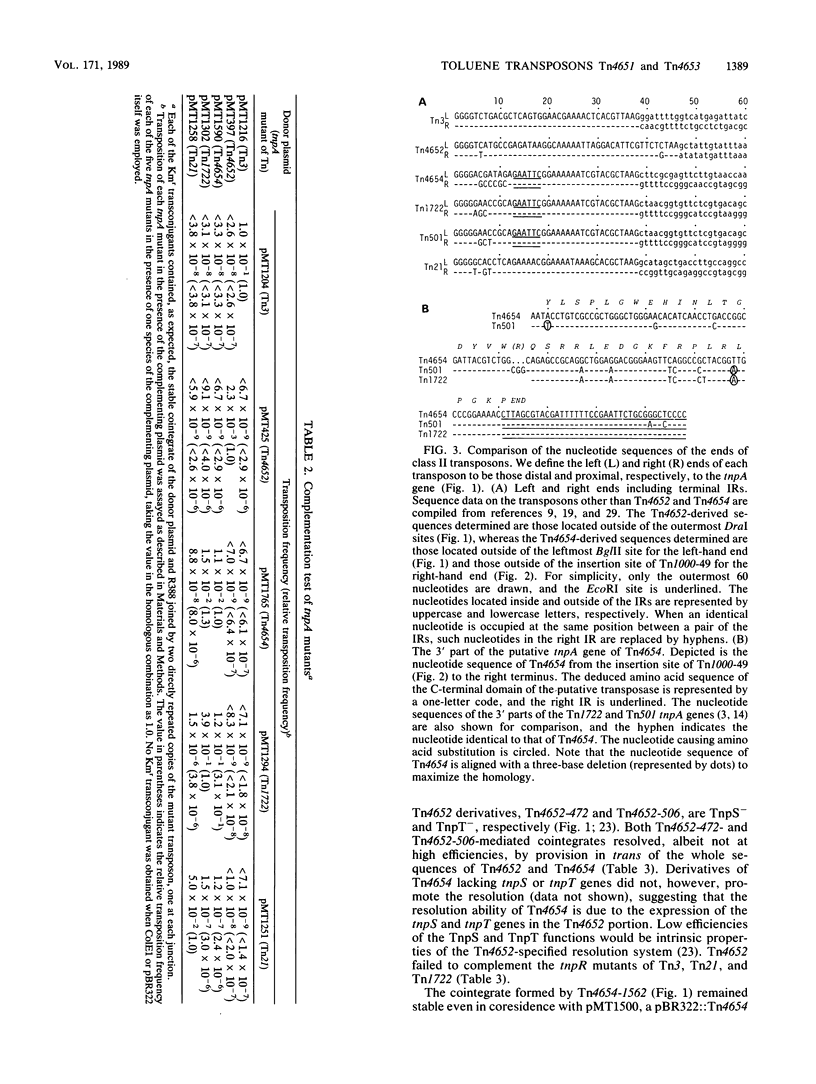
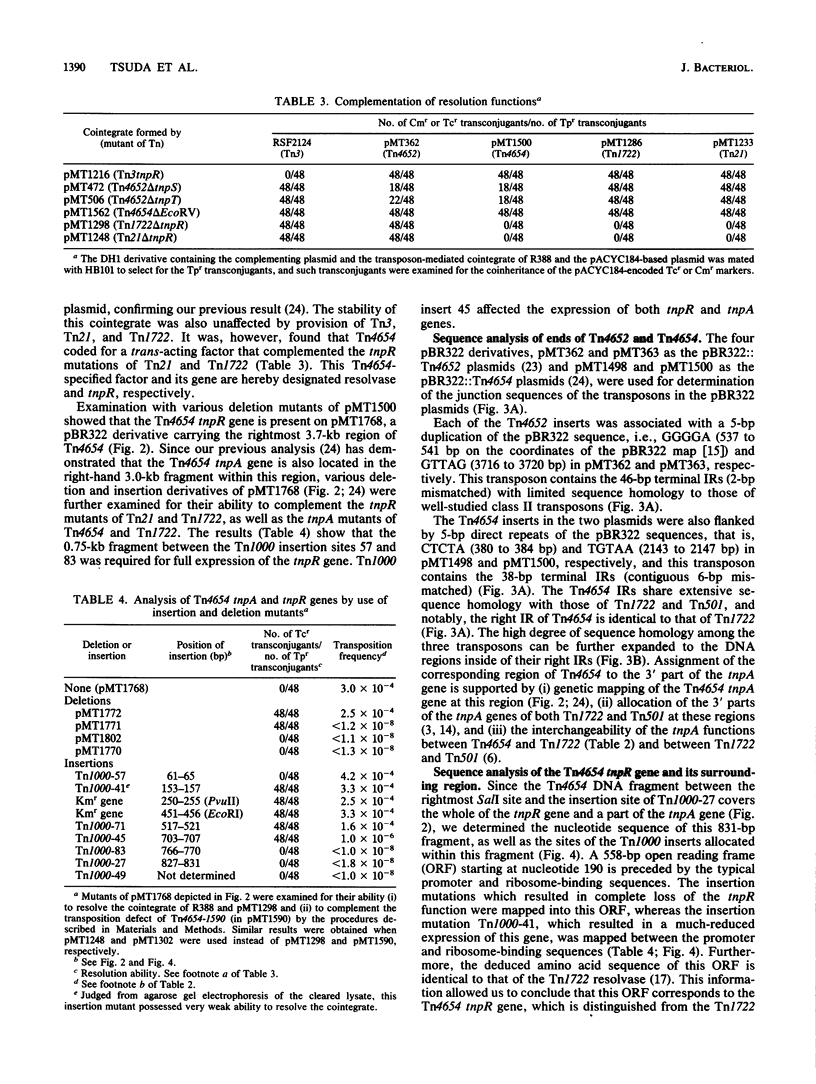
- Tsuda M., Iino T. Genetic analysis of a transposon carrying toluene degrading genes on a TOL plasmid pWW0. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):270–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00325693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Iino T. Identification and characterization of Tn4653, a transposon covering the toluene transposon Tn4651 on TOL plasmid pWW0. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):72–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00333400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubben D., Schmitt R. Tn1721 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis, restriction mapping and nucleotide sequence analysis. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Grinsted J. Physical and genetic analysis of the Inc-W group plasmids R388, Sa, and R7K. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Z. X., Chandler M., Hipskind R., Clerget M., Caro L. Dissection of the r-determinant of the plasmid R100.1: the sequence at the extremities of Tn21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6265–6278. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz F., Grinsted J. Genetic and molecular characterization of Tn21, a multiple resistance transposon from R100.1. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):222–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.222-228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


