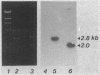
Abstract
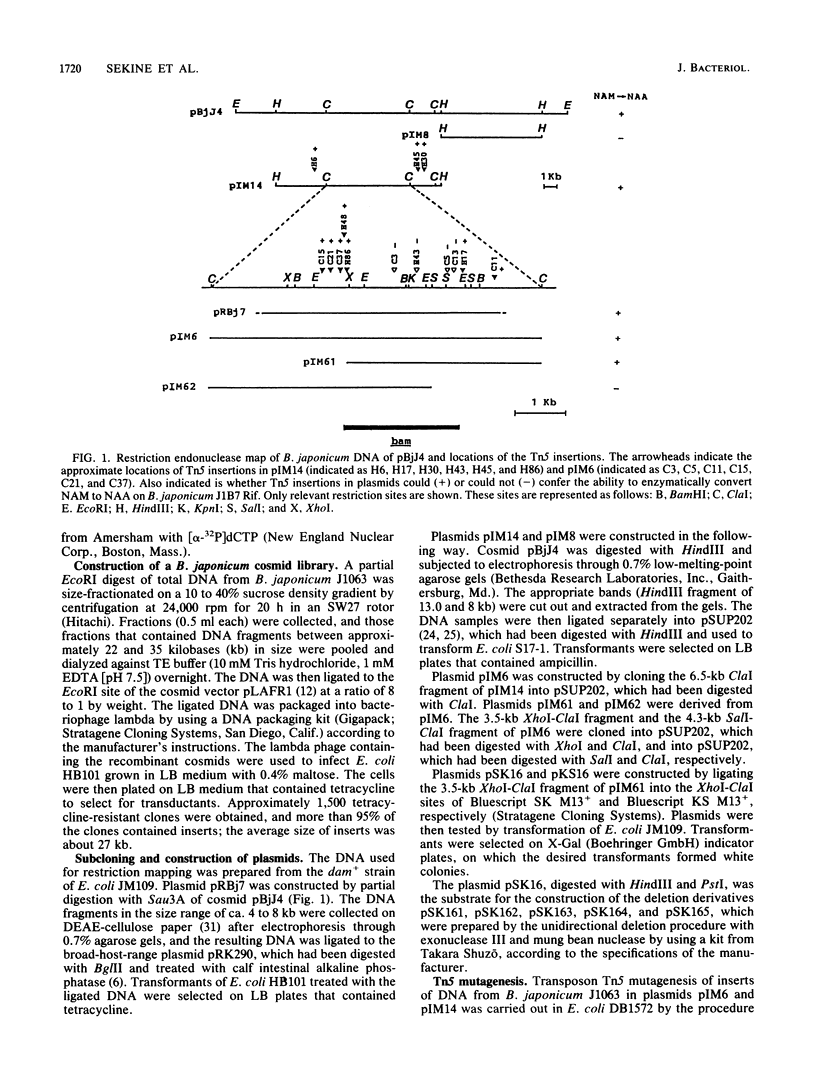
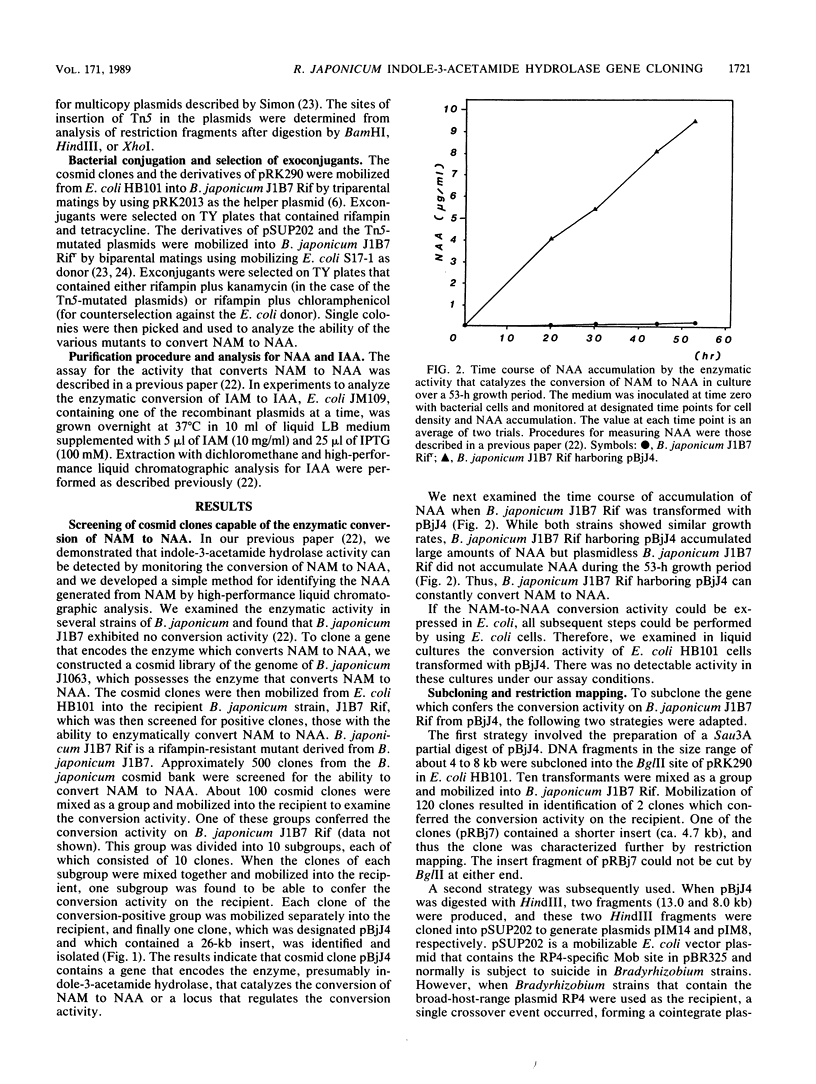
A pLAFR1 cosmid genomic library of wild-type Bradyrhizobium japonicum J1063 was constructed. A cosmid clone designated pBjJ4, containing a 26-kilobase (kb) DNA insert, was identified as being able to confer the ability to convert alpha-naphthaleneacetamide acid on B. japonicum J1B7 Rifr, which cannot perform this conversion. The gene coding for the enzyme that converts alpha-naphthaleneacetamide to alpha-naphthaleneacetic acid was localized in the 3.5-kb region of pBjJ4 by recloning in plasmid pSUP202. The gene coding for the enzyme was also mapped by Tn5 insertion mutagenesis to a region of ca. 2.3 kb. When the gene was placed behind the lacZ promoter and used to transform Escherichia coli, a high level of expression of indole-3-acetamide hydrolase activity was found. Since there have been no reports of this activity in E. coli, we have thus confirmed that the gene cloned here is a structural gene for indole-3-acetamide hydrolase and have designated it as the bam (Bradyrhizobium amidehydrolase) gene. Southern hybridization with the central region of the bam gene indicated that a high degree of similarity exists among the bam gene, the iaaH gene from Pseudomonas savastonoi, and the tms-2 gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The result suggests that there is a common origin for the gene that encodes the enzyme that catalyzes the biosynthesis of indoleacetic acid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badenoch-Jones J., Summons R. E., Djordjevic M. A., Shine J., Letham D. S., Rolfe B. G. Mass spectrometric quantification of indole-3-acetic Acid in Rhizobium culture supernatants: relation to root hair curling and nodule initiation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):275–280. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.275-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Cloning characterization of iaaM, a virulence determinant of Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):40–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.40-46.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Involvement of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in indoleacetic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.950-957.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusha I., Schröder J., Putnoky P., Bánfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. A cell-free system from Rhizobium meliloti to study the specific expression of nodulation genes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Hahn M., Hennecke H. Repeated sequences similar to insertion elements clustered around the nif region of the Rhizobium japonicum genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):535–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.535-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Prakash R. K., Atherly A. G. Conservation of symbiotic nitrogen fixation gene sequences in Rhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.21-26.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., O'Connell M., Labes M., Pühler A. Plasmid vectors for the genetic analysis and manipulation of rhizobia and other gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:640–659. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Reeves S., Thomashow M. F. Crown gall oncogenesis: evidence that a T-DNA gene from the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid pTiA6 encodes an enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of indoleacetic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Hugly S., Buchholz W. G., Thomashow L. S. Molecular basis for the auxin-independent phenotype of crown gall tumor tissues. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):616–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3511528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Palm C. J., Brooks B., Kosuge T. Nucleotide sequences of the Pseudomonas savastanoi indoleacetic acid genes show homology with Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]