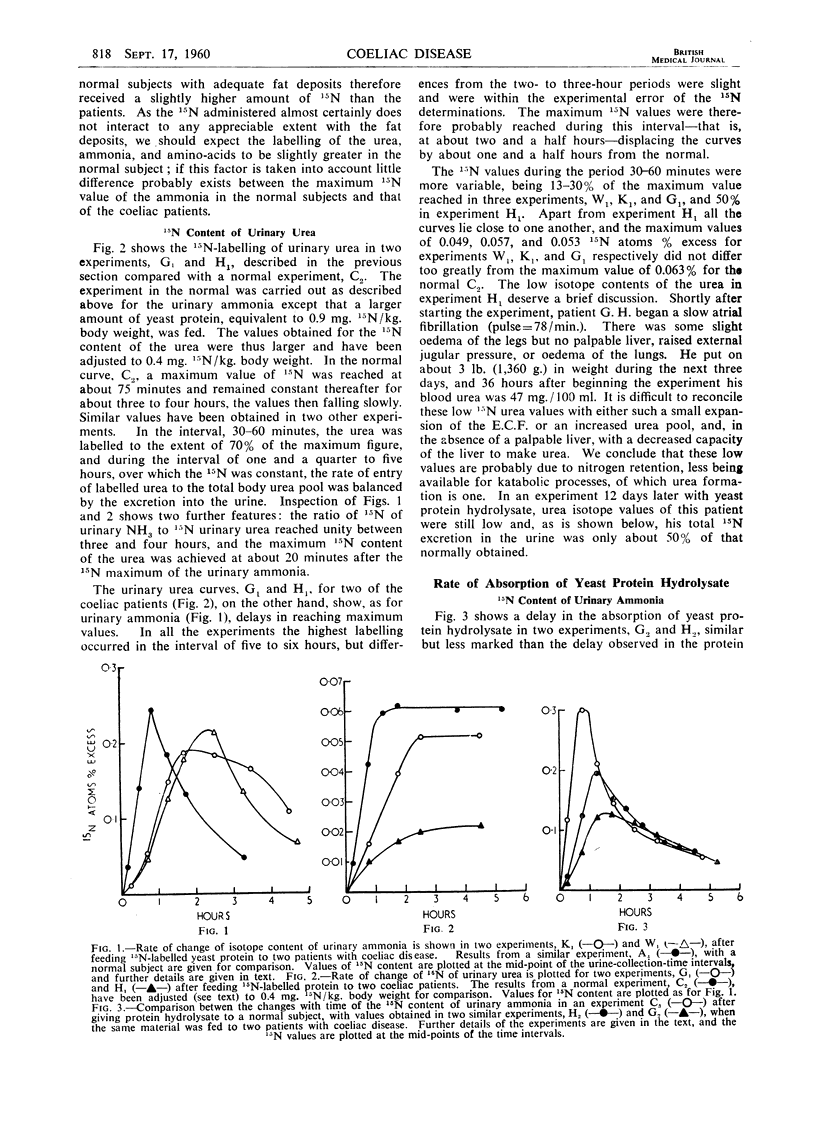
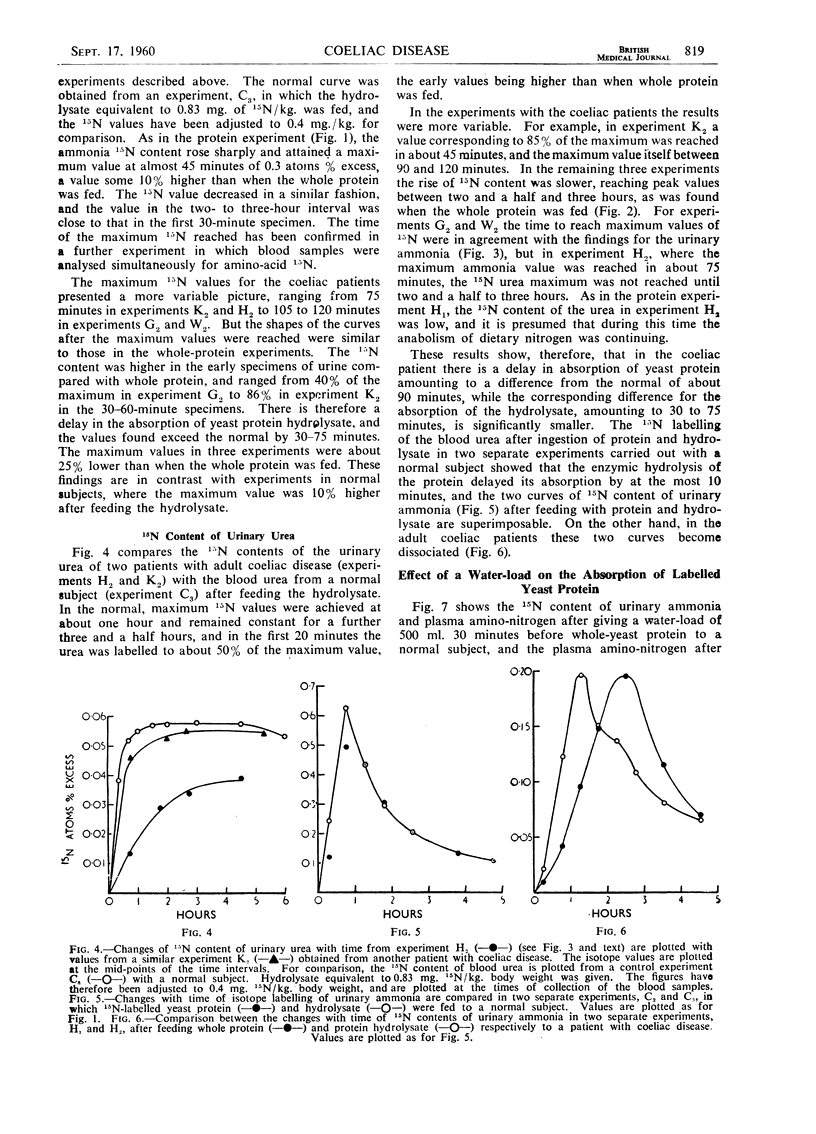
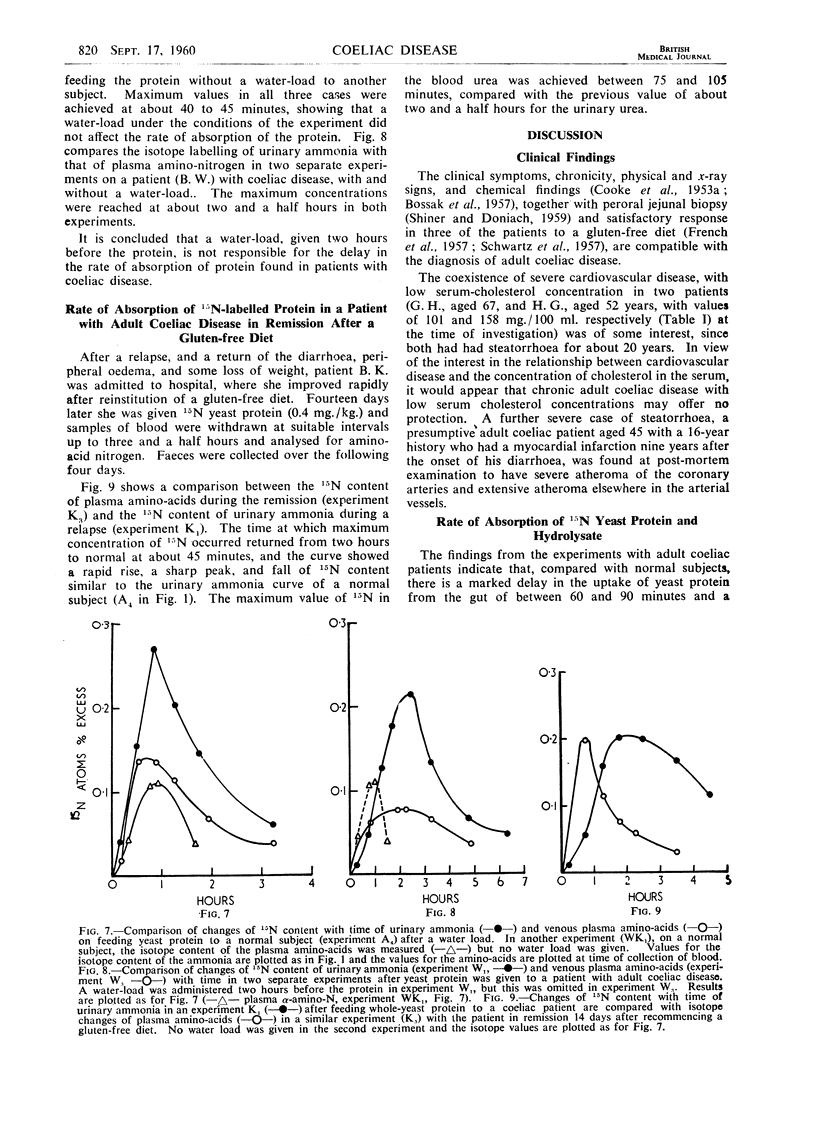
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON M., NORDIN B. E., SHERLOCK S. Malabsorption and bone disease in prolonged obstructive jaundice. Q J Med. 1956 Jul;25(99):299–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON J. A., Jr, CULVER P. J., RAGLAND S., JONES C. M., DRUMMEY G. D., BOUGAS E. The d-xylose absorption test in malabsorption syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1957 Feb 21;256(8):335–339. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195702212560802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., LUNDH G., SJOVALL J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1521–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOSSAK E. T., WANG C. I., ADLERSBERG D. Clinical aspects of the malabsorption syndrome (idiopathic sprue); observations in 94 patients. J Mt Sinai Hosp N Y. 1957 May-Jun;24(3):286–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CODE C. F., HIGGINS J. A., ORVIS A. L. The influence of motility on the rate of absorption of sodium and water from the small intestine of healthy persons. Gastroenterology. 1956 Dec;31(6):708-15; discussion, 715-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE W. T., PEENEY A. L. P., HAWKINS C. F. Symptoms, signs and diagnostic features of idiopathic steatorrhoea. Q J Med. 1953 Jan;22(85):59–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE W. T., THOMAS G., MANGALL D., CROSS H. Observations on the faecal excretion of total solids, nitrogen, sodium, potassium, water and fat in the steatorrhoea syndrome. Clin Sci. 1953;12(3):223–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE C. W., NEUBERGER A. The digestion and absorption of protein by normal man. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:313–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0740313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS A. J., ALMY T. P. Studies on the relationship between motility and absorption in the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1953 Feb;23(2):179–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A. M., ISSELBACHER K. J. The esterification of palmitate-1-C14 by homogenates of intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:150–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI104014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erf L. A., Rhoads C. P. THE GLYCINE TOLERANCE TEST IN SPRUE AND PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. J Clin Invest. 1940 Mar;19(2):409–421. doi: 10.1172/JCI101143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZER A. C., FRENCH J. M., THOMAS G., THOMPSON M. D. The absorption of glucose and urea from the upper small intestine in the sprue syndrome. Clin Sci. 1952 May;11(2):141–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH J. M., HAWKINS C. F., SMITH N. The effect of a wheat-gluten-free diet in adult idiopathic steatorrhoea; a study of 22 cases. Q J Med. 1957 Oct;26(104):481–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J. B., COMFORT M. W., WOLLAEGER E. E., POWER M. H. Total solids, fat and nitrogen in the feces: V. A study of patients with primary parenchymatous hepatic disease. Gastroenterology. 1950 Sep;16(1):140–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUPTA J. D., DAKROURY A. M., HARPER A. E. Observations on protein digestion in vivo. I. Rate of disappearance of ingested protein from the gastrointestinal tract. J Nutr. 1958 Mar 10;64(3):447–456. doi: 10.1093/jn/64.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATLEY N. G. Mucosubstance as a barrier to diffusion. Gastroenterology. 1959 Sep;37:313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS J. A., LEE P. R., SCHOLER J. F., REITEMEIER R. J., CODE C. F., WOLLAEGER E. E. Absorption of water and sodium from the small intestine of patients with nontropical sprue. J Clin Invest. 1957 Feb;36(2):265–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI103420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWEY H., SMYTH D. H. The intestinal absorption of some dipeptides. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):48–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULLEY J. W. Observation on the aetiology of idiopathic steatorrhoea; jejunal and lymph-node biopsies. Br Med J. 1954 Dec 4;2(4900):1318–1321. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4900.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL S., NASSET E. S. Gastric emptying and intestinal absorption of carbohydrate and protein as influenced by the nature of the test meal. J Nutr. 1958 Sep 10;66(1):91–103. doi: 10.1093/jn/66.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN C. E., BRANDBORG L. L., PHELPS P. C., TAYLOR H. C., Jr Studies of celiac disease. I. The apparent identical and specific nature of the duodenal and proximal jejunal lesion in celiac disease and idiopathic sprue. Gastroenterology. 1960 Jan;38:28–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAINT E. G., WEIDEN S. The malabsorption syndrome. Australas Ann Med. 1952 May;1(1):58–67. doi: 10.1111/imj.1952.1.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ M. K., SLEISENGER M. H., PERT J. H., ROBERTS K. E., RANDALL H. T., ALMY T. P. The effect of a gluten-free diet on fat, nitrogen, and mineral metabolism in patients with sprue. Gastroenterology. 1957 Feb;32(2):232-46; discussion, 246-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP G. S., LASSEN S., SHANKMAN S., GEBHART A. F., Jr, HAZLET J. W. Studies of protein absorption using nitrogen 15 as a tag. J Nutr. 1956 Apr 10;58(4):443–457. doi: 10.1093/jn/58.4.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. B., WOLLAEGER E. E., COMFORT M. W., POWER M. H. The effect of cortisone on nontropical sprue (idiopathic steatorrhea). Gastroenterology. 1952 Feb;20(2):203–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE A. G. C., PARSON W. Comparative studies on nitrogen excretion. Arch Biochem. 1950 Apr;26(2):205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


