Abstract
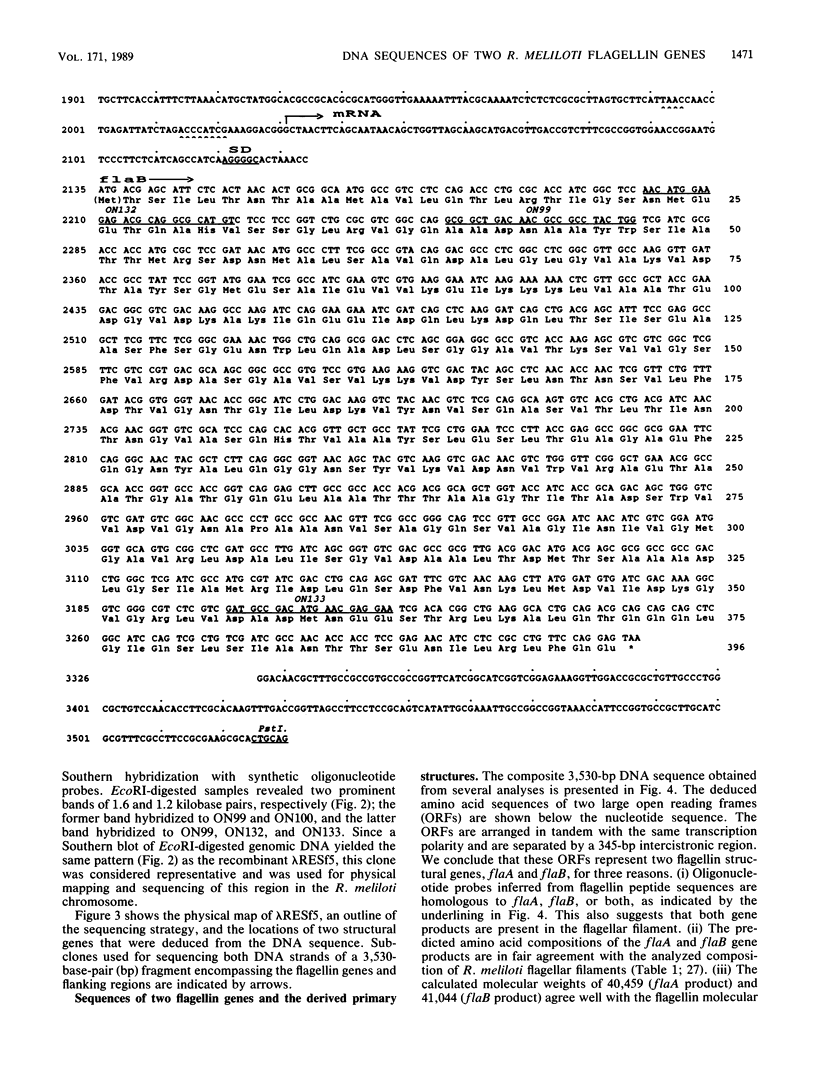
The genomic region that codes for the flagellin subunits of the complex flagellar filaments of Rhizobium meliloti was cloned and sequenced. Two structural genes, flaA and flaB, that encode 395- and 396-amino-acid polypeptides, respectively, were identified. These exhibit 87% sequence identity. The amino acid sequences of tryptic peptides suggest that both of these subunit proteins are represented in the flagellar filaments. The N-terminal methionine was absent from the mature flagellin subunits. Their derived primary structures show almost no relationship to flagellins from Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, or Bacillus subtilis but exhibit up to 60% similarity to the N- and C-terminal portions of flagellin from Caulobacter crescentus. It is suggested that the complex flagellar filaments of R. meliloti are unique in being assembled from heterodimers of two related flagellin subunits. The tandemly arranged flagellin genes were shown to be transcribed separately from unusual promoter sequences.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delange R. J., Chang J. Y., Shaper J. H., Martinez R. J., Komatsu S. K., Glazer A. N. On the amino-acid sequence of flagellin from Bacillus subtilis 168: comparison with other bacterial flagellins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3428–3431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerl L., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are encoded by a multigene family. Characterization of five flagellin genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13246–13251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. The nucleotide sequence of the Mr = 28,500 flagellin gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7395–7401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wiggs J. L., Chamberlin M. J. Nucleotide sequences of two Bacillus subtilis promoters used by Bacillus subtilis sigma-28 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5991–6000. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz R., Schmitt R. Rhizobium meliloti swims by unidirectional, intermittent rotation of right-handed flagellar helices. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3146–3150. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3146-3150.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. DNA sequence analysis suggests that expression of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is controlled by an alternative sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6422–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Komeda Y., Iino T., Macnab R. M. The flaFIX gene product of Salmonella typhimurium is a flagellar basal body component with a signal peptide for export. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1493-1498.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
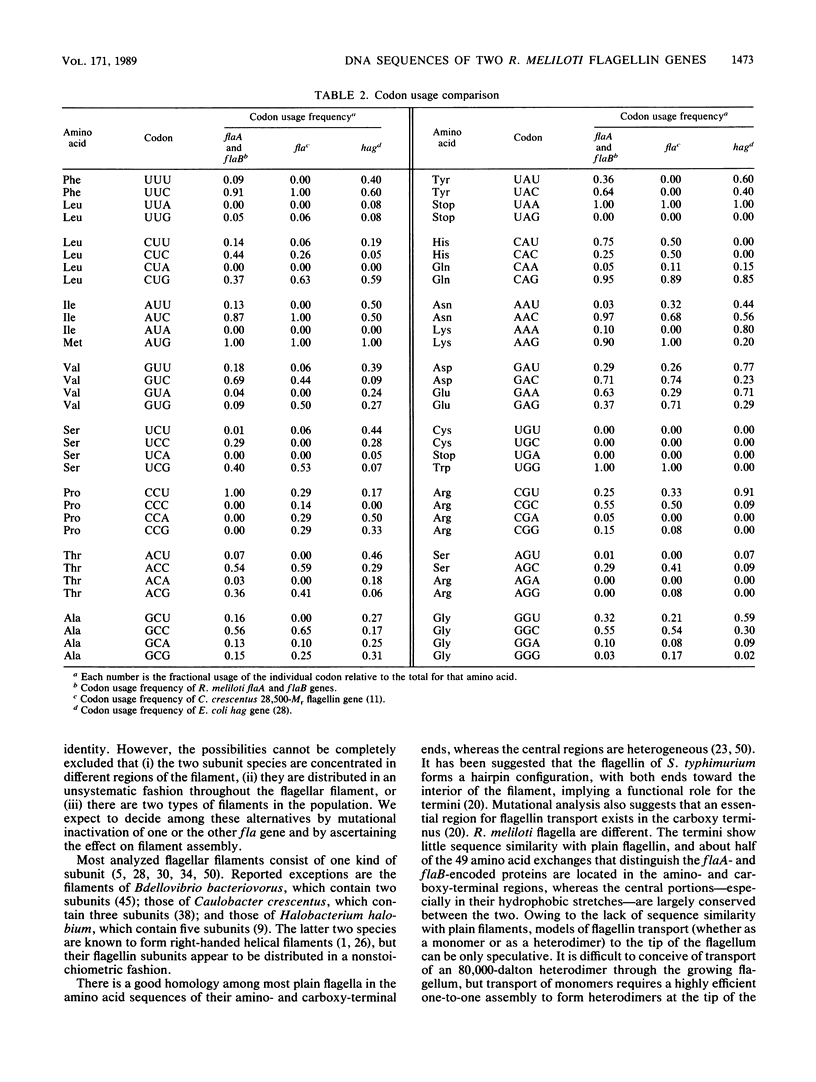
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner K., Mandelkow E. M. Tubulin domains responsible for assembly of dimers and protofilaments. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2397–2402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Shirakihara Y. Caulobacter crescentus flagellar filament has a right-handed helical form. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupski G., Götz R., Ober K., Pleier E., Schmitt R. Structure of complex flagellar filaments in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.361-366.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G., Asaka J., Fujiwara T., Fujiwara T., Node K., Kondo E. Nucleotide sequence of the hag gene encoding flagellin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1479–1483. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1479-1483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. A., Williams P. H., Ditta G. S. Analysis of the 5' regulatory region of the gene for delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase of Rhizobium meliloti. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5965–5976. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Harris L. A., Trust T. J. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter flagellins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5072–5077. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5072-5077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Ornston M. K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Savage D. C. Purification and characterization of flagella from Roseburia cecicola, an obligately anaerobic bacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):2075–2078. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-2075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Lodderstaedt G., Schmitt R. Purification and biochemical properties of complex flagella isolated from Rhizobium lupini H13-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 21;535(1):110–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich S. A., Ohta N., Taylor N., Newton A. Role of the 25-, 27-, and 29-kilodalton flagellins in Caulobacter crescentus cell motility: method for construction of deletion and Tn5 insertion mutants by gene replacement. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3953–3960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3953-3960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P., Halford S. E., Schmitt R. Definition of three resolvase binding sites at the res loci of Tn21 and Tn1721. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2135–2141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R., Raska I., Mayer F. Plain and complex flagella of Pseudomonas rhodos: analysis of fine structure and composition. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):844–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.844-857.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
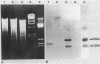
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Rittenberg S. C. Waveform analysis and structure of flagella and basal complexes from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1038–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1038-1046.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg S., DeRosier D. J., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Pairwise perturbation of flagellin subunits. The structural basis for the differences between plain and complex bacterial flagellar filaments. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg S., DeRosier D. J., Macnab R. M. Three-dimensional structure of the complex flagellar filament of Rhizobium lupini and its relation to the structure of the plain filament. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):603–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubben D., Schmitt R. Tn1721 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis, restriction mapping and nucleotide sequence analysis. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]