Abstract
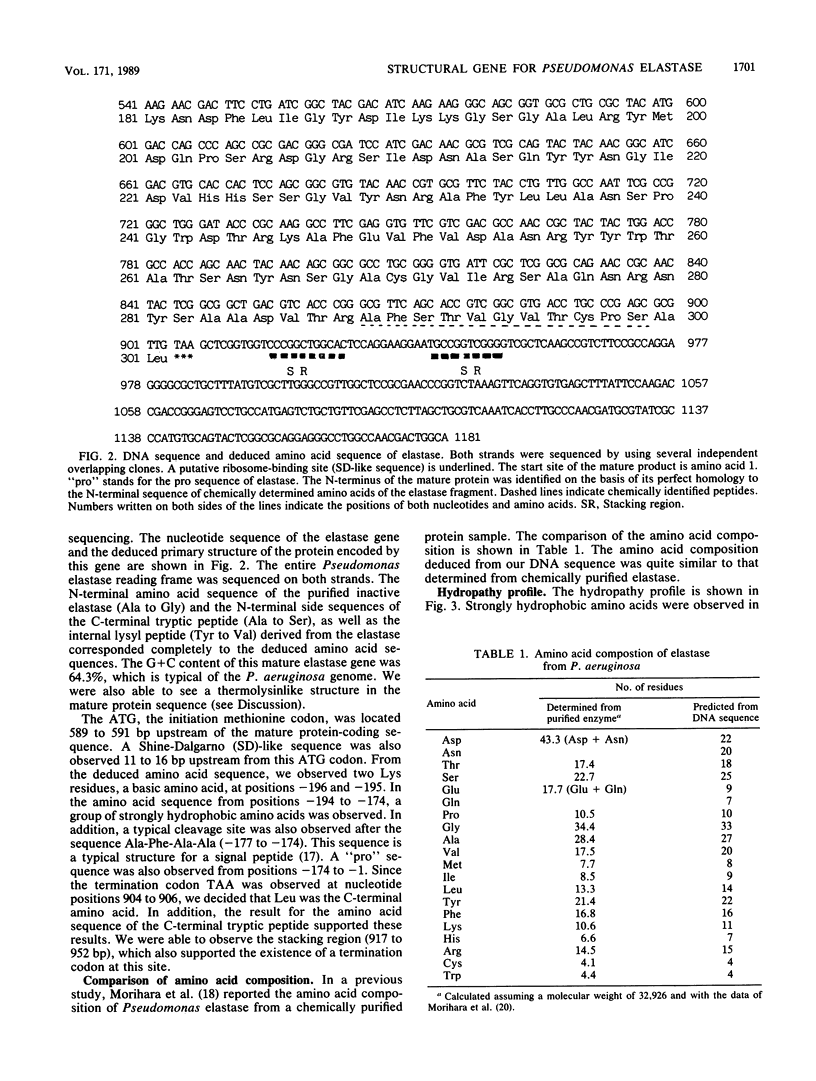
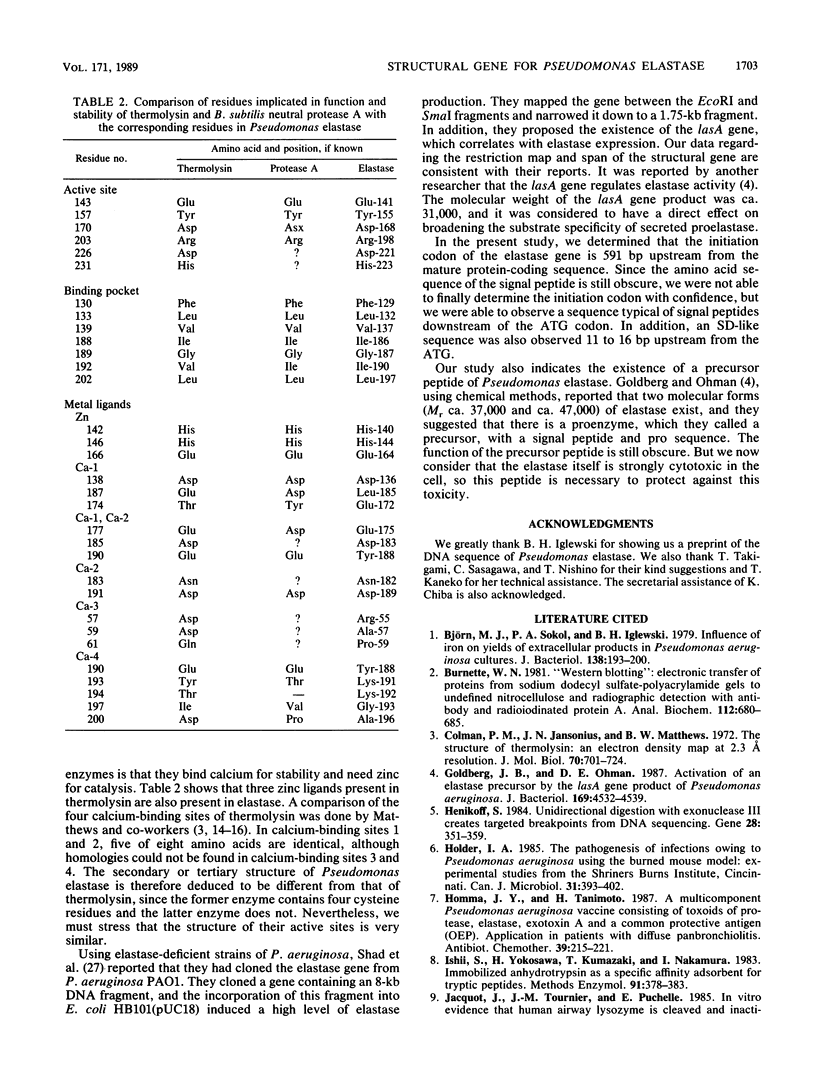
The DNA encoding the elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO 3455 was cloned, and its complete nucleotide sequence was determined. When the cloned gene was ligated to pUC18, the Escherichia coli expression vector, bacteria carrying the gene exhibited high levels of both elastase activity and elastase antigens. The amino acid sequence, deduced from the nucleotide sequence, revealed that the mature elastase consisted of 301 amino acids with a relative molecular mass of 32,926 daltons. The amino acid composition predicted from the DNA sequence was quite similar to the chemically determined composition of purified elastase reported previously. We also observed nucleotide sequence encoding a signal peptide and "pro" sequence consisting of 197 amino acids upstream from the mature elastase protein gene. The amino acid sequence analysis revealed that both the N-terminal sequence of the purified elastase and the N-terminal side sequences of the C-terminal tryptic peptide as well as the internal lysyl peptide fragment were completely identical to the deduced amino acid sequences. The pattern of identity of amino acid sequences was quite evident in the regions that include structurally and functionally important residues of Bacillus subtilis thermolysin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H. Influence of iron on yields of extracellular products in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):193–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.193-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Jansonius J. N., Matthews B. W. The structure of thermolysin: an electron density map at 2-3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):701–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90569-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillenz M. Hypothesis for a neuronal mechanism involved in memory. Nature. 1972 Jul 7;238(5358):41–43. doi: 10.1038/238041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujishima A., Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature. 1972 Jul 7;238(5358):37–38. doi: 10.1038/238037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Activation of an elastase precursor by the lasA gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4532–4539. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4532-4539.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A. The pathogenesis of infections owing to Pseudomonas aeruginosa using the burned mouse model: experimental studies from the Shriners Burns Institute, Cincinnati. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Apr;31(4):393–402. doi: 10.1139/m85-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Tanimoto H. A multicomponent Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine consisting of toxoids of protease, elastase, exotoxin A and a common protective antigen (OEP). Application in patients with diffuse panbronchiolitis. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:215–221. doi: 10.1159/000414347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Yokosawa H., Kumazaki T., Nakamura I. Immobilized anhydrotrypsin as a specific affinity adsorbent for tryptic peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:378–383. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Carter-Hamm B., Dralle W. M. Inactivation of human bronchial mucosal proteinase inhibitor by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):1070–1073. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Döring G., Høiby N., Valerius N. H. Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):161–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.161-165.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Høiby N., Döring G., Valerius N. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteases inhibit human neutrophil chemiluminescence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):587–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.587-591.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy P. L., Pangburn M. K., Burstein Y., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Evidence of homologous relationship between thermolysin and neutral protease A of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Homma J. Y. New method of preparing elastase toxoid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):53–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.53-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. The role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 May;11 (Suppl B):1–13. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Wretlind B. Assessment of protease (elastase) as a Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor in experimental mouse burn infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):181–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.181-187.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B. K., Kharazmi A. Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):986–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.986-989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schad P. A., Bever R. A., Nicas T. I., Leduc F., Hanne L. F., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and characterization of elastase genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2691–2696. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2691-2696.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Wadström T. Purification and properties of a protease with elastase activity from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):319–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Fukushima J., Atsumi Y., Takeuchi H., Kawamoto S., Okuda K., Morihara K. Cloning and characterization of elastase structural gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO 3455. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1117–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80400-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



